Consecration is the solemn dedication of a person, object, or place to a sacred purpose, often marked by a formal religious ceremony. This spiritual act signifies a transformation, setting apart what is consecrated for divine use or worship. Explore the rest of this article to understand the profound significance and diverse practices of consecration.
Table of Comparison
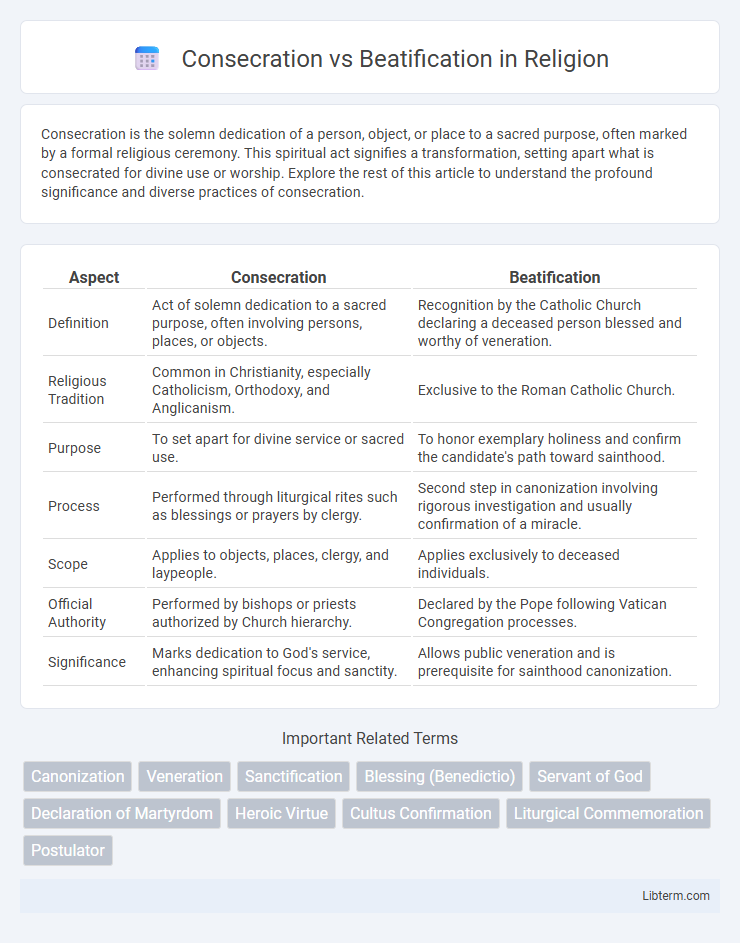
| Aspect | Consecration | Beatification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Act of solemn dedication to a sacred purpose, often involving persons, places, or objects. | Recognition by the Catholic Church declaring a deceased person blessed and worthy of veneration. |
| Religious Tradition | Common in Christianity, especially Catholicism, Orthodoxy, and Anglicanism. | Exclusive to the Roman Catholic Church. |
| Purpose | To set apart for divine service or sacred use. | To honor exemplary holiness and confirm the candidate's path toward sainthood. |
| Process | Performed through liturgical rites such as blessings or prayers by clergy. | Second step in canonization involving rigorous investigation and usually confirmation of a miracle. |
| Scope | Applies to objects, places, clergy, and laypeople. | Applies exclusively to deceased individuals. |
| Official Authority | Performed by bishops or priests authorized by Church hierarchy. | Declared by the Pope following Vatican Congregation processes. |
| Significance | Marks dedication to God's service, enhancing spiritual focus and sanctity. | Allows public veneration and is prerequisite for sainthood canonization. |
Understanding Consecration and Beatification
Consecration is the solemn dedication of a person, place, or object to a sacred purpose, often involving rituals and vows that signify a permanent commitment to religious life or service. Beatification is a recognition by the Catholic Church that a deceased person led a holy life and is blessed, allowing public veneration and serving as a step toward sainthood. Understanding these distinctions highlights the difference between consecration as an act of devotion or sanctification and beatification as a formal acknowledgment of virtue and holiness.
Historical Origins of Consecration and Beatification
Consecration traces its historical origins to early Christian rituals where individuals, objects, or places were solemnly dedicated to divine service, often linked to biblical practices of sanctification. Beatification emerged during the Middle Ages as a formal recognition by the Catholic Church, marking a step before sainthood and allowing veneration of a person believed to have led a holy life. Both rites have evolved distinctly, with consecration emphasizing dedication and beatification focusing on acknowledging exemplary virtue and miracles.
Theological Foundations: Consecration vs Beatification
Consecration in theology signifies a solemn dedication to God, often involving sacramental rites that set a person or object apart for divine service, reflecting an unchangeable spiritual transformation. Beatification, however, is a recognition by the Catholic Church of a deceased person's entrance into heaven and ability to intercede for the faithful, serving as a step toward canonization rather than a sacramental act. The theological foundation of consecration emphasizes sanctification and divine empowerment, while beatification focuses on heavenly acknowledgment and ecclesiastical validation of holiness.
Key Differences Between Consecration and Beatification
Consecration is the solemn dedication of a person, place, or object to a sacred purpose, often involving a religious ritual that establishes its holy status, while beatification is a formal recognition by the Catholic Church of a deceased person's entrance into heaven and their ability to intercede on behalf of individuals who pray in their name. Consecration typically applies to living individuals, sacred objects, or spaces, whereas beatification pertains exclusively to deceased persons deemed to have lived holy lives or martyrs. The key difference lies in consecration's role in establishing ongoing sacred service and beatification's function as a step toward sainthood in the canonization process.
The Process of Consecration Explained
Consecration involves a solemn dedication to a sacred purpose, often requiring formal rites such as the laying on of hands and a specific prayer of invocation. The process includes an official ceremony conducted by a bishop or ecclesiastical authority, symbolizing the total commitment of a person, place, or object to divine service. Unlike beatification, which is a recognition of a person's heroic virtues and a step toward sainthood, consecration confers a permanent spiritual status often linked to liturgical or religious function.
The Steps Involved in Beatification
Beatification is a key step in the Catholic Church's process toward sainthood, involving rigorous verification of a candidate's virtuous life and a confirmed miracle attributed to their intercession. The process begins with a local bishop's investigation, followed by the Vatican's Congregation for the Causes of Saints examining the evidence and theological aspects. After approval, the Pope officially declares the individual Blessed, permitting public veneration and moving the cause closer to potential canonization.
Iconic Examples of Consecrated and Beatified Individuals
Consecration refers to the solemn dedication of a person or object to a sacred purpose, exemplified by figures like Saint Teresa of Avila, who was consecrated as a Carmelite nun and mystic. Beatification is a recognition by the Catholic Church of a deceased person's entrance into heaven and capacity to intercede for those on earth, with iconic beatified individuals such as Blessed Carlo Acutis, known for his devotion to the Eucharist and use of technology to spread faith. These distinctions highlight the different spiritual honors and stages of formal sainthood within the Church.
Significance in the Catholic Church
Consecration in the Catholic Church signifies the solemn dedication of a person, place, or object to God's service, embodying a sacred commitment and spiritual transformation. Beatification, a key step in the canonization process, recognizes a deceased individual's entrance into heaven and their ability to intercede for people on earth, highlighting their exemplary holiness and virtue. Both practices emphasize the Church's role in sanctifying and venerating individuals and elements crucial to Catholic faith and devotion.
Common Misconceptions About Consecration and Beatification
Consecration and beatification are often confused despite their distinct roles in Catholic tradition; consecration is the solemn dedication of a person, place, or thing to God, while beatification is a recognition by the Church declaring a deceased person as blessed and a step toward sainthood. A common misconception is that consecration automatically implies sainthood, whereas it primarily signifies a sacred commitment rather than a formal canonization process. Beatification requires verified miracles attributed to the candidate's intercession, whereas consecration involves ritual acts without the necessity of such validations.
Consecration vs Beatification: Why the Distinction Matters
Consecration involves dedicating a person, place, or object to a sacred purpose, signifying a permanent and solemn commitment within religious traditions, especially in Christianity. Beatification is a recognition by the Catholic Church declaring a deceased person's entrance into heaven and capacity to intercede for those who pray in his or her name, serving as a step toward sainthood. Understanding the distinction matters as consecration pertains to sacred dedication, while beatification validates holiness and paves the way for public veneration and eventual canonization.
Consecration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com