Puja is a sacred ritual in Hinduism that involves offering prayers, flowers, and food to deities to seek blessings and spiritual connection. It holds immense cultural and religious significance, fostering mindfulness and devotion in everyday life. Explore this article to deepen your understanding of how Puja can enrich your spiritual practice.
Table of Comparison
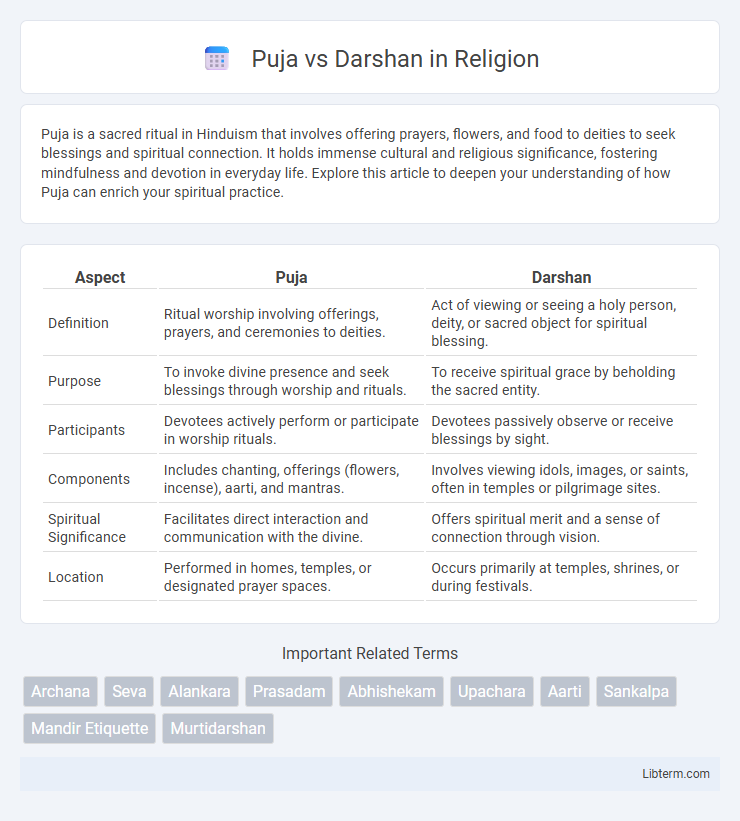
| Aspect | Puja | Darshan |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ritual worship involving offerings, prayers, and ceremonies to deities. | Act of viewing or seeing a holy person, deity, or sacred object for spiritual blessing. |
| Purpose | To invoke divine presence and seek blessings through worship and rituals. | To receive spiritual grace by beholding the sacred entity. |
| Participants | Devotees actively perform or participate in worship rituals. | Devotees passively observe or receive blessings by sight. |
| Components | Includes chanting, offerings (flowers, incense), aarti, and mantras. | Involves viewing idols, images, or saints, often in temples or pilgrimage sites. |
| Spiritual Significance | Facilitates direct interaction and communication with the divine. | Offers spiritual merit and a sense of connection through vision. |
| Location | Performed in homes, temples, or designated prayer spaces. | Occurs primarily at temples, shrines, or during festivals. |
Understanding the Concepts: What Are Puja and Darshan?
Puja is a ritualistic worship involving offerings, chants, and prayers to invoke and honor deities in Hinduism. Darshan refers to the sacred act of seeing and being seen by the deity, creating a spiritual connection between the devotee and the divine. Both Puja and Darshan are integral to Hindu worship, serving complementary roles in expressing devotion and receiving divine blessings.
Historical Origins of Puja and Darshan
Puja and Darshan have distinct historical origins rooted in ancient Indian religious practices, with Puja emerging as a ritualistic worship involving offerings to deities, documented in Vedic texts dating back to 1500 BCE. Darshan, meaning "sight" or "viewing," originated as the act of beholding a sacred image or deity, emphasizing the visual and spiritual connection between devotee and divine, prevalent in early Hindu temple traditions from around the 1st millennium CE. These practices evolved within different contexts, where Puja represents active devotional service and Darshan focuses on receiving divine grace through visual communion.
Purpose and Significance in Hindu Worship
Puja serves as a ritualistic offering to deities, aiming to establish a direct connection and seek blessings through prayers, flowers, and sacred items. Darshan emphasizes the act of beholding a deity's image or idol, allowing devotees to receive spiritual grace and reinforce their faith. Both practices hold profound significance in Hindu worship, fostering devotion and spiritual communion with the divine.
Rituals Involved in Puja
Puja rituals involve a series of ceremonial acts such as invoking the deity through mantras, offering flowers, incense, and food items to symbolize devotion and purity. The ritual often includes lighting a lamp or diya, performing an aarti, and chanting hymns to invoke divine blessings. Puja emphasizes active participation and symbolic offerings, contrasting with darshan, which primarily involves visual reverence of the deity.
The Experience of Darshan in Temples
Darshan in temples offers a direct, immersive experience where devotees visually connect with the deity, fostering a profound spiritual bond and immediate sense of divine presence. Unlike Puja, which involves ritual worship performed by priests, Darshan emphasizes personal viewing and silent contemplation, enhancing devotional focus through eye contact with the sacred image. This experience cultivates inner peace and spiritual fulfillment by allowing individual reflection within the temple's sacred ambiance.
Key Differences Between Puja and Darshan
Puja is a ritualistic worship involving offerings, prayers, and ceremonies conducted to honor deities, invoking divine presence and blessings. Darshan, on the other hand, refers to the act of seeing or beholding a deity or holy person, emphasizing visual and spiritual connection rather than ritual performance. Key differences include Puja's active participation in worship through rituals, whereas Darshan is a more passive experience centered on receiving grace through sight.
Spiritual Benefits: Puja vs. Darshan
Puja offers a structured ritual that actively engages the devotee in worship through mantras, offerings, and meditation, fostering a deep personal connection with the divine. Darshan provides a visual and spiritual experience by allowing devotees to see and receive blessings from the deity, promoting immediate devotional energy and inner peace. Both practices nourish the soul, but Puja emphasizes participatory devotion while Darshan centers on contemplative presence and reverence.
Regional Variations and Practices
Puja and Darshan exhibit notable regional variations across India, where Puja often involves elaborate rituals and offerings unique to local deities and customs, such as the grand Durga Puja in West Bengal emphasizing artistic decorations and community participation. In contrast, Darshan typically centers on the act of seeing and being seen by the deity, with practices varying from the quick, orderly glimpses in South Indian temples to the prolonged, meditative gazes encouraged in the Himalayan shrines. These differences reflect the diverse cultural, linguistic, and theological landscapes that shape how devotees engage with divinity in various parts of the country.
Role of Priests in Puja and Darshan
Priests play a crucial role in Puja by performing intricate rituals and chanting sacred mantras to invoke divine blessings, ensuring the spiritual sanctity of the worship. In Darshan, their role shifts to facilitating devotees' direct visual connection with the deity, maintaining temple decorum and guiding the flow of worshippers. Both Puja and Darshan rely on priests to uphold religious traditions and enhance the devotees' spiritual experience through their expertise and presence.
Contemporary Relevance in Modern Hinduism
Puja and Darshan remain central practices in modern Hinduism, with Puja involving ritualistic worship that fosters personal devotion and community participation, while Darshan emphasizes the spiritual experience of sighting deities or holy persons, reinforcing faith and connection. Contemporary Hindu worship integrates technology, enabling virtual Puja and Darshan, which expands accessibility beyond physical temple visits, adapting tradition to a digital age. These practices sustain cultural identity, offering spiritual solace and continuity in an increasingly globalized and fast-paced world.
Puja Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com