Salah, also known as prayer in Islam, is a fundamental act of worship performed five times daily, serving as a direct link between the worshiper and Allah. It involves specific physical movements and recitations that reinforce spiritual discipline and mindfulness throughout the day. Explore the rest of this article to deepen your understanding of Salah's significance and practice.
Table of Comparison
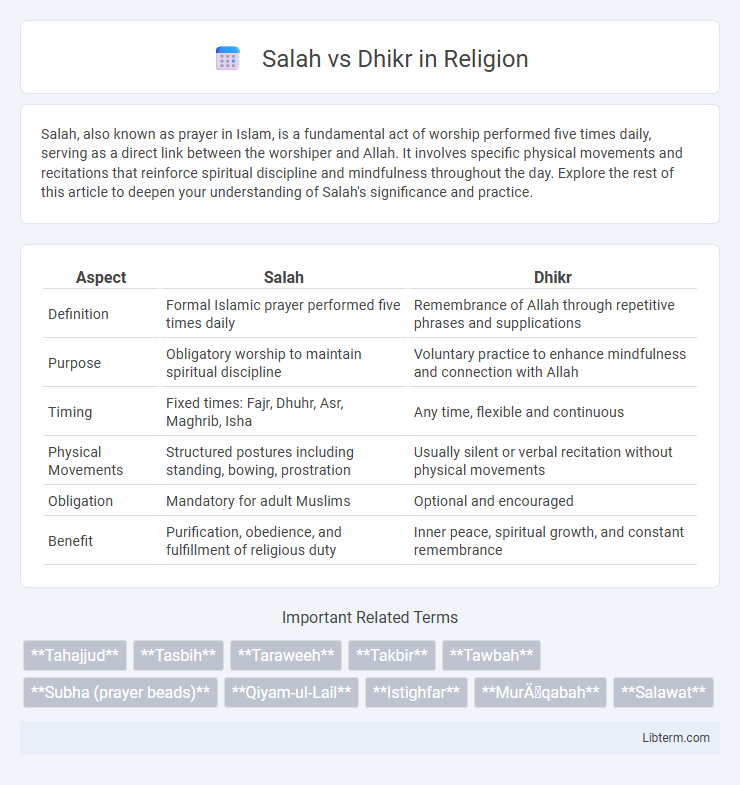
| Aspect | Salah | Dhikr |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal Islamic prayer performed five times daily | Remembrance of Allah through repetitive phrases and supplications |
| Purpose | Obligatory worship to maintain spiritual discipline | Voluntary practice to enhance mindfulness and connection with Allah |
| Timing | Fixed times: Fajr, Dhuhr, Asr, Maghrib, Isha | Any time, flexible and continuous |
| Physical Movements | Structured postures including standing, bowing, prostration | Usually silent or verbal recitation without physical movements |
| Obligation | Mandatory for adult Muslims | Optional and encouraged |
| Benefit | Purification, obedience, and fulfillment of religious duty | Inner peace, spiritual growth, and constant remembrance |
Understanding Salah: The Ritual Prayer
Salah, the ritual prayer in Islam, serves as a structured form of worship performed five times daily, encompassing physical postures, recitations, and specific timings to maintain spiritual discipline and connection with Allah. Unlike Dhikr, which involves repetitive remembrance of Allah through phrases or supplications at any time, Salah follows a prescribed format including Quranic verses, movements such as bowing (ruku) and prostration (sujud), symbolizing submission. Mastery of Salah rituals enhances mindfulness and devotion, anchoring a Muslim's spiritual routine beyond spontaneous remembrance practices.
Exploring Dhikr: The Remembrance of Allah
Dhikr, the remembrance of Allah, involves the repetitive recitation of divine names and phrases to cultivate spiritual mindfulness and deepen the believer's connection with God. Unlike Salah, which is a structured prayer performed five times daily at specific times, Dhikr can be practiced anytime and anywhere, offering continuous spiritual nourishment. This practice enhances inner peace and reinforces faith by constantly invoking Allah's presence in the heart and mind.
Core Differences Between Salah and Dhikr
Salah is the formal, ritual prayer performed five times daily with prescribed physical movements and specific recitations from the Quran, serving as a pillar of Islamic worship. Dhikr involves the remembrance of Allah through repetitive verbal phrases or silent meditation, which can be practiced anytime without physical postures or fixed timings. While Salah emphasizes structured worship with set rituals, Dhikr offers flexibility and continuous spiritual connection beyond formal prayers.
Spiritual Benefits of Salah
Salah, the Islamic ritual prayer performed five times daily, fosters a deep spiritual connection with Allah, enhancing mindfulness and inner peace. It acts as a structured form of worship that encourages discipline, tranquility, and self-purification through physical actions combined with heartfelt devotion. Unlike Dhikr, which primarily involves verbal remembrance of Allah, Salah integrates body, mind, and soul, leading to heightened spiritual awareness and a stronger sense of submission and gratitude.
The Significance of Dhikr in Daily Life
Dhikr, the practice of remembering and invoking Allah through repeated phrases and prayers, holds profound significance in daily life by fostering spiritual mindfulness and inner peace. Unlike Salah, which is a structured ritual performed five times a day, Dhikr can be practiced anytime, helping believers maintain a constant connection with the Divine. This continuous remembrance enhances emotional resilience, reduces stress, and deepens faith, making Dhikr a vital complement to formal worship in Islamic spirituality.
Salah: Structure, Timings, and Obligations
Salah, the Islamic ritual prayer, consists of five daily prayers performed at specific times: Fajr (pre-dawn), Dhuhr (midday), Asr (afternoon), Maghrib (sunset), and Isha (night). Each prayer includes a structured sequence of physical movements and recitations, such as standing (Qiyam), bowing (Ruku), prostration (Sujood), and sitting (Jalsa), following prescribed verses from the Quran and Tashahhud. Observing Salah is obligatory for all adult Muslims, serving as a central act of worship and spiritual discipline that strengthens faith and connection to Allah.
Dhikr: Types, Methods, and Flexibility
Dhikr, the remembrance of Allah, encompasses various types including vocal (Qawli), silent (Sirr), and physical (Jism) forms, each facilitating spiritual connection beyond formal worship. Methods range from reciting phrases like "SubhanAllah," to meditative breathing and heart-focused contemplation, allowing practitioners to engage in remembrance anytime and anywhere. Dhikr offers flexibility unmatched by Salah, as it requires no specific time, place, or ritual purity, making it accessible for continuous spiritual mindfulness throughout daily life.
Integrating Salah and Dhikr for Holistic Worship
Integrating Salah and Dhikr enhances holistic worship by combining structured prayer with continuous remembrance of Allah, fostering spiritual depth and mindfulness. Salah, the prescribed five daily prayers, grounds the believer in discipline and submission, while Dhikr, the practice of repeating divine names and phrases, cultivates constant awareness of God's presence beyond formal rituals. Together, they create a balanced spiritual practice that nurtures inner peace, strengthens faith, and promotes a seamless connection with the Divine throughout daily life.
Common Misconceptions About Salah and Dhikr
Many mistakenly believe Salah and Dhikr serve identical spiritual purposes, but Salah is a mandatory, structured prayer performed five times daily, while Dhikr comprises voluntary remembrance of Allah through phrases and supplications. Another misconception is that Dhikr can replace Salah; in reality, Dhikr complements Salah by enhancing mindfulness and connection beyond obligatory worship. Understanding distinct roles clarifies their importance within Islamic spirituality and prevents overlooking the foundational obligation of Salah.
Enhancing Spiritual Connection Through Salah and Dhikr
Salah, the prescribed Islamic prayers performed five times daily, establishes a structured rhythm fostering mindfulness and direct communication with Allah, enhancing spiritual connection. Dhikr, the repetitive remembrance of Allah through phrases and supplications, deepens this connection by cultivating constant awareness and inner tranquility beyond formal prayer times. Combining Salah with Dhikr strengthens devotion, enriching both the heart and soul through disciplined worship and continuous spiritual reflection.
Salah Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com