Liturgy encompasses the structured forms of public worship and ritual practices in many religious traditions, shaping communal spiritual experiences and connecting participants to sacred history. Its components include prayers, hymns, readings, and ceremonies that follow established patterns to foster reverence and reflection. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of how liturgy influences faith and worship across cultures.
Table of Comparison
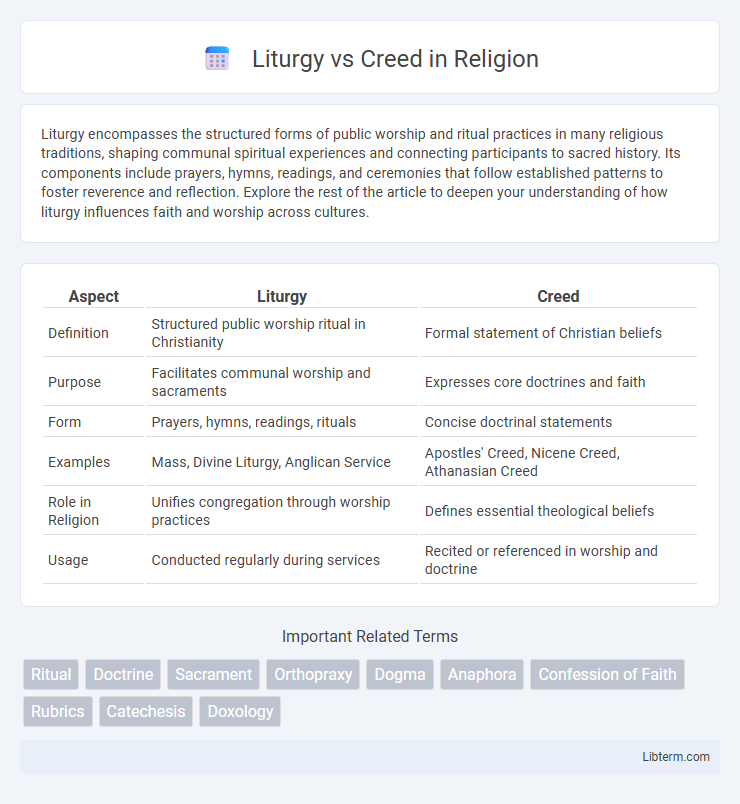
| Aspect | Liturgy | Creed |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured public worship ritual in Christianity | Formal statement of Christian beliefs |
| Purpose | Facilitates communal worship and sacraments | Expresses core doctrines and faith |
| Form | Prayers, hymns, readings, rituals | Concise doctrinal statements |
| Examples | Mass, Divine Liturgy, Anglican Service | Apostles' Creed, Nicene Creed, Athanasian Creed |
| Role in Religion | Unifies congregation through worship practices | Defines essential theological beliefs |
| Usage | Conducted regularly during services | Recited or referenced in worship and doctrine |
Defining Liturgy and Creed
Liturgy refers to the formal public worship practices and rituals conducted by a religious community, encompassing prayers, readings, and ceremonies designed to express and reinforce collective faith. Creed is a concise statement of core religious beliefs, serving as a doctrinal summary that defines the essential theological principles adhered to by a faith tradition. While liturgy involves the enactment of worship, creed provides the foundational confessions that guide and unify the community's beliefs.
Historical Origins of Liturgy and Creed
The historical origins of liturgy trace back to ancient religious rituals and communal worship practices that evolved in early Christianity to structure public prayer and sacraments. The creed emerged as a concise doctrinal statement formulated during early church councils, such as the Council of Nicaea in 325 AD, to unify Christian belief and counter heresies. Both liturgy and creed served foundational roles in shaping Christian worship and doctrinal identity from the 1st to 4th centuries.
Key Components of Christian Liturgy
Christian liturgy centers on key components such as the Eucharist, prayers, hymns, scripture readings, and rituals that structure communal worship and spiritual expression. The creed, including the Nicene or Apostles' Creed, functions as a concise summary of Christian beliefs affirming foundational doctrines like the Trinity and the resurrection. While liturgy engages the congregation in active worship through rituals and participation, the creed serves as a doctrinal anchor, uniting believers in shared faith declarations.
The Structure and Purpose of Creeds
Creeds are structured statements of faith that summarize core Christian beliefs, serving as doctrinal anchors during worship and theological teaching. Their clear, concise format enables congregations to affirm shared truths, reinforcing communal identity and doctrinal consistency across diverse Christian traditions. Unlike liturgies, which encompass entire worship services and rituals, creeds specifically focus on articulating foundational beliefs in a reproducible and memorized format.
Liturgy: Worship in Practice
Liturgy encompasses the structured forms of worship practiced by congregations, including prayers, readings, and rituals that foster communal participation. It serves as a tangible expression of faith, allowing believers to engage with spiritual traditions and reinforce theological beliefs through action. Unlike creeds, which are concise statements of doctrine, liturgy embodies worship in practice by guiding the rhythm and flow of religious ceremonies.
Creeds: Foundations of Belief
Creeds serve as foundational statements of Christian belief, summarizing essential doctrines such as the Trinity, the divinity of Christ, and salvation through grace. These concise declarations, like the Nicene and Apostles' Creeds, provide a unified framework for faith across diverse Christian traditions. By articulating core theological truths, creeds reinforce communal identity and guide worship practices within liturgical settings.
How Liturgy and Creed Intersect
Liturgy and Creed intersect as core expressions of Christian faith, where liturgy embodies the communal worship practice grounded in the theological affirmations of the creed. The creed functions as a doctrinal blueprint, guiding the content and structure of liturgical prayers and rituals that reinforce key beliefs such as the Trinity and Christ's resurrection. Together, they unify doctrinal truth and worship experience, ensuring consistent transmission of faith across generations.
Differences in Function and Emphasis
Liturgy primarily functions as a structured set of rituals and prayers designed for communal worship, emphasizing collective participation and sacramental practices. Creed serves as a concise statement of core Christian beliefs, focusing on doctrinal affirmation and individual confession of faith. While liturgy centers on experiential worship and ritual enactment, creed concentrates on theological clarity and doctrinal orthodoxy.
Liturgy and Creed Across Denominations
Liturgy and Creed serve distinct but complementary roles across Christian denominations, with liturgy encompassing the structured worship practices and rituals, while creed represents formal statements of faith. Liturgical traditions vary widely, from the highly ritualized Catholic Mass and Orthodox Divine Liturgy to the simpler services in many Protestant churches, reflecting diverse theological emphases and historical developments. Creeds like the Nicene Creed and Apostles' Creed unify denominations by articulating foundational Christian beliefs, even as liturgical expressions adapt to cultural and denominational contexts.
Contemporary Relevance of Liturgy and Creed
Liturgy remains a vital element in contemporary worship, providing structured rituals that enhance communal participation and spiritual experience within modern faith communities. The Creed continues to offer a concise summary of core theological beliefs, serving as a foundation for doctrinal clarity and unity in diverse religious contexts. Together, both Liturgy and Creed sustain the transmission of tradition while addressing the evolving spiritual needs of present-day congregations.
Liturgy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com