Karma is the principle that your actions directly influence your future experiences, shaping both your present and future realities. Understanding how positive and negative deeds generate corresponding outcomes can empower you to live more mindfully and intentionally. Explore the deeper aspects of karma and how it affects your life in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
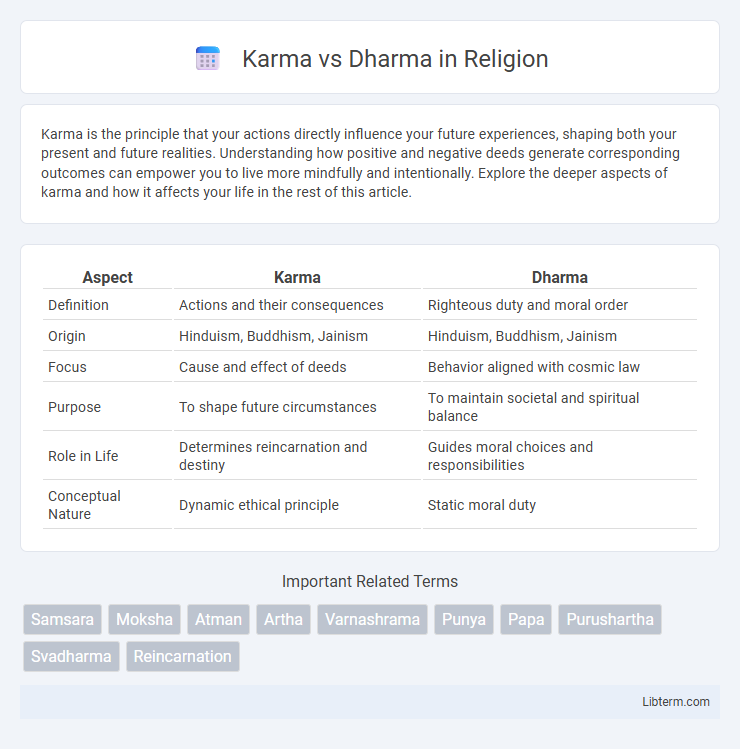
| Aspect | Karma | Dharma |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Actions and their consequences | Righteous duty and moral order |
| Origin | Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism | Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism |
| Focus | Cause and effect of deeds | Behavior aligned with cosmic law |
| Purpose | To shape future circumstances | To maintain societal and spiritual balance |
| Role in Life | Determines reincarnation and destiny | Guides moral choices and responsibilities |
| Conceptual Nature | Dynamic ethical principle | Static moral duty |
Understanding Karma: Definition and Origins
Karma originates from ancient Indian spiritual traditions, primarily Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism, and refers to the principle of cause and effect where actions influence future outcomes. It encompasses ethical conduct and moral responsibility, emphasizing that good deeds lead to positive results while harmful actions generate negative consequences. Understanding karma involves recognizing its role in shaping one's destiny and spiritual evolution across lifetimes.
Exploring Dharma: Meaning and Significance
Dharma, a core concept in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism, represents the ethical and moral duties that sustain social and cosmic order. It emphasizes righteous living, fulfilling one's responsibilities, and upholding justice, truth, and virtue according to one's role in society and stage of life. Understanding Dharma guides individuals toward harmony with universal laws, fostering spiritual growth and societal balance.
Karma vs Dharma: Core Differences
Karma refers to the principle of cause and effect where every action generates consequences influencing future experiences. Dharma represents the moral and ethical duties or righteous path an individual must follow according to their role in society or life stage. The core difference lies in Karma being the results of actions, while Dharma prescribes the right actions to maintain cosmic order and personal integrity.
Historical Context in Hindu Philosophy
Karma and Dharma are central concepts in Hindu philosophy, deeply rooted in ancient texts like the Vedas and Upanishads, dating back to 1500-500 BCE. Karma refers to the law of cause and effect, emphasizing actions and their consequences throughout samsara, the cycle of rebirth. Dharma represents the moral and ethical duties prescribed to individuals according to their caste, stage of life, and social role, serving as a guide to righteous living and spiritual progress.
How Karma Influences Daily Life
Karma, the principle of cause and effect, directly shapes daily actions and their consequences, influencing an individual's experiences and outcomes. Every intentional thought, word, and deed generates energy that returns in kind, affecting personal well-being, relationships, and opportunities. Understanding karma encourages mindful behavior, fostering positive habits that align with ethical living and spiritual growth.
The Role of Dharma in Moral Choices
Dharma serves as the fundamental ethical framework guiding individuals in making moral choices aligned with their duties and societal roles, ensuring harmony and balance in personal and communal life. It emphasizes adherence to righteous conduct, which influences the consequences of one's actions beyond physical outcomes, intertwining with Karma's cause-and-effect principle. By prioritizing Dharma, individuals uphold moral integrity and contribute to the overall cosmic order, reinforcing the interconnectedness of ethical behavior and spiritual growth.
Interconnection of Karma and Dharma
Karma and Dharma are intrinsically connected concepts in Indian philosophy, where Dharma represents the moral law or duty guiding righteous living, and Karma refers to the actions performed according to that duty. The interconnection lies in the principle that performing one's Dharma with intention and mindfulness generates positive Karma, influencing the cycle of cause and effect in life. Understanding this dynamic encourages individuals to align their actions with their ethical responsibilities, ultimately shaping their spiritual progress and destiny.
Lessons from Sacred Texts
Sacred texts like the Bhagavad Gita emphasize karma as the principle of cause and effect, teaching that every action produces consequences influencing one's spiritual journey. Dharma, described in the same texts, refers to righteous duty and moral order, guiding individuals to perform their obligations aligned with cosmic law. These scriptures underscore the lesson that adherence to dharma through selfless karma leads to liberation and spiritual fulfillment.
Modern Perspectives on Karma and Dharma
Modern perspectives on karma emphasize its role as a principle of cause and effect that shapes personal growth and ethical living, rather than a system of cosmic justice tied solely to religious doctrine. Dharma is increasingly interpreted as an individual's duty aligned with their values and social responsibilities, encouraging purposeful action in contemporary life. Both concepts are integrated into motivational psychology and mindfulness practices, promoting self-awareness and accountability in daily behavior.
Applying Karma and Dharma in Contemporary Society
Applying karma in contemporary society emphasizes ethical actions and their consequences, promoting personal accountability and social harmony. Dharma guides individuals to fulfill their societal roles and responsibilities, fostering a sense of duty and moral integrity in diverse cultural contexts. Integrating karma and dharma encourages balanced decision-making, nurturing community well-being and sustainable ethical practices.
Karma Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com