Monophysitism is a Christological doctrine asserting that Jesus Christ has a single, divine nature rather than two distinct natures, divine and human. This belief contrasts with the Chalcedonian definition, which affirms both fully divine and fully human natures in one person. Explore the article to understand the historical context and theological implications of Monophysitism.
Table of Comparison
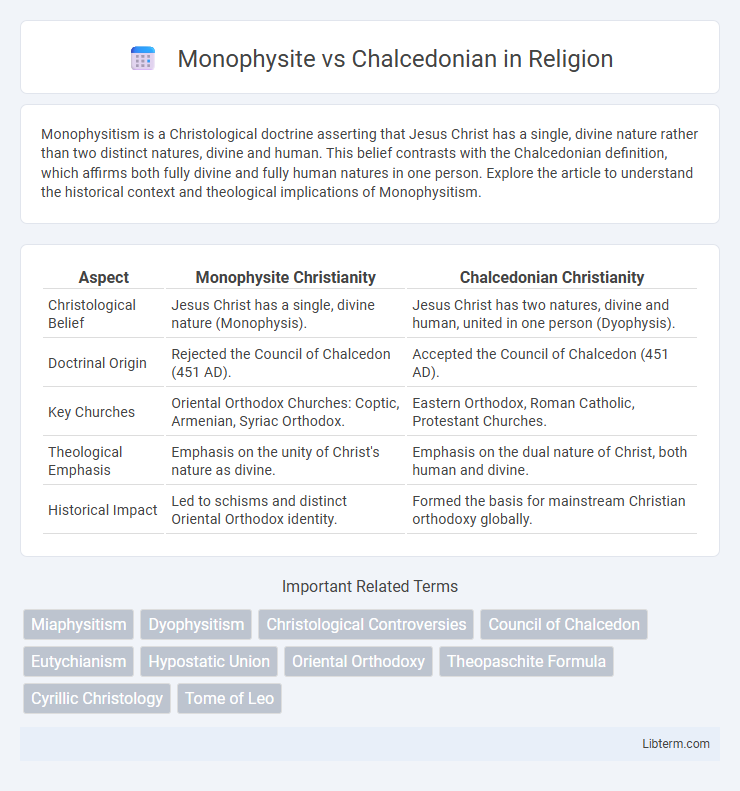
| Aspect | Monophysite Christianity | Chalcedonian Christianity |
|---|---|---|
| Christological Belief | Jesus Christ has a single, divine nature (Monophysis). | Jesus Christ has two natures, divine and human, united in one person (Dyophysis). |
| Doctrinal Origin | Rejected the Council of Chalcedon (451 AD). | Accepted the Council of Chalcedon (451 AD). |
| Key Churches | Oriental Orthodox Churches: Coptic, Armenian, Syriac Orthodox. | Eastern Orthodox, Roman Catholic, Protestant Churches. |
| Theological Emphasis | Emphasis on the unity of Christ's nature as divine. | Emphasis on the dual nature of Christ, both human and divine. |
| Historical Impact | Led to schisms and distinct Oriental Orthodox identity. | Formed the basis for mainstream Christian orthodoxy globally. |
Introduction to Monophysitism and Chalcedonian Christianity
Monophysitism asserts that Christ has a single, divine nature, emphasizing the unity of His divinity over His humanity, a doctrine that diverged significantly from Chalcedonian Christianity. Chalcedonian Christianity, defined by the Council of Chalcedon in 451 AD, teaches the doctrine of two distinct natures in Christ, divine and human, unified in one person "without confusion, change, division, or separation." This Christological difference became a pivotal theological divide influencing early Christian doctrine, ecclesiastical relations, and regional church affiliations.
Historical Context and Origins
The Monophysite controversy originated in the 5th century as a theological response to the Council of Chalcedon in 451 AD, which affirmed that Jesus Christ has two distinct natures, divine and human, in one person. Monophysitism, emphasizing a single divine nature, gained prominence in regions like Egypt and Syria, challenging Chalcedonian orthodoxy upheld by the Byzantine Empire. This doctrinal dispute significantly influenced the schism between Eastern Orthodox and Oriental Orthodox churches.
Core Theological Differences
Monophysitism asserts that Christ has a single, divine nature, merging His humanity into His divinity, while Chalcedonian doctrine affirms the dual nature of Christ as both fully divine and fully human, distinct yet united in one person. The Chalcedonian Definition, established in 451 AD, emphasizes the coexistence of two natures "without confusion, change, division, or separation," contrasting with Monophysite views that reject this duality. This theological divergence directly impacts Christology, ecclesiology, and soteriology within Eastern Christian traditions.
Key Councils and Decrees
The Monophysite controversy primarily centers on the nature of Christ, asserting a single divine nature, as opposed to the Chalcedonian definition from the Council of Chalcedon in 451 AD, which declared Christ in two natures, divine and human, "without confusion, without change, without division, without separation." The Council of Ephesus (431 AD) initially condemned Nestorianism and upheld the title Theotokos for Mary, setting the stage for later disputes, while the Chalcedonian Creed became a significant point of doctrinal divergence leading to schisms with Monophysite groups rejecting Chalcedon's dual-nature doctrine. These key ecumenical councils shaped early Christian theological boundaries and ecclesiastical authority, deeply influencing both Eastern Orthodox and Oriental Orthodox traditions.
Notable Figures and Proponents
Notable figures in the Monophysite movement include Severus of Antioch and Dioscorus of Alexandria, who asserted the single divine nature of Christ against Chalcedonian doctrine. Chalcedonian proponents like Pope Leo I and Emperor Justinian I upheld the dual nature of Christ as both fully divine and fully human, defined at the Council of Chalcedon in 451 AD. The theological conflict between these figures significantly shaped early Christian doctrinal developments and ecclesiastical alignments.
Impact on Early Christian Communities
The Monophysite controversy, stemming from the belief in Christ's single divine nature, caused significant divisions within early Christian communities, particularly in Egypt, Syria, and Armenia, leading to the formation of distinct ecclesiastical structures. Chalcedonian Christianity, established by the Council of Chalcedon in 451 AD, affirmed the doctrine of two natures--divine and human--in Christ, which was accepted chiefly by the Byzantine Empire and Western churches. This theological rift contributed to enduring schisms, influencing the political and cultural identities of regions and fostering the development of independent Oriental Orthodox churches.
Political and Cultural Influences
The Monophysite controversy deeply influenced the political landscape of the Byzantine Empire by fueling tension between imperial authorities and regional leaders, particularly in Egypt and Syria, where Monophysitism found strong support. Chalcedonian Christianity, endorsed by the Council of Chalcedon in 451, became a tool for imperial cohesion and uniformity, often marginalizing Monophysite populations and contributing to cultural divisions within the Eastern Mediterranean. The rivalry between these doctrinal positions not only shaped ecclesiastical policy but also played a critical role in the formation of distinct ethnic and national identities across the Christian Middle East.
Schism and Long-term Religious Consequences
The Monophysite-Chalcedonian schism emerged from the Council of Chalcedon's 451 AD declaration affirming Christ's dual nature, which Monophysites rejected, insisting on a single divine nature. This theological rift led to significant ecclesiastical divisions, particularly between the Eastern Orthodox and Oriental Orthodox Churches. Long-term religious consequences include enduring doctrinal disputes, the formation of distinct Christian communities, and ongoing challenges to church unity across Armenia, Egypt, and Syria.
Modern Perspectives and Reconciliation Efforts
Modern perspectives on Monophysite and Chalcedonian Christologies emphasize a nuanced understanding of early doctrinal disputes, highlighting the shared commitment to Christ's divinity and humanity despite differing terminologies. Recent ecumenical dialogues, particularly between the Oriental Orthodox Churches and the Chalcedonian Orthodox and Catholic Churches, have fostered theological clarifications and mutual recognition, promoting reconciliation. These efforts focus on addressing historical misunderstandings and affirming a common faith in the dual nature of Christ as expressed in complementary theological language.
Lasting Legacy in Contemporary Christianity
The Monophysite controversy, centered on the nature of Christ, profoundly shaped early Christian doctrinal development and ecclesiastical boundaries, leading to the establishment of Oriental Orthodox Churches, which persist today with distinct liturgical traditions and theological perspectives. Chalcedonian Christianity, affirmed by the Council of Chalcedon in 451 AD, remains foundational to the Eastern Orthodox, Roman Catholic, and most Protestant denominations, emphasizing the dual nature of Christ as fully divine and fully human. The ongoing dialogue and coexistence between Monophysite and Chalcedonian traditions continue to influence ecumenical efforts and theological discourse in contemporary Christianity.
Monophysite Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com