Petitionary refers to the act of formally requesting or appealing to an authority, often through a written petition aimed at influencing decisions or policies. This concept plays a crucial role in civic engagement, allowing individuals and groups to voice their concerns or demands effectively. Discover how petitionary actions can empower your participation in shaping societal outcomes by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
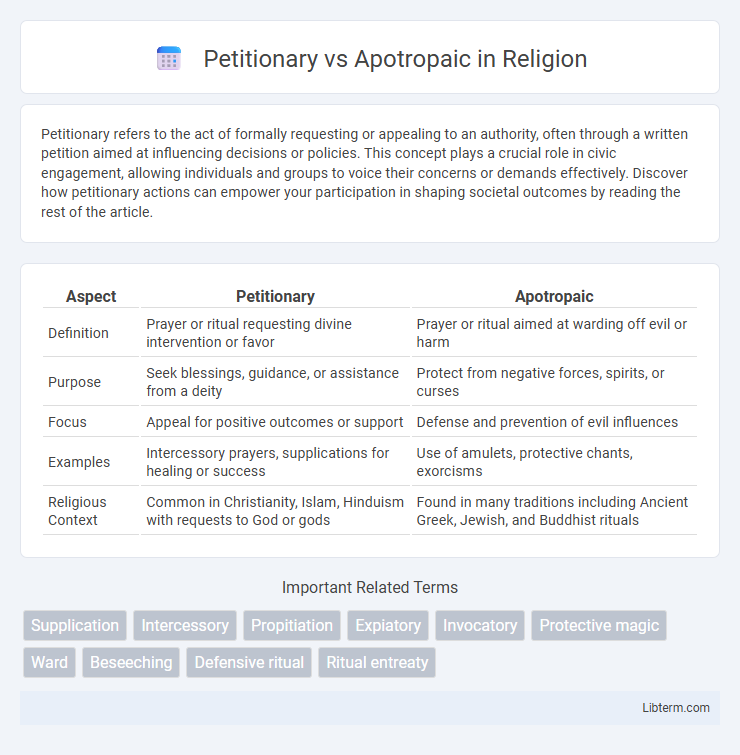
| Aspect | Petitionary | Apotropaic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prayer or ritual requesting divine intervention or favor | Prayer or ritual aimed at warding off evil or harm |
| Purpose | Seek blessings, guidance, or assistance from a deity | Protect from negative forces, spirits, or curses |
| Focus | Appeal for positive outcomes or support | Defense and prevention of evil influences |
| Examples | Intercessory prayers, supplications for healing or success | Use of amulets, protective chants, exorcisms |
| Religious Context | Common in Christianity, Islam, Hinduism with requests to God or gods | Found in many traditions including Ancient Greek, Jewish, and Buddhist rituals |
Understanding Petitionary and Apotropaic Practices
Petitionary practices involve direct requests or prayers to deities or spirits for specific favors, protection, or assistance, often reflecting a relational approach between humans and the divine. Apotropaic practices, by contrast, aim to ward off evil or misfortune through symbolic actions, objects, or rituals designed to repel harmful forces without direct petition. Understanding these distinctions highlights the diverse ways cultures seek influence over supernatural elements, either through supplication or protective measures.
Definitions: Petitionary vs Apotropaic
Petitionary rituals are practices aimed at requesting or appealing for divine intervention and blessings, reflecting a proactive communication with deities to fulfill specific desires or needs. Apotropaic rituals, by contrast, are designed to ward off evil, misfortune, or harmful supernatural influences, serving as protective measures rather than requests. These two categories represent fundamental types of religious and cultural responses to the unseen world, with petitionary acts seeking favor and apotropaic acts seeking defense.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Petitionary rituals historically emerged from early human societies seeking divine intervention through prayers and offerings to deities for favors or protection. Apotropaic practices originated in ancient cultures as defensive measures involving symbols, amulets, or gestures designed to ward off evil spirits and misfortune. Over time, petitionary rituals evolved to incorporate structured religious ceremonies, while apotropaic actions became ingrained in folklore and everyday customs for safeguarding individuals and communities.
Core Purposes and Motivations
Petitionary acts are driven by the core purpose of requesting divine intervention or assistance, often motivated by hope for blessings, favors, or solutions to personal and communal problems. Apotropaic actions focus on warding off evil, misfortune, or harmful spirits, motivated by the desire for protection and maintaining spiritual or physical safety. These distinct motivations shape the intent and practice of ritualistic behaviors in religious and cultural contexts.
Rituals and Methods in Each Practice
Petitionary rituals involve practitioners performing specific prayers, offerings, or invocations aimed at requesting favors, blessings, or intervention from deities or spirits. Apotropaic methods utilize symbolic actions such as the use of talismans, protective amulets, gestures, and incantations designed to ward off evil influences, negative energies, or harm. Both practices rely on established ritual frameworks, but petitionary focuses on supplication while apotropaic emphasizes protection through symbolic deterrence.
Cultural Contexts and Religious Significance
Petitionary rituals involve appeals or requests to deities for blessings, protection, or intervention, reflecting a direct communication with the divine in many religious traditions worldwide. Apotropaic practices, rooted in cultural contexts, emphasize warding off evil influences or harmful spirits through symbols, amulets, or rituals, serving as protective measures in spiritual belief systems. These differing ritual forms showcase the complex relationship between communities and their understanding of divine power, where petitionary acts seek aid while apotropaic actions aim to repel negativity.
Key Examples Across Traditions
Petitionary practices involve prayers and rituals requesting divine intervention, exemplified by Christian supplications like the Lord's Prayer and Islamic Du'a for protection and blessings. Apotropaic traditions use objects or actions to ward off evil, such as the use of the Eye of Horus in Ancient Egypt, garlic in Mediterranean cultures, and Tibetan prayer flags believed to disperse negative energy. Both approaches appear across global religions, including Hinduism's mantra recitations for divine favor and African Vodun rituals employing symbolic amulets for spiritual defense.
Psychological and Social Impacts
Petitionary rituals involve requests or prayers directed at deities or spirits, often fostering a sense of hope and agency that can alleviate anxiety and promote psychological resilience. Apotropaic practices aim to ward off negative influences or evil, providing social cohesion by reinforcing shared beliefs and protective norms within a community. Both ritual types influence mental well-being through mechanisms of control and social bonding, shaping cultural responses to uncertainty and stress.
Common Misconceptions
Petitionary and apotropaic practices are often misunderstood as interchangeable spiritual actions, but petitionary rituals specifically request favors or intervention from deities, while apotropaic rituals aim to ward off evil and misfortune. A common misconception is that all protective rituals are apotropaic, neglecting that some petitionary prayers seek protection as a granted favor rather than through repelling forces. Understanding this distinction clarifies ritual intentions and enhances interpretation of religious practices across cultures.
Modern Relevance and Adaptations
Petitionary practices, involving direct appeals to deities or supernatural forces for intervention, remain prevalent in modern religious rituals, demonstrating their ongoing relevance in contemporary spirituality and community cohesion. Apotropaic measures, designed to ward off evil or harm, have evolved into modern symbols such as protective charms, security technologies, and superstitious behaviors reflecting cultural adaptations of ancient beliefs. The intersection of these practices illustrates how traditional spiritual concepts continue to shape modern approaches to coping with uncertainty and seeking protection.
Petitionary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com