Amillennialism interprets the thousand-year reign mentioned in the Book of Revelation as a symbolic period representing Christ's current reign from heaven, rather than a literal earthly kingdom. This theological perspective views the millennium as the present church age, emphasizing spiritual victory over physical rule. Discover how amillennialism shapes Christian eschatology and impacts your understanding of biblical prophecy by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
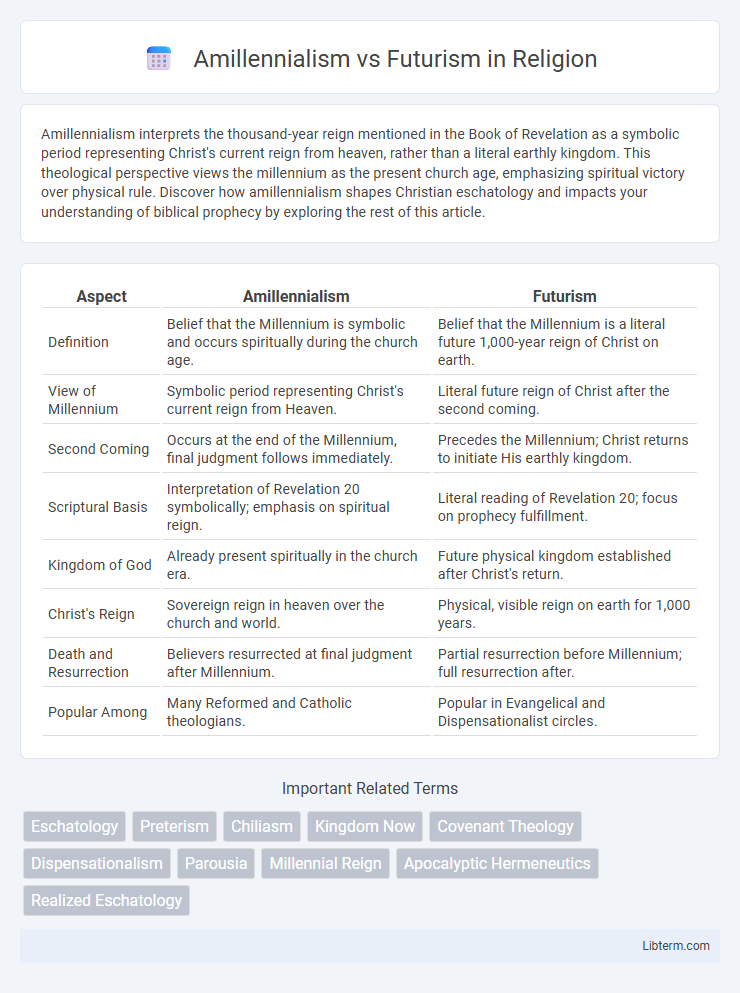
| Aspect | Amillennialism | Futurism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief that the Millennium is symbolic and occurs spiritually during the church age. | Belief that the Millennium is a literal future 1,000-year reign of Christ on earth. |
| View of Millennium | Symbolic period representing Christ's current reign from Heaven. | Literal future reign of Christ after the second coming. |
| Second Coming | Occurs at the end of the Millennium, final judgment follows immediately. | Precedes the Millennium; Christ returns to initiate His earthly kingdom. |
| Scriptural Basis | Interpretation of Revelation 20 symbolically; emphasis on spiritual reign. | Literal reading of Revelation 20; focus on prophecy fulfillment. |
| Kingdom of God | Already present spiritually in the church era. | Future physical kingdom established after Christ's return. |
| Christ's Reign | Sovereign reign in heaven over the church and world. | Physical, visible reign on earth for 1,000 years. |
| Death and Resurrection | Believers resurrected at final judgment after Millennium. | Partial resurrection before Millennium; full resurrection after. |
| Popular Among | Many Reformed and Catholic theologians. | Popular in Evangelical and Dispensationalist circles. |
Introduction to Amillennialism and Futurism
Amillennialism interprets the millennium mentioned in Revelation 20 figuratively, viewing it as the current church age characterized by Christ's spiritual reign rather than a literal thousand-year earthly kingdom. Futurism, on the other hand, anticipates a literal future fulfillment of end-time prophecies, including a forthcoming millennium distinct from the present age. These contrasting eschatological perspectives influence interpretations of biblical prophecy, the nature of Christ's kingdom, and the timing of the final judgment.
Historical Origins of Both Eschatological Views
Amillennialism traces its roots to early church fathers like Augustine, who interpreted the millennium symbolically rather than as a literal 1,000-year reign, emphasizing the spiritual reign of Christ in the present church age. Futurism emerged during the Reformation and gained prominence through theologians such as Francisco Ribera and later John Nelson Darby, who advocated for a literal, future fulfillment of biblical prophecies, including a distinct millennial kingdom. The historical divergence between these eschatological views centers on different hermeneutical approaches to Revelation and prophetic scripture, reflecting evolving theological and ecclesiastical contexts.
Key Scriptural Interpretations
Amillennialism interprets Revelation 20 symbolically, viewing the thousand-year reign as the current church age rather than a literal future event, emphasizing Christ's spiritual reign from heaven. Futurism interprets key prophecies in Daniel and Revelation as yet to be fulfilled, including a literal thousand-year millennial kingdom following Christ's second coming. Amillennialists focus on the present kingdom established through Christ's resurrection, while futurists anticipate distinct, literal end-time events detailed in biblical prophecy.
Differences in Understanding the Millennium
Amillennialism interprets the millennium described in Revelation 20 as a symbolic period representing the current church age, where Christ reigns spiritually rather than a literal thousand-year earthly kingdom. Futurism views the millennium as a future, literal thousand-year reign of Christ on earth following His second coming, emphasizing a physical restoration and fulfillment of prophetic promises. This fundamental difference shapes eschatological expectations, influencing doctrines on Christ's kingdom, the nature of Satan's binding, and the resurrection order.
Views on Christ’s Second Coming
Amillennialism interprets Christ's Second Coming as a singular, future event coinciding with the final judgment and the full establishment of God's kingdom, emphasizing a symbolic millennium in the present church age. Futurism views the Second Coming as a literal, imminent event that will occur after a future seven-year tribulation period, followed by Christ's thousand-year reign on earth. These contrasting eschatological perspectives shape how each tradition understands the timing, nature, and significance of Christ's return.
The Role of Israel and the Church
Amillennialism interprets the promises made to Israel as being fulfilled spiritually through the Church, viewing Israel as the Old Testament community now embodied in the New Testament believers. Futurism distinguishes Israel and the Church as separate entities, expecting a future restoration of Israel with a literal fulfillment of biblical prophecies during Christ's millennial reign. This divergence shapes eschatological perspectives on God's plan, with Amillennialism emphasizing spiritual continuity and Futurism highlighting ethnic and covenantal distinctions.
Perspectives on Prophecy Fulfillment
Amillennialism interprets biblical prophecies, especially in Revelation and Daniel, as largely symbolic and fulfilled spiritually throughout the Church age rather than as literal future events. Futurism, in contrast, views most prophetic passages as awaiting fulfillment during a future tribulation period, culminating in Christ's visible Second Coming. These differing hermeneutical approaches significantly influence eschatological timelines and expectations regarding the Kingdom of God.
Impact on Christian Theology and Practice
Amillennialism influences Christian theology by interpreting the millennium symbolically, emphasizing the present reign of Christ and the church's role in spiritual growth and ethical living. Futurism, by anticipating a literal future thousand-year reign, shapes eschatological expectations, often encouraging believers to prepare for an imminent apocalyptic fulfillment and the physical return of Christ. These differing views impact Christian practice through varied emphases on social engagement, evangelism, and hope in present versus future divine intervention.
Contemporary Debates and Influences
Contemporary debates between Amillennialism and Futurism center on their differing interpretations of biblical prophecy, particularly regarding the millennium and end-times events. Amillennialism, which views the millennium symbolically and believes Christ's reign is currently manifested in the church age, contrasts with Futurism's literal expectation of a future thousand-year reign following the Second Coming. These perspectives significantly influence modern evangelical theology, shaping eschatological teachings and affecting how Christian communities engage with cultural and geopolitical issues related to prophecy.
Conclusion: Evaluating Amillennialism and Futurism
Amillennialism interprets the millennium symbolically, viewing Christ's reign as currently spiritual rather than a literal future event, while Futurism anticipates a distinct, forthcoming thousand-year reign on Earth. Evaluating these perspectives involves assessing scriptural interpretations, historical context, and theological implications concerning eschatology and the nature of Christ's kingdom. Both frameworks offer valuable insights, but their validity depends on one's hermeneutical approach to prophetic biblical texts like Revelation and Daniel.
Amillennialism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com