Blasphemy involves showing disrespect or irreverence toward sacred beliefs, deities, or religious symbols, often provoking intense emotional and social reactions. Laws and cultural attitudes regarding blasphemy differ widely, influencing freedom of expression and religious tolerance around the world. Discover more about blasphemy's impact and debates in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
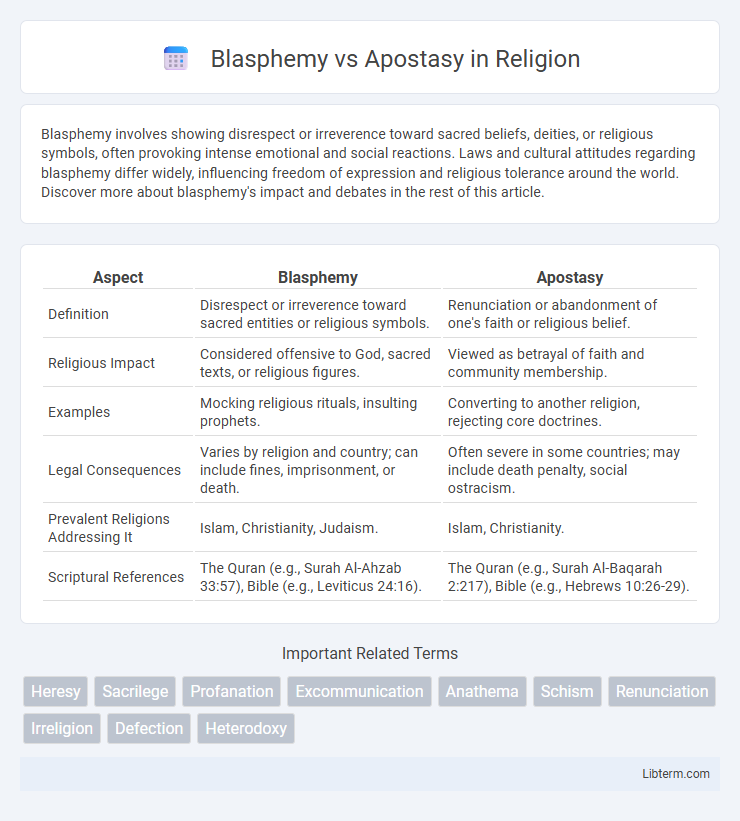
| Aspect | Blasphemy | Apostasy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Disrespect or irreverence toward sacred entities or religious symbols. | Renunciation or abandonment of one's faith or religious belief. |
| Religious Impact | Considered offensive to God, sacred texts, or religious figures. | Viewed as betrayal of faith and community membership. |
| Examples | Mocking religious rituals, insulting prophets. | Converting to another religion, rejecting core doctrines. |
| Legal Consequences | Varies by religion and country; can include fines, imprisonment, or death. | Often severe in some countries; may include death penalty, social ostracism. |
| Prevalent Religions Addressing It | Islam, Christianity, Judaism. | Islam, Christianity. |
| Scriptural References | The Quran (e.g., Surah Al-Ahzab 33:57), Bible (e.g., Leviticus 24:16). | The Quran (e.g., Surah Al-Baqarah 2:217), Bible (e.g., Hebrews 10:26-29). |
Defining Blasphemy: Meaning and Contexts
Blasphemy refers to the act of showing disrespect or irreverence toward sacred entities, deities, or religious symbols, often considered offensive within various faith traditions. This concept varies across cultures and legal systems, where it may encompass speech, actions, or expressions that insult or mock religious beliefs. Understanding blasphemy requires examining its role in societal norms, religious sensitivities, and legal frameworks that aim to balance freedom of expression with respect for religious sentiments.
Understanding Apostasy: Origins and Interpretations
Apostasy refers to the formal disaffiliation from or abandonment of a religion, often explored through historical interpretations dating back to ancient religious texts and sects. The origins of apostasy are deeply rooted in theological debates where different religious traditions define the boundaries of faith and community loyalty, impacting legal and social consequences. Diverse interpretations arise across religions, with apostasy sometimes perceived as a private act of belief change and other times as a public betrayal mandating specific sanctions or penalties.
Historical Perspectives on Blasphemy
Historical perspectives on blasphemy highlight its treatment as a serious offense against religious doctrines and societal order, often punishable by law or social sanctions in various cultures. Ancient and medieval societies frequently enforced blasphemy laws to protect religious authorities and maintain communal harmony, with penalties ranging from fines to capital punishment. These historical contexts reflect deep intertwining of religion and governance, underscoring blasphemy's impact on legal and cultural frameworks throughout history.
Apostasy through the Ages: A Historical Overview
Apostasy, the formal renunciation of a religious belief, has been met with varying degrees of intolerance and punishment throughout history, often reflecting the prevailing socio-political contexts. In ancient times, apostasy was frequently viewed as a betrayal of community and divine law, leading to severe penalties in many societies, including imprisonment or execution under Roman and Islamic laws. Over the centuries, the treatment of apostates evolved, with modern legal systems increasingly upholding freedom of belief, though apostasy laws persist in some countries, continuing to provoke international human rights debates.
Legal Frameworks: Blasphemy Laws Worldwide
Blasphemy laws exist in over 70 countries, predominantly in Muslim-majority states such as Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, and Iran, where penalties can include fines, imprisonment, or even the death penalty. These legal frameworks often overlap with apostasy laws, which criminalize renouncing a religion, notably in countries like Saudi Arabia and Sudan, intensifying the restrictions on freedom of belief and expression. International human rights organizations consistently criticize blasphemy and apostasy laws for violating freedom of speech and religion as enshrined in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
Apostasy in Religious Law and Doctrine
Apostasy in religious law refers to the formal abandonment or renunciation of one's faith, often considered a grave offense in many religious traditions including Islam, Christianity, and Judaism. In Islamic jurisprudence, apostasy (ridda) is traditionally met with severe legal consequences, ranging from social ostracism to capital punishment, reflecting its perceived threat to religious and communal identity. Apostasy laws vary widely in application and severity, with some countries enforcing strict penalties, while others adopt more lenient or symbolic responses within their religious or legal frameworks.
Social and Cultural Impacts of Blasphemy Accusations
Blasphemy accusations often lead to severe social ostracism, marginalizing individuals within their communities and limiting their access to social and economic opportunities. Culturally, these accusations reinforce rigid norms around religious conformity, stifling freedom of expression and promoting intolerance towards diverse beliefs. In many societies, the fear of blasphemy charges fuels communal tensions and violence, undermining social cohesion and perpetuating cycles of distrust among different religious or ethnic groups.
The Consequences of Apostasy in Different Societies
Consequences of apostasy vary widely across societies, often reflecting religious, cultural, and legal frameworks. In some countries, apostasy can lead to social ostracism, legal penalties including imprisonment or death, particularly in states governed by strict interpretations of Sharia law. Conversely, secular societies generally protect freedom of belief, mitigating legal consequences but social repercussions may persist depending on community norms.
Case Studies: Notable Instances of Blasphemy and Apostasy
Notable case studies of blasphemy and apostasy reveal diverse legal and social consequences across countries like Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, and Iran, where blasphemy laws often result in severe punishments including imprisonment or death. The case of Asia Bibi in Pakistan highlights international human rights debates around blasphemy accusations, while apostasy cases such as those involving Iranian ex-Muslims demonstrate ongoing challenges to religious freedom. These instances underscore the complex intersection of religion, law, and human rights in different cultural contexts.
Contemporary Debates: Freedom of Expression vs. Religious Boundaries
Contemporary debates on blasphemy and apostasy center on the tension between freedom of expression and religious boundaries, especially in pluralistic societies where diverse beliefs coexist. Governments and human rights organizations often clash over laws that criminalize blasphemy or apostasy, as such laws may suppress free speech while aiming to protect religious sentiments. The challenge lies in balancing respect for religious doctrines with the universal right to criticize or reject belief systems without fear of legal or social persecution.
Blasphemy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com