Riwayah represents a distinctive narrative style that intertwines cultural heritage with storytelling, enriching the reader's understanding of traditional values. This form of storytelling often emphasizes emotional depth and intricate character development, making it resonate on a personal level. Explore the full article to discover how Riwayah can transform your appreciation for cultural narratives.
Table of Comparison
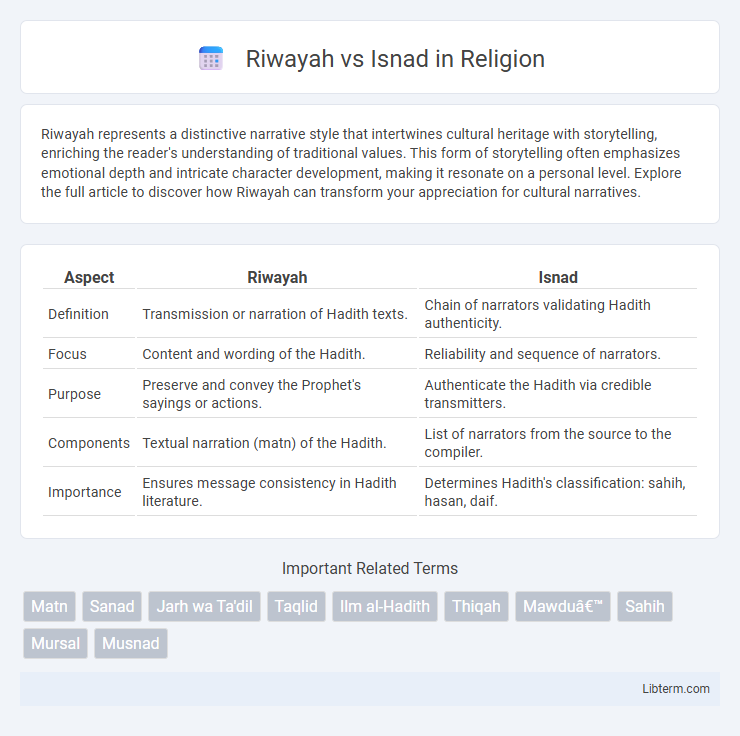
| Aspect | Riwayah | Isnad |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transmission or narration of Hadith texts. | Chain of narrators validating Hadith authenticity. |
| Focus | Content and wording of the Hadith. | Reliability and sequence of narrators. |
| Purpose | Preserve and convey the Prophet's sayings or actions. | Authenticate the Hadith via credible transmitters. |
| Components | Textual narration (matn) of the Hadith. | List of narrators from the source to the compiler. |
| Importance | Ensures message consistency in Hadith literature. | Determines Hadith's classification: sahih, hasan, daif. |
Understanding Riwayah: Definition and Scope
Riwayah refers to the transmission or narration of hadith, encompassing the actual content and wording conveyed by narrators in the chain. It involves the preservation and accurate reporting of prophetic sayings, actions, or approvals, emphasizing the authenticity and integrity of the text. Understanding Riwayah is crucial for assessing the reliability of hadith literature and differentiating between transmitted content and the chain of narrators known as Isnad.
What is Isnad? Clarifying the Concept
Isnad refers to the chain of narrators who transmit a particular hadith, serving as a critical tool to verify the authenticity and reliability of the report. Each narrator in the isnad must be scrutinized for their trustworthiness, memory, and continuity to ensure the hadith's credibility. This rigorous process of isnad evaluation distinguishes authentic prophetic traditions from fabricated or weak narrations in Islamic scholarship.
Historical Evolution of Riwayah and Isnad
The historical evolution of Riwayah and Isnad reveals a meticulous system developed by early Islamic scholars to ensure the authenticity of Hadith transmission. Riwayah refers to the narrated content of a Hadith, while Isnad represents the chain of narrators validating its reliability. Over centuries, the refinement of Isnad established rigorous criteria for scrutinizing narrators' trustworthiness, shaping the preservation and classification of prophetic traditions.
Key Differences Between Riwayah and Isnad
Riwayah refers to the transmission or narration of a specific hadith text, focusing on the content being passed down, while Isnad denotes the chain of narrators who have conveyed that hadith from the original source. The key difference lies in Riwayah emphasizing the actual wording and text of the hadith, whereas Isnad concentrates on the reliability and authenticity of each narrator within the transmission chain. Understanding Isnad is crucial for verifying the credibility of the Riwayah and ensuring the integrity of Islamic teachings.
The Role of Riwayah in Islamic Scholarship
Riwayah plays a crucial role in Islamic scholarship by preserving the exact wording of prophetic traditions, ensuring authenticity through meticulous transmission. It complements Isnad by providing the content or narration that Isnad's chain of trust verifies, thus maintaining the integrity of Hadith literature. The rigorous documentation and comparison of Riwayah enable scholars to authenticate teachings and resolve textual variations across Islamic sources.
Importance of Isnad in Hadith Authentication
Isnad plays a crucial role in hadith authentication by providing a verifiable chain of narrators that ensures the reliability and credibility of the transmitted sayings and actions of the Prophet Muhammad. This rigorous scrutiny of each narrator's trustworthiness, memory, and integrity protects the hadith from fabrication and errors, distinguishing authentic reports from weak or fabricated ones. While the riwayah focuses on the content of the hadith, the isnad guarantees its authenticity by establishing an unbroken and trustworthy transmission lineage essential for Islamic jurisprudence and scholarship.
How Riwayah and Isnad Complement Each Other
Riwayah and Isnad serve as fundamental elements in the transmission of Islamic knowledge, with Riwayah representing the actual narration or text of a hadith and Isnad referring to the chain of narrators verifying its authenticity. The integrity of a hadith relies on the Isnad's rigorous scrutiny of each narrator's reliability, ensuring that the Riwayah is accurately preserved and free from corruption. Together, Riwayah and Isnad establish a cohesive system of validation that upholds the credibility of Islamic teachings and scholarly tradition.
Common Misconceptions About Riwayah and Isnad
Riwayah and Isnad in Hadith studies are often confused, with many mistakenly believing Riwayah refers solely to the narration text, while Isnad specifically denotes the chain of transmitters. A common misconception is treating Riwayah as the content without recognizing its reliance on the authenticity of Isnad for validation. Accurate Hadith analysis requires distinguishing Riwayah as the content transmission and Isnad as the critical evaluative framework ensuring the Hadith's reliability.
Modern Perspectives on Riwayah vs Isnad
Modern perspectives on Riwayah vs Isnad emphasize the evolving methodologies in Hadith authentication, where Riwayah pertains to the actual content and transmission of the hadith text, while Isnad focuses on the chain of narrators ensuring reliability. Contemporary scholars apply advanced historiographical and textual criticism tools to analyze riwayah, integrating digital databases to assess the accuracy of isnad chains more efficiently. This dual approach enhances the verification process, reflecting a synthesis of traditional Islamic scholarship with modern analytical frameworks.
Conclusion: Riwayah and Isnad in Contemporary Islamic Studies
Riwayah and Isnad serve as foundational elements in contemporary Islamic studies for authenticating Hadith literature, with Riwayah representing the textual transmission and Isnad encompassing the chain of narrators. Modern scholarship increasingly employs Isnad analysis combined with Riwayah scrutiny to assess the reliability and context of prophetic traditions, enhancing the precision of Islamic jurisprudence and theology. This integrated approach underscores the dynamic role of both Riwayah and Isnad in preserving the integrity of Islamic knowledge in academic research.
Riwayah Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com