An altar serves as a sacred space for religious rituals and spiritual ceremonies, symbolizing devotion and connection with the divine. Its design and materials vary across cultures, reflecting unique traditions and beliefs. Explore the significance and diverse uses of altars to deepen your understanding of their role in various faiths.
Table of Comparison
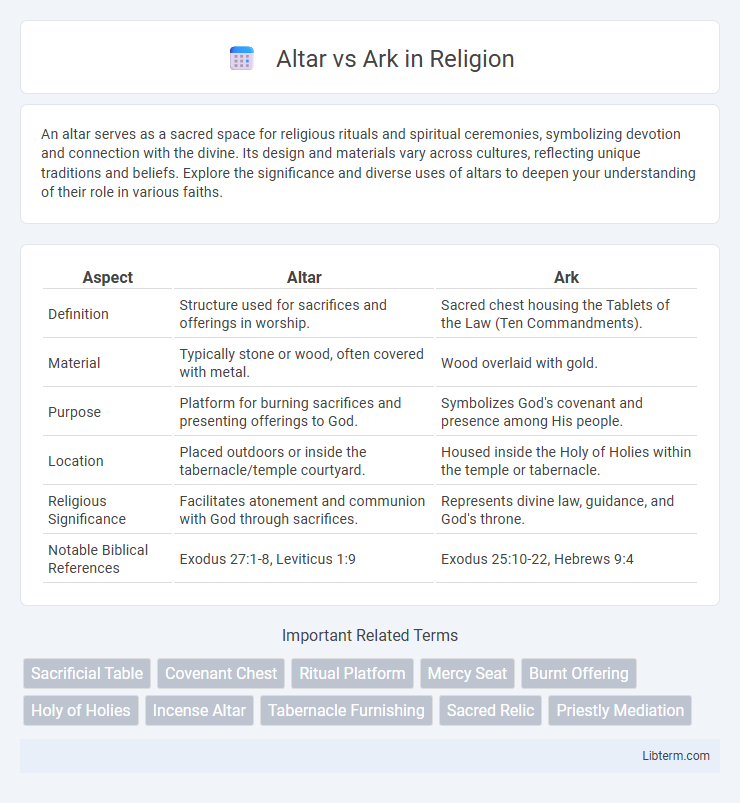
| Aspect | Altar | Ark |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structure used for sacrifices and offerings in worship. | Sacred chest housing the Tablets of the Law (Ten Commandments). |
| Material | Typically stone or wood, often covered with metal. | Wood overlaid with gold. |
| Purpose | Platform for burning sacrifices and presenting offerings to God. | Symbolizes God's covenant and presence among His people. |
| Location | Placed outdoors or inside the tabernacle/temple courtyard. | Housed inside the Holy of Holies within the temple or tabernacle. |
| Religious Significance | Facilitates atonement and communion with God through sacrifices. | Represents divine law, guidance, and God's throne. |
| Notable Biblical References | Exodus 27:1-8, Leviticus 1:9 | Exodus 25:10-22, Hebrews 9:4 |
Introduction to Altars and Arks
Altars and arks hold significant roles in religious and cultural contexts, serving as sacred symbols and functional objects within worship practices. Altars function primarily as platforms for offerings, sacrifices, and rituals, symbolizing a place of communion between the divine and humanity. Arks, often depicted as sacred containers, house sacred relics or texts, emphasizing protection and reverence within spiritual traditions.
Historical Origins of Altars
Altars have their historical origins in ancient religious practices, serving as symbolic sites for offerings and sacrifices to gods or deities, dating back to early Mesopotamian and Egyptian civilizations. Unlike the ark, which historically functioned as a sacred container or chest, altars were constructed as platforms or tables designed to facilitate ritualistic ceremonies. Archaeological evidence reveals that altars evolved to embody spiritual significance across diverse cultures, reflecting humanity's enduring quest to connect with the divine.
Historical Origins of Arks
The historical origins of arks trace back to ancient Mesopotamian and Hebrew traditions where arks served as sacred containers for divine presence, most notably the Ark of the Covenant housing the Tablets of the Law in Israelite culture. Unlike altars that function as sites of sacrifice and offerings, arks symbolized covenantal relationships and divine protection, reflecting their unique role in religious rituals and community identity. Archaeological and textual evidence reveals arks evolving from simple wooden boxes to intricately designed sanctuaries central to worship and cultural heritage throughout ancient Near Eastern societies.
Symbolic Meaning of Altars
Altars symbolize a sacred space for offerings, representing a connection between the earthly and divine realms in various religious traditions. They embody a focal point for worship, sacrifice, and communication with deities, often signifying purification and commitment. Unlike the Ark, which is typically a vessel for preserving sacred objects, altars emphasize the active expression of faith and devotion through rituals.
Symbolic Meaning of Arks
Arks symbolize divine presence and covenant in religious traditions, serving as sacred vessels that embody God's promise and protection. Unlike altars, which primarily represent sacrifice and worship, arks often function as repositories of holy relics and commandments, symbolizing spiritual authority and continuity. The Ark of the Covenant, for example, epitomizes God's guidance and eternal bond with His people in Judaic theology.
Key Differences Between Altar and Ark
The altar serves as a sacred platform for offerings and sacrifices, symbolizing worship and communion with the divine, while the ark functions as a sacred container or chest, housing holy objects like the Tablets of the Covenant. The altar is typically a fixed structure made of wood, stone, or metal, used actively in rituals, whereas the ark is a portable repository, heavily associated with divine presence and protection. Key distinctions include purpose--altar for sacrificial rites, ark for safekeeping sacred items--and form, with the altar open for use and the ark enclosed for preservation.
Functions and Uses in Religious Rituals
The altar functions as a sacred table where offerings, sacrifices, and rituals are performed to honor deities, serving as a focal point in worship ceremonies across various religions. The ark, often a sacred chest or container, holds religious artifacts, such as tablets, scriptures, or relics, symbolizing divine presence and covenant. Together, the altar facilitates active ritual practices, while the ark preserves and represents sacred connections between the divine and worshippers.
Altar and Ark in Various Religions
The altar serves as a sacred platform for offerings and rituals across Christianity, Hinduism, and ancient Greco-Roman religions, symbolizing devotion and sacrifice. The ark appears prominently in Judaism and Christianity as a holy container for sacred objects, such as the Torah scrolls or the Ark of the Covenant housing the Ten Commandments. Both altar and ark function as focal points in religious ceremonies, embodying divine presence and spiritual significance in their respective traditions.
Modern Interpretations and Practices
Modern interpretations distinguish the altar as a place for sacrifice and worship in contemporary religious rituals, while the ark symbolizes divine presence and covenant in spiritual practices. In many churches, altars serve as focal points for Eucharistic celebrations, reflecting ongoing themes of sacrifice and redemption. Arks, especially in Jewish synagogues, function as sacred containers for Torah scrolls, emphasizing preservation of scripture and religious heritage.
Conclusion: Altar vs Ark Significance
The altar symbolizes ritual sacrifice and divine worship, serving as a focal point for offerings and spiritual connection in religious practices. The ark represents God's covenant, housing sacred tablets and embodying divine presence and guidance for the community. Together, the altar and ark highlight distinct but complementary aspects of faith: the altar centers on devotion and atonement, while the ark signifies divine promise and protection.
Altar Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com