A priest serves as a spiritual leader, guiding communities through religious teachings, rituals, and pastoral care. They play a vital role in fostering faith, offering support during life's challenges, and performing sacred ceremonies that enrich spiritual life. Discover how a priest's dedication can inspire and transform your spiritual journey by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
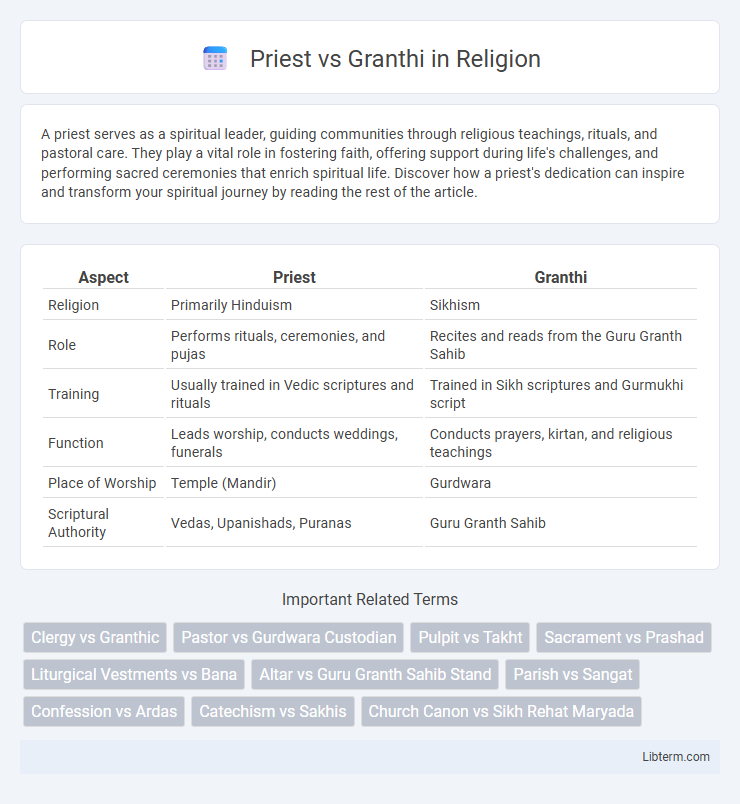
| Aspect | Priest | Granthi |
|---|---|---|
| Religion | Primarily Hinduism | Sikhism |
| Role | Performs rituals, ceremonies, and pujas | Recites and reads from the Guru Granth Sahib |
| Training | Usually trained in Vedic scriptures and rituals | Trained in Sikh scriptures and Gurmukhi script |
| Function | Leads worship, conducts weddings, funerals | Conducts prayers, kirtan, and religious teachings |
| Place of Worship | Temple (Mandir) | Gurdwara |
| Scriptural Authority | Vedas, Upanishads, Puranas | Guru Granth Sahib |
Introduction: Understanding Priest and Granthi
Priests serve as religious leaders who perform rituals, offer prayers, and guide worshippers across various faiths, while Granthis specifically officiate Sikh religious ceremonies and manage the Guru Granth Sahib, the central scripture of Sikhism. Priests' roles vary widely depending on religious traditions such as Christianity, Hinduism, or Buddhism, involving sacramental duties and spiritual counseling. Granthis hold specialized knowledge of Sikh scriptures and liturgy, ensuring the preservation and proper recitation of sacred texts in Gurdwaras.
Historical Origins of Priests and Granthis
Priests originated in ancient religious traditions as intermediaries between deities and worshippers, performing rituals and maintaining temples. Granthis, specifically in Sikhism, trace their origins to the early Gurus who appointed Granthis to recite and uphold the Guru Granth Sahib, the central scripture. Historical records show that while priests serve in diverse religious contexts, Granthis hold a unique role centered around the Sikh holy text and community worship.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Priests primarily perform religious rituals, ceremonies, and sacraments within temples or churches, serving as spiritual leaders and mediators between the divine and the community. Granthis, specifically in Sikhism, are custodians of the Guru Granth Sahib, responsible for reading, interpreting, and preserving the sacred scripture while guiding congregational hymns and prayers. Both roles emphasize spiritual guidance, but Granthis uniquely uphold scripture-based teachings and Sikh liturgical traditions.
Religious Texts and Rituals
Priests primarily serve in mainstream Hindu temples, performing rituals based on the Vedas, Upanishads, and Puranas, following strict guidelines for daily worship, ceremonies, and festivals. Granthis, specifically found in Sikhism, recite and interpret the Guru Granth Sahib during congregational worship, emphasizing hymns and teachings rather than elaborate rituals. The distinction lies in the Hindu priest's focus on ritualistic rites and the Granthi's role as a custodian and reader of sacred scripture without ritualistic ceremonies.
Training and Qualification Requirements
Priests typically undergo formal theological education and seminary training focused on liturgical rituals, religious texts, and pastoral care, often requiring ordination through a religious institution. Granthis, specifically in Sikhism, must memorize and interpret the Guru Granth Sahib, with rigorous training in Gurmukhi script, Sikh history, and recitation techniques, passing community-led evaluations rather than formalized seminary programs. Both roles demand deep spiritual knowledge and commitment, but the Granthi's training emphasizes scriptural continuity and communal service distinct from the broader clerical education of priests.
Dress Codes and Symbols
Priests typically wear robes or cassocks, often in plain colors symbolizing purity and devotion, while Granthis don traditional Sikh attire including the keski (turban) and white kurta pajamas, representing humility and spirituality. The priest's dress may include specific vestments such as stoles or chasubles that signify their liturgical role, whereas Granthis prominently display the Kara (steel bracelet) and kirpan (ceremonial sword), essential symbols of Sikh faith and duty. These distinctive dress codes and symbols reflect the respective religious traditions and roles within Christian and Sikh worship practices.
Community Engagement and Leadership
Priests primarily lead religious ceremonies and provide spiritual guidance within traditional temple settings, fostering community engagement through ritual participation and scriptural teachings. Granthis hold a distinctive leadership role in Sikhism by managing gurdwara affairs, reading from the Guru Granth Sahib, and facilitating community services such as langar (community kitchen) and educational programs. Their engagement extends beyond ritual duties to include active promotion of social cohesion and ethical values among congregants.
Differences in Worship Practices
Priest worship practices primarily involve conducting rituals and ceremonies according to specific religious texts and traditions, often emphasizing individual or community prayer, sacrificial rites, and maintaining temple sanctity. Granthis, particularly in Sikhism, focus on reading and interpreting the Guru Granth Sahib, leading congregational singing (kirtan), and facilitating spiritual guidance rather than performing sacrificial or elaborate ritualistic worship. The key difference lies in the Priest's ritual-centered approach versus the Granthi's role as a custodian of scripture and facilitator of devotional music and collective worship.
Gender Roles and Inclusivity
Priests in many religious traditions have historically been male, reflecting traditional gender roles that often exclude women from certain rites and leadership positions. Granthis, particularly in Sikhism, serve as scripture readers and caretakers of the Guru Granth Sahib and can include individuals regardless of gender, promoting inclusivity. The evolving roles of women as Granthis highlight a shift toward gender equality and broader participation in spiritual leadership.
Priest vs Granthi: Major Similarities and Differences
Priests and Granthis both serve spiritual roles in religious contexts, performing rituals, leading worship, and offering guidance to devotees. The primary difference lies in their religious traditions: priests commonly serve in various faiths such as Christianity and Hinduism, while Granthis specifically act as ceremonial readers and guardians of Sikh scripture in Gurdwaras. Both roles emphasize maintaining religious practices and fostering community faith, but Granthis uniquely focus on preserving and reciting the Guru Granth Sahib, the central scripture of Sikhism.
Priest Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com