Islam is a monotheistic religion centered on the belief in one God, Allah, and the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad as conveyed in the Quran. It emphasizes five pillars: faith, prayer, charity, fasting, and pilgrimage, guiding the spiritual and daily life of its followers. Explore this article to deepen your understanding of Islam's core principles and cultural significance worldwide.
Table of Comparison
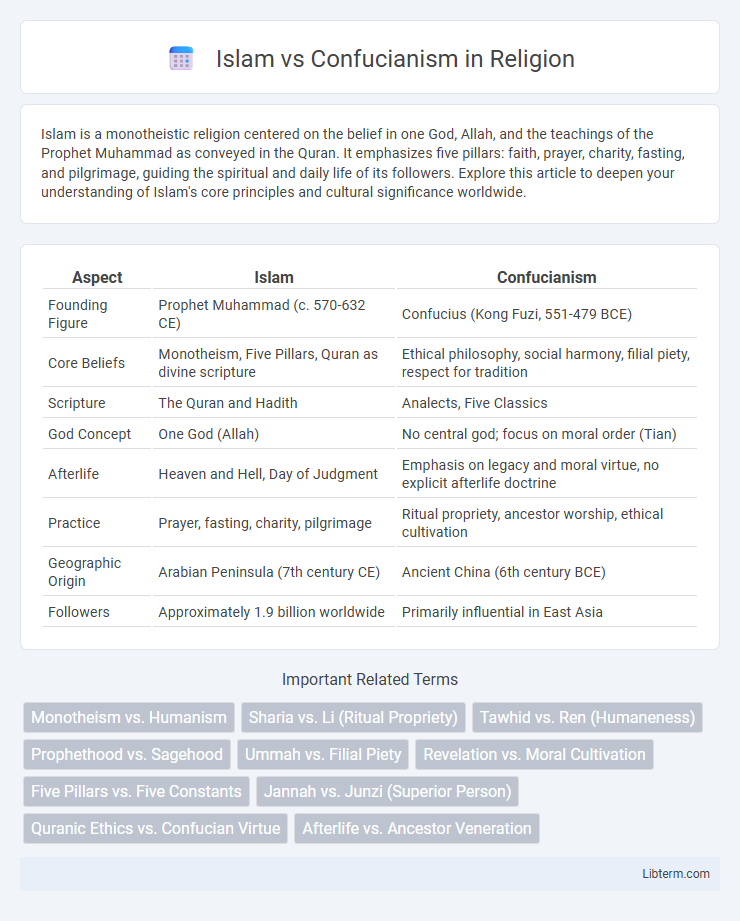
| Aspect | Islam | Confucianism |
|---|---|---|
| Founding Figure | Prophet Muhammad (c. 570-632 CE) | Confucius (Kong Fuzi, 551-479 BCE) |
| Core Beliefs | Monotheism, Five Pillars, Quran as divine scripture | Ethical philosophy, social harmony, filial piety, respect for tradition |
| Scripture | The Quran and Hadith | Analects, Five Classics |
| God Concept | One God (Allah) | No central god; focus on moral order (Tian) |
| Afterlife | Heaven and Hell, Day of Judgment | Emphasis on legacy and moral virtue, no explicit afterlife doctrine |
| Practice | Prayer, fasting, charity, pilgrimage | Ritual propriety, ancestor worship, ethical cultivation |
| Geographic Origin | Arabian Peninsula (7th century CE) | Ancient China (6th century BCE) |
| Followers | Approximately 1.9 billion worldwide | Primarily influential in East Asia |
Origins and Historical Context
Islam originated in the 7th century CE in the Arabian Peninsula, founded by the Prophet Muhammad, whose teachings are recorded in the Quran and emphasize monotheism and submission to Allah. Confucianism emerged in 6th century BCE China, developed from the teachings of Confucius, focusing on ethics, social harmony, and proper conduct based on hierarchical relationships. Islam's historical context reflects a unifying religious and political force across the Middle East, while Confucianism shaped East Asian cultural, social, and political structures through moral philosophy and governance principles.
Core Beliefs and Philosophies
Islam centers on monotheism, emphasizing submission to Allah's will through the Five Pillars, which guide faith, prayer, charity, fasting, and pilgrimage. Confucianism focuses on ethical relationships, social harmony, and the cultivation of virtues like benevolence, righteousness, and filial piety within a hierarchical society. Both systems offer comprehensive frameworks for personal conduct and community order, with Islam rooted in divine revelation and Confucianism grounded in humanistic and pragmatic principles.
Concept of God and the Divine
Islam centers on the belief in a singular, omnipotent God (Allah) who is transcendent, creator, and sustainer of the universe, emphasizing monotheism and direct worship. Confucianism, lacking a concept of a personal God, focuses instead on reverence for Heaven (Tian) as a moral force and cosmic order, guiding ethical conduct and social harmony. The divine in Confucianism is impersonal and abstract, rooted in ancestral worship and natural order, contrasting sharply with Islam's personal and actively involved deity.
Moral and Ethical Frameworks
Islamic moral and ethical frameworks are rooted in the Quran and Hadith, emphasizing submission to Allah's will, justice, compassion, and communal responsibility. Confucianism centers on virtues such as filial piety, righteousness, benevolence, and social harmony, focusing on interpersonal relationships and societal roles. Both systems promote ethical conduct but differ as Islam prioritizes divine commandments, while Confucianism emphasizes human-centered moral cultivation.
Religious Practices and Rites
Islamic religious practices center on the Five Pillars, including daily prayers (Salat), fasting during Ramadan, almsgiving (Zakat), pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj), and declaration of faith (Shahada), emphasizing submission to Allah. Confucianism, primarily a philosophical system, stresses rituals (Li) that govern social harmony, ancestor veneration, and rites of passage, focusing on moral conduct rather than worship of deities. While Islamic rites involve prescribed worship acts and communal rituals, Confucian practices are deeply embedded in social customs and ethical traditions.
Social Structure and Community Life
Islam promotes a community centered on the ummah, emphasizing equality before God and social responsibilities such as zakat (almsgiving) to support the needy. Confucianism structures society around hierarchical relationships and filial piety, stressing harmony and duty within family and social roles to maintain order. Both systems integrate ethics and social obligations but differ in the basis of authority: divine law in Islam versus human-centered moral principles in Confucianism.
Role of Family and Filial Piety
Islam emphasizes strong family bonds rooted in mutual rights and responsibilities, with clear guidance on respect and care for parents as a religious duty central to social harmony. Confucianism places filial piety (xiao) at the heart of its ethical system, promoting reverence, obedience, and support for one's parents and ancestors as foundational to moral conduct and social order. Both traditions uphold family loyalty and intergenerational respect, yet Islam frames these within divine commandments, while Confucianism grounds them in philosophical and societal principles.
Approach to Governance and Law
Islamic governance centers on Sharia law derived from the Quran and Hadith, emphasizing the integration of religious principles into legal and political systems. Confucianism prioritizes moral virtue and social harmony, advocating rule by benevolent leaders guided by ethical teachings instead of codified laws. Theocratic elements in Islam contrast with Confucianism's secular emphasis on hierarchical relationships and communal order.
View on Education and Knowledge
Islam emphasizes the pursuit of knowledge as a religious duty, encouraging lifelong learning through studying the Quran and Hadith alongside various sciences. Confucianism prioritizes education as a means of moral development and social harmony, emphasizing classical texts and rites to cultivate virtue and proper conduct. Both traditions value education highly but differ in focus: Islam integrates spiritual and practical knowledge, while Confucianism centers on ethical self-cultivation and societal roles.
Influence on Contemporary Societies
Islam shapes contemporary societies through its comprehensive legal frameworks, ethical guidelines, and community-oriented values, prominently influencing governance and social norms across the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Asia. Confucianism underpins East Asian cultures by emphasizing hierarchical relationships, social harmony, and educational attainment, significantly impacting modern social structures and governmental policies in China, South Korea, and Japan. Both systems contribute enduring philosophical foundations that continue to guide moral conduct, social cohesion, and political stability in their respective regions.
Islam Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com