Doctrine serves as a fundamental framework guiding legal principles, organizational beliefs, or religious teachings to ensure consistent application and understanding. It shapes how rules are interpreted and enforced across various contexts, influencing decision-making processes and strategic planning. Explore the rest of this article to understand how doctrine impacts your everyday decisions and legal outcomes.
Table of Comparison
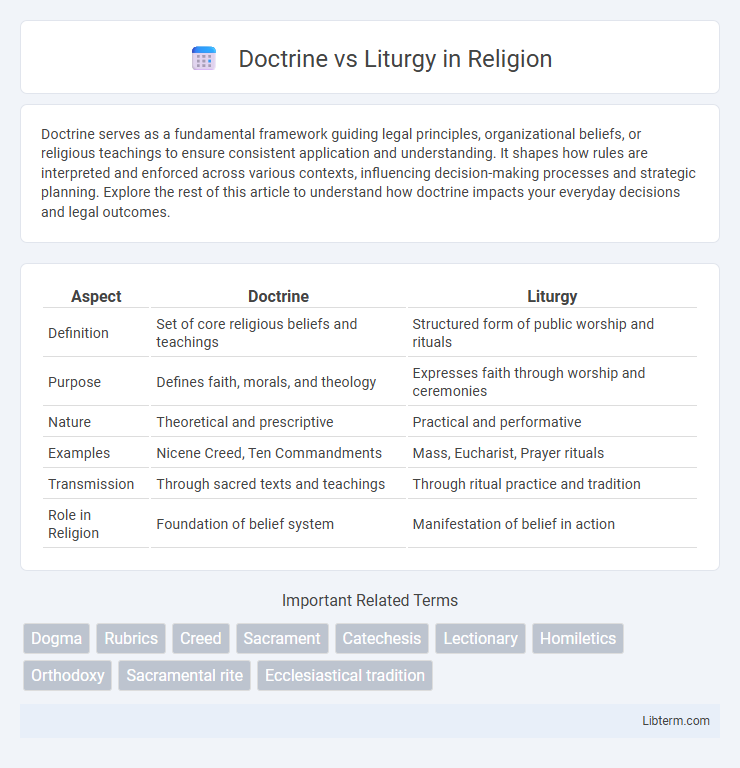
| Aspect | Doctrine | Liturgy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Set of core religious beliefs and teachings | Structured form of public worship and rituals |
| Purpose | Defines faith, morals, and theology | Expresses faith through worship and ceremonies |
| Nature | Theoretical and prescriptive | Practical and performative |
| Examples | Nicene Creed, Ten Commandments | Mass, Eucharist, Prayer rituals |
| Transmission | Through sacred texts and teachings | Through ritual practice and tradition |
| Role in Religion | Foundation of belief system | Manifestation of belief in action |
Understanding Doctrine: Definition and Purpose
Doctrine represents the core beliefs and theological principles that define a religious tradition, serving as the framework for faith and moral guidance. It provides clarity on fundamental truths about God, humanity, and salvation, shaping the community's identity and practices. Understanding doctrine is essential for interpreting liturgy, as it informs the meanings and intentions behind worship rituals and ceremonies.
Defining Liturgy: Meaning and Significance
Liturgy refers to the prescribed form of public worship practiced by a religious community, encompassing rituals, prayers, and ceremonies that express collective faith and devotion. Its significance lies in uniting believers through shared experiences that reinforce theological truths and foster spiritual discipline. Unlike doctrine, which defines core beliefs, liturgy manifests those beliefs in tangible, communal acts of worship.
Historical Development of Doctrine and Liturgy
The historical development of doctrine and liturgy in Christianity reflects distinct but interrelated processes shaped by theological, cultural, and ecclesiastical factors. Doctrine, formulated through ecumenical councils such as Nicaea (325 AD) and Chalcedon (451 AD), established foundational beliefs like the Trinity and Christ's dual nature, guiding church teachings and creeds. Liturgy evolved simultaneously, influenced by early Christian worship practices, Jewish traditions, and regional customs, formalizing rituals and sacraments that expressed and reinforced doctrinal truths within communal worship.
Key Differences Between Doctrine and Liturgy
Doctrine refers to the established beliefs and teachings of a religious tradition that define its core theological principles and moral guidelines. Liturgy encompasses the structured forms of public worship, rituals, and ceremonies practiced by a faith community to express and reinforce those beliefs. Key differences include doctrine's focus on theological content and instruction, while liturgy centers on communal worship practices and sacramental actions.
How Doctrine Shapes Belief Systems
Doctrine establishes foundational beliefs that guide religious communities' understanding of morality, existence, and divine authority, shaping individual and collective identity. It codifies sacred texts and theological interpretations, serving as a framework for consistent belief systems across diverse congregations. This structured guidance influences rituals and liturgical practices by providing the underlying principles that reinforce faith and communal coherence.
The Role of Liturgy in Worship Practices
Liturgy serves as the structured framework for worship practices, providing a communal expression of faith that embodies and reinforces doctrinal beliefs through ritual and symbolism. It facilitates a tangible encounter with the sacred, enabling worshippers to experience theological truths in a participatory context. The role of liturgy extends beyond mere ritual; it educates, unites, and shapes the spiritual identity of the faith community in alignment with doctrinal principles.
Interplay Between Doctrine and Liturgy
The interplay between doctrine and liturgy is essential in shaping both theological understanding and worship practices within religious communities. Doctrine provides the foundational beliefs and theological frameworks, while liturgy embodies these beliefs through ritual, prayer, and sacrament, making abstract principles tangible for adherents. This dynamic relationship ensures that liturgical acts reinforce doctrinal truths, and lived worship experiences, in turn, deepen comprehension and commitment to core teachings.
Examples of Doctrine and Liturgy Across Denominations
Doctrine in Christianity includes core beliefs such as the Nicene Creed, affirming the Trinity and Christ's divinity, and Calvinism's predestination teachings in Reformed traditions. Liturgy varies widely, from the highly structured Roman Catholic Mass with its Eucharistic prayers and sacraments to the more spontaneous and contemporary worship styles found in many Evangelical churches. Orthodox Christianity combines both through the Divine Liturgy, a rich, ancient ritual that expresses and reinforces theological doctrines like the incarnation and resurrection.
Impact on Faith Communities: Doctrine vs Liturgy
Doctrine shapes faith communities by providing a foundational framework of beliefs that unify members through shared theological principles and moral guidelines. Liturgy impacts faith communities by facilitating communal worship experiences that embody and reinforce those doctrines, fostering a sense of spiritual connection and collective identity. The dynamic interaction between doctrine and liturgy enables faith communities to both understand their beliefs intellectually and express them emotionally and ritually.
Contemporary Debates: The Relevance of Doctrine and Liturgy
Contemporary debates on Doctrine versus Liturgy emphasize the dynamic interplay between theological principles and worship practices in shaping modern Christian identity. Doctrine provides a framework for interpreting faith and moral guidance, while Liturgy embodies communal expressions and rituals that cultivate spiritual experience. Scholars argue that balancing doctrinal fidelity with liturgical innovation is crucial for churches addressing cultural relevance and congregational engagement in the 21st century.
Doctrine Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com