Lust is an intense emotional and physical desire that can drive human behavior and influence relationships. Understanding the psychological and physiological aspects of lust helps uncover its impact on attraction and decision-making. Explore the article to learn more about how lust shapes your connections and emotions.
Table of Comparison
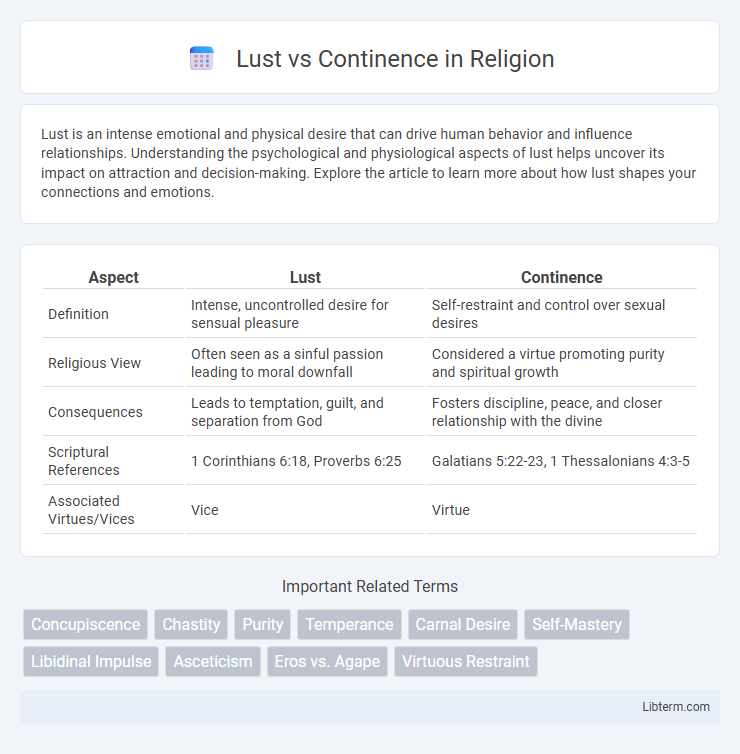
| Aspect | Lust | Continence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intense, uncontrolled desire for sensual pleasure | Self-restraint and control over sexual desires |
| Religious View | Often seen as a sinful passion leading to moral downfall | Considered a virtue promoting purity and spiritual growth |
| Consequences | Leads to temptation, guilt, and separation from God | Fosters discipline, peace, and closer relationship with the divine |
| Scriptural References | 1 Corinthians 6:18, Proverbs 6:25 | Galatians 5:22-23, 1 Thessalonians 4:3-5 |
| Associated Virtues/Vices | Vice | Virtue |
Understanding Lust: Definition and Origins
Lust is an intense, often uncontrollable desire primarily rooted in physical attraction and biological impulses, driven by the brain's reward system involving dopamine release. Its origins can be traced to evolutionary mechanisms aimed at reproduction and species survival, deeply embedded in human psychology and social behavior. Understanding lust requires examining both its physiological basis and its cultural interpretations, which shape how individuals experience and manage these urges.
What is Continence? Exploring Its Meaning
Continence refers to the self-control and restraint over bodily desires and impulses, especially sexual urges, promoting disciplined behavior and moral integrity. It is a fundamental concept in ethics and philosophy, emphasizing moderation and the ability to make rational decisions despite temptations. Practicing continence supports mental clarity and emotional stability, contrasting with the indulgence seen in lust.
Lust vs Continence: Key Differences
Lust and continence differ primarily in their expression of desire and self-control; lust represents overwhelming sexual desire without restraint, while continence involves the deliberate regulation or abstinence from such impulses. Lust is often linked to impulsive behavior driven by immediate gratification, whereas continence reflects mastery over one's passions through reason and discipline. Understanding these contrasts is essential in ethical discussions where lust is viewed as excess and continence as virtue promoting moral integrity.
The Psychology Behind Lust and Self-Control
The psychology behind lust and self-control reveals a complex interplay between primal desires and executive functions in the brain. Lust activates the limbic system, particularly the hypothalamus, triggering intense motivation for sexual gratification, while continence engages the prefrontal cortex to regulate impulses and enforce delayed gratification. Understanding these neural mechanisms highlights the challenges of balancing immediate biological drives with long-term goals in human behavior.
Historical and Cultural Perspectives
Historical and cultural perspectives on lust versus continence reveal diverse interpretations shaped by religious, philosophical, and societal norms. In ancient Greek philosophy, continence was esteemed as self-control and virtue, contrasting with lust, often depicted as a base desire requiring restraint. Various religious traditions, including Christianity and Buddhism, emphasize continence as a moral ideal to overcome the temptations of lust, underscoring its role in spiritual purity and ethical conduct.
The Role of Lust in Human Relationships
Lust drives intense physical attraction and sexual desire, influencing initial stages of romantic relationships by triggering powerful hormonal responses like increased dopamine and testosterone. This primal urge often initiates intimacy, but can also lead to impulsive behaviors if unchecked. Balancing lust with emotional connection and continence promotes healthier and more enduring partnerships.
Benefits of Practicing Continence
Practicing continence enhances mental clarity, emotional stability, and physical health by reducing impulsive behaviors associated with lust. It promotes self-discipline, leading to better decision-making and increased energy levels. This restraint supports long-term well-being and strengthens interpersonal relationships through mindful and respectful interactions.
Challenges in Overcoming Lust
Overcoming lust involves confronting intense biological urges and deeply ingrained psychological patterns that perpetuate desire. The challenge lies in retraining the mind to prioritize long-term self-control and virtue over immediate gratification, often requiring disciplined practices such as meditation, cognitive restructuring, and ethical reflection. Persistent exposure to stimuli and societal normalization of lustful behavior further complicate efforts to maintain continence and achieve emotional balance.
Balancing Desire and Discipline
Balancing desire and discipline requires mastering the tension between lust and continence, where controlling impulses fosters emotional stability and long-term fulfillment. Strong willpower coupled with mindful awareness helps regulate sensual cravings without suppressing natural human needs. Cultivating this equilibrium enhances personal growth, improves relationships, and supports ethical decision-making.
Practical Tips for Cultivating Continence
Cultivating continence requires intentional practices such as mindfulness meditation to increase self-awareness and recognize urges before they escalate. Implementing regular physical exercise can redirect sexual energy and improve impulse control by promoting overall mental and physical resilience. Establishing clear personal boundaries and avoiding triggers like explicit media or provocative environments enhances the ability to maintain self-discipline and long-term continence.
Lust Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com