Faithfulness embodies unwavering loyalty and trustworthiness in relationships, fostering deep emotional bonds and mutual respect. It is essential for building long-lasting connections that thrive on honesty and commitment. Discover how embracing faithfulness can transform Your personal and professional life by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
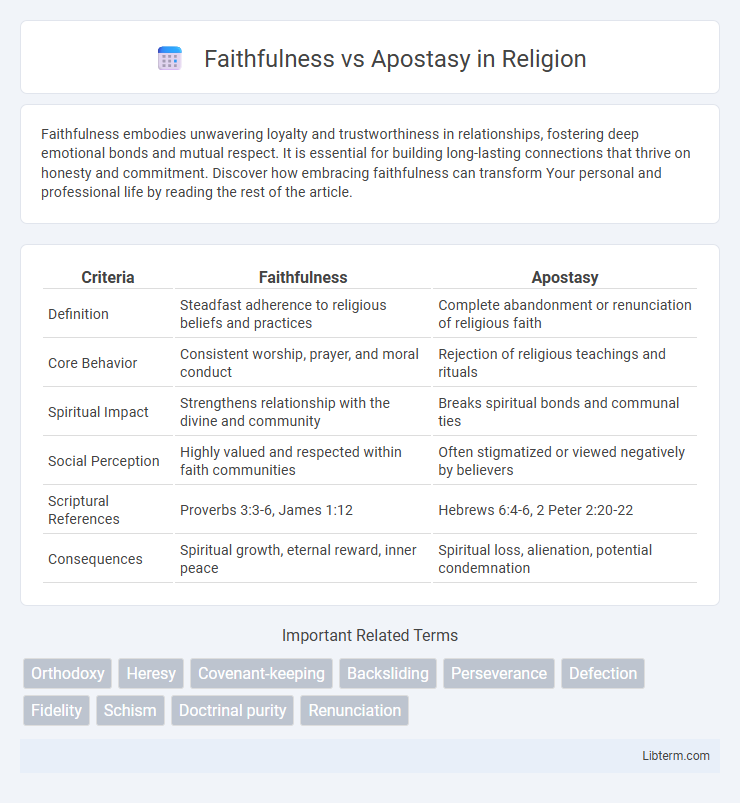
| Criteria | Faithfulness | Apostasy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Steadfast adherence to religious beliefs and practices | Complete abandonment or renunciation of religious faith |
| Core Behavior | Consistent worship, prayer, and moral conduct | Rejection of religious teachings and rituals |
| Spiritual Impact | Strengthens relationship with the divine and community | Breaks spiritual bonds and communal ties |
| Social Perception | Highly valued and respected within faith communities | Often stigmatized or viewed negatively by believers |
| Scriptural References | Proverbs 3:3-6, James 1:12 | Hebrews 6:4-6, 2 Peter 2:20-22 |
| Consequences | Spiritual growth, eternal reward, inner peace | Spiritual loss, alienation, potential condemnation |
Understanding Faithfulness: Core Meanings
Faithfulness embodies unwavering loyalty, trust, and commitment to a person, cause, or belief, reflecting consistency in actions and intentions over time. It is characterized by integrity, reliability, and adherence to moral or spiritual principles despite challenges or temptations. Understanding faithfulness requires recognizing its role as a foundation for trust, stability, and enduring relationships within religious, personal, and social contexts.
Defining Apostasy: Origins and Implications
Apostasy, originating from the Greek term "apostasia" meaning defection or rebellion, signifies the deliberate renunciation or abandonment of religious faith, particularly within Christian theology. Its implications extend beyond personal belief, often triggering social ostracism, theological condemnation, and legal repercussions in various religious communities worldwide. Understanding apostasy involves examining its historical roots and the diverse doctrinal responses that shape religious identity and community boundaries.
Historical Perspectives on Faithfulness and Apostasy
Historical perspectives on faithfulness and apostasy reveal complex dynamics across religious traditions, illustrating how steadfast adherence to doctrines often defined communal identity while apostasy was met with varying degrees of ostracism or persecution. In ancient Christianity, early church fathers characterized apostasy as a grave spiritual failure threatening salvation, leading to the establishment of penance systems for repentant apostates. Similarly, Islamic history documents rigorous responses to apostasy, with theological debates influencing legal rulings and social consequences, reflecting the profound impact of faithfulness and apostasy on societal cohesion and religious authority.
Faithfulness in Religious Texts
Faithfulness in religious texts is often depicted as unwavering devotion and loyalty to divine commandments, exemplified by figures like Abraham in the Bible and Prophet Muhammad in the Quran. These scriptures emphasize that faithfulness leads to spiritual rewards and divine favor, reinforcing moral conduct and perseverance in trials. The consistent portrayal of faithfulness underscores its central role as a foundational virtue that sustains the believer's relationship with God and community.
Causes and Triggers of Apostasy
Apostasy often arises from intense personal doubts, social pressures, or disillusionment with religious institutions, leading individuals to question or reject previously held beliefs. Key triggers include exposure to conflicting ideologies, moral conflicts within religious teachings, and negative experiences with religious communities. Psychological factors such as cognitive dissonance and crises of identity also play significant roles in causing apostasy.
Faithfulness vs Apostasy: Key Differences
Faithfulness entails unwavering loyalty and commitment to religious beliefs, while apostasy involves the complete renunciation or abandonment of those beliefs. Key differences include faithfulness's emphasis on spiritual perseverance, obedience, and adherence to divine commandments, contrasted with apostasy's rejection of core doctrines and often public disavowal of faith. These distinctions highlight faithfulness as a marker of spiritual integrity, whereas apostasy signals a transformative departure from foundational religious identity.
Social and Cultural Impact of Each Path
Faithfulness fosters community cohesion by reinforcing shared values, rituals, and traditions that strengthen social bonds and cultural identity. Apostasy often challenges societal norms, leading to marginalized groups or social conflict as individuals reject established beliefs and practices. The tension between faithfulness and apostasy can significantly influence social dynamics, cultural evolution, and the preservation or transformation of collective heritage.
Personal Stories: Choosing Faithfulness or Apostasy
Personal stories of faithfulness often reveal resilience amid adversity, showcasing individuals who prioritize spiritual commitment over societal pressures. Experiences of apostasy highlight complex journeys marked by doubt, self-discovery, and sometimes alienation from religious communities. These narratives deepen understanding of the human struggle between loyalty to belief systems and the search for personal truth.
Repercussions and Rewards: Societal and Spiritual
Faithfulness cultivates social cohesion and spiritual well-being, often leading to communal respect and divine favor, enriching both the individual's societal standing and inner peace. Apostasy frequently results in social ostracism and spiritual alienation, creating barriers to community participation and divine connection. The interplay of societal repercussions and spiritual rewards underscores the profound impact of loyalty or abandonment on individual and collective experiences.
Navigating Modern Challenges: Maintaining Faith or Facing Apostasy
Navigating modern challenges requires steadfast commitment to doctrinal truths and consistent spiritual disciplines to maintain faithfulness amidst societal pressures promoting apostasy. Engagement with faith-based communities and critical examination of contemporary ideologies strengthens resilience against doubts and secular influences. Cultivating a deep, personal relationship with core religious teachings enables believers to confront modern skepticism without compromising their spiritual integrity.
Faithfulness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com