Divine sovereignty embodies the ultimate authority and control that a higher power holds over the universe, shaping existence according to a grand, purposeful design. This concept underscores the belief that all events unfold under divine will, offering reassurance and a framework for understanding life's uncertainties. Explore the article further to deepen your understanding of how divine sovereignty influences faith and human experience.
Table of Comparison
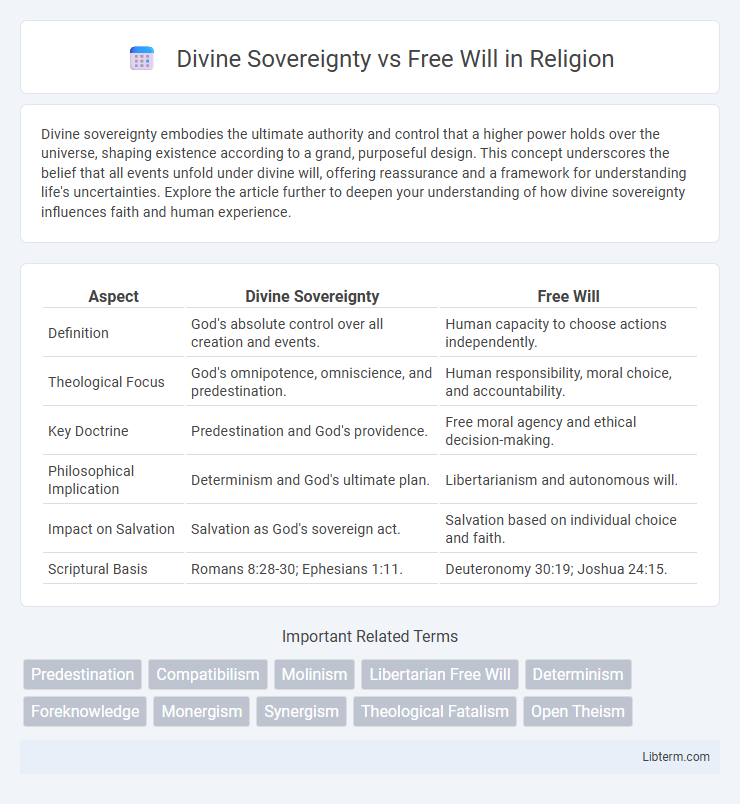
| Aspect | Divine Sovereignty | Free Will |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | God's absolute control over all creation and events. | Human capacity to choose actions independently. |
| Theological Focus | God's omnipotence, omniscience, and predestination. | Human responsibility, moral choice, and accountability. |
| Key Doctrine | Predestination and God's providence. | Free moral agency and ethical decision-making. |
| Philosophical Implication | Determinism and God's ultimate plan. | Libertarianism and autonomous will. |
| Impact on Salvation | Salvation as God's sovereign act. | Salvation based on individual choice and faith. |
| Scriptural Basis | Romans 8:28-30; Ephesians 1:11. | Deuteronomy 30:19; Joshua 24:15. |
Understanding Divine Sovereignty: Foundations and Definitions
Divine sovereignty refers to the absolute authority and supreme power of God over all creation, encompassing His control, knowledge, and governance of the universe. It is foundational in theology, illustrating God's unrestricted ability to enact His will without external limitation, while simultaneously implying a purposeful design behind all events. Definitions emphasize God's omnipotence and omniscience, asserting that His sovereign plan harmonizes with the existence of human free will, despite varying theological interpretations.
The Concept of Free Will in Human Existence
The concept of free will in human existence centers on the ability to make choices independently of divine predestination or external coercion. Free will empowers individuals to act according to personal desires and moral reasoning, shaping their destiny through conscious decision-making. This autonomy is essential in understanding human responsibility and the meaningfulness of ethical accountability within theological and philosophical frameworks.
Historical Perspectives: Debates through the Ages
Historical debates on Divine Sovereignty versus Free Will trace back to early Christian theologians like Augustine and Pelagius, who disputed humanity's capacity for free choice under divine omnipotence. Medieval scholastics such as Thomas Aquinas balanced God's absolute power with human free will through nuanced interpretations of grace and predestination. The Reformation intensified these discussions, with figures like John Calvin emphasizing predestination and divine decree, while Arminius advocated for conditional election reflecting human free will.
Scriptural Interpretations: Key Passages Analyzed
Scriptural interpretations of divine sovereignty versus free will often focus on key passages such as Romans 8:28-30, which emphasizes God's predestining purposes, and Joshua 24:15, highlighting human choice in serving God. Ephesians 1:11 underscores God's sovereign plan being accomplished according to His will, whereas Deuteronomy 30:19 demonstrates the clear human responsibility to choose life or death. These passages reveal the biblical tension between God's ultimate authority and human decision-making, shaping theological debates on predestination and moral accountability.
Philosophical Arguments for Divine Control
Philosophical arguments for divine sovereignty emphasize God's omnipotence, omniscience, and perfect will as foundational to absolute control over the universe and human actions. The Principle of Causality supports divine determinism by asserting that all events, including human choices, are contingent upon God's prior decree. Compatibilist perspectives argue that free will and divine sovereignty coexist, as human decisions are freely made within the framework of God's providential control and foreordination.
The Case for Human Autonomy: Ethical Implications
Human autonomy highlights the ethical imperative of individual moral responsibility within the framework of divine sovereignty, emphasizing the capacity for free will in decision-making. Ethical implications arise from acknowledging personal accountability, which shapes justice systems and moral evaluations, reinforcing the significance of choice in human actions. This perspective supports the idea that divine sovereignty coexists with human freedom, ensuring meaningful ethical engagement and moral growth.
Theological Reconciliation: Bridging the Divide
Theological reconciliation between divine sovereignty and free will involves affirming God's ultimate authority while recognizing human responsibility in moral decision-making. Scholars propose models like compatibilism, where God's sovereign plan encompasses human choices without coercing them, maintaining both divine control and genuine human freedom. This approach bridges doctrinal divides by emphasizing a dynamic interplay, preserving God's omnipotence and human accountability within a unified theological framework.
Divine Sovereignty vs Free Will in Daily Life
Divine sovereignty shapes daily life by affirming that all events unfold under God's ultimate control, guiding believers to trust in divine providence despite uncertainties. Free will enables individuals to make personal choices, fostering moral responsibility and accountability in everyday decisions. The dynamic tension between divine sovereignty and human freedom encourages a balanced perspective where faith and choice coexist in practical living.
Impact on Faith and Belief Systems
Divine sovereignty asserts God's ultimate authority over all events, shaping faith systems that emphasize trust in divine providence and predestination. Free will highlights human autonomy in moral choices, influencing beliefs that prioritize personal responsibility and the capacity to shape one's spiritual destiny. The tension between these concepts impacts theological interpretations, ethical frameworks, and believers' understanding of salvation and accountability.
Contemporary Views and Future Discussions
Contemporary views on Divine Sovereignty versus Free Will explore the balance between God's omnipotent control and human autonomy, emphasizing compatibilism as a leading theological perspective. Scholars analyze biblical texts alongside quantum physics insights to argue that divine foreknowledge does not negate genuine human choice. Future discussions are anticipated to incorporate advancements in neuroscience and artificial intelligence to deepen understanding of free will within a divinely sovereign framework.
Divine Sovereignty Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com