Karma is the universal principle of cause and effect, where every action influences future experiences. Understanding karma enables you to cultivate positive behavior and create a meaningful impact on your life and others. Explore the rest of this article to uncover how karma shapes your destiny and practical ways to harness its power.
Table of Comparison
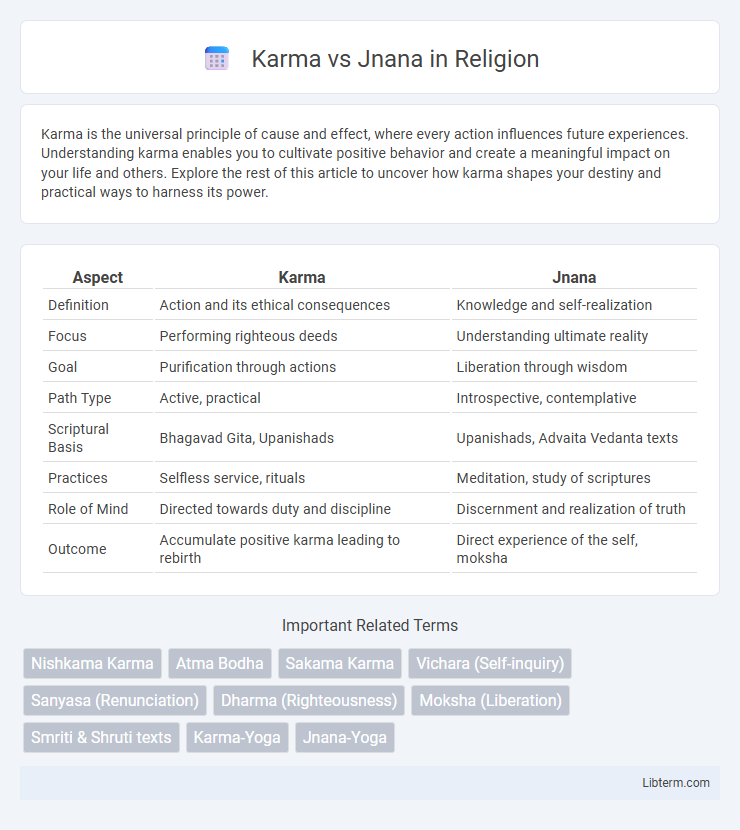
| Aspect | Karma | Jnana |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Action and its ethical consequences | Knowledge and self-realization |
| Focus | Performing righteous deeds | Understanding ultimate reality |
| Goal | Purification through actions | Liberation through wisdom |
| Path Type | Active, practical | Introspective, contemplative |
| Scriptural Basis | Bhagavad Gita, Upanishads | Upanishads, Advaita Vedanta texts |
| Practices | Selfless service, rituals | Meditation, study of scriptures |
| Role of Mind | Directed towards duty and discipline | Discernment and realization of truth |
| Outcome | Accumulate positive karma leading to rebirth | Direct experience of the self, moksha |
Understanding Karma: The Path of Action
Karma, the path of action, emphasizes performing duties selflessly without attachment to outcomes, fostering spiritual growth through ethical conduct and disciplined practice. It is rooted in the Bhagavad Gita's teachings, which advocate for dedicated action aligned with dharma to purify the mind and reduce ego. Understanding karma involves recognizing that every action has consequences (Karma-phala), encouraging mindfulness and responsibility in daily life to achieve liberation (moksha).
Exploring Jnana: The Path of Knowledge
Jnana, the path of knowledge, emphasizes self-realization through deep inquiry and meditation, aiming to transcend ignorance by understanding the true nature of the self (Atman) and its unity with Brahman. It involves rigorous study of scriptures, discernment (viveka), and detachment (vairagya) to dissolve ego and illusion (maya), leading to liberation (moksha). Unlike Karma Yoga's focus on selfless action, Jnana Yoga prioritizes wisdom and inner enlightenment as the ultimate means to spiritual freedom.
Philosophical Foundations: Karma and Jnana in Hinduism
Karma and Jnana in Hinduism represent two foundational paths for spiritual liberation, with Karma emphasizing selfless action and ethical duties as means to purify the mind and affect one's future rebirths, while Jnana focuses on knowledge, introspection, and realization of the self's unity with Brahman. The Bhagavad Gita elaborates on Karma Yoga as performing one's prescribed duties without attachment to results, contrasting it with Jnana Yoga's pursuit of wisdom through discrimination between the eternal self (Atman) and the impermanent body. Both philosophies converge on the ultimate goal of moksha, the liberation from the cycle of samsara, but differ significantly in their method--Karma advocates action grounded in dharma, whereas Jnana prioritizes discernment and spiritual insight.
Key Differences Between Karma and Jnana Yoga
Karma Yoga emphasizes selfless action and performing duties without attachment to results, serving as a path to spiritual liberation through disciplined work. Jnana Yoga centers on knowledge, wisdom, and self-inquiry, guiding practitioners toward realization of the true self (Atman) and ultimate truth (Brahman) through meditation and study of scriptures. While Karma Yoga involves active engagement in the world, Jnana Yoga focuses on intellectual discernment and inner contemplation for attaining moksha.
The Role of Intention in Karma and Jnana
In the context of Karma and Jnana, intention plays a pivotal role in determining the spiritual impact of actions and knowledge. Karma emphasizes the purity and selflessness of intention behind each action, as only actions performed without attachment to results lead to spiritual liberation. Jnana, focusing on the realization of the self through wisdom and discernment, requires an intention rooted in seeking truth and transcendence beyond ego-driven desires.
Spiritual Goals: Liberation Through Action or Knowledge
Karma yoga emphasizes liberation through selfless action and fulfilling one's duties without attachment to results, aligning the mind with dharma to purify the soul. Jnana yoga advocates for liberation through deep knowledge, discernment, and direct realization of the self as Brahman, transcending ignorance and duality. Both paths aim for moksha, but Karma seeks liberation via transformative action, while Jnana prioritizes intellectual insight and spiritual wisdom.
Famous Teachings: Bhagavad Gita on Karma vs Jnana
The Bhagavad Gita emphasizes the complementary paths of Karma Yoga (the yoga of action) and Jnana Yoga (the yoga of knowledge) as means to spiritual liberation. Krishna teaches that selfless action performed without attachment to results purifies the mind, while Jnana involves discerning the eternal self (Atman) from the temporary body and mind. Together, these teachings highlight that balancing dedicated action with profound wisdom leads to liberation (Moksha) and inner peace.
Practical Applications in Daily Life
Karma emphasizes selfless action and ethical behavior, encouraging individuals to perform duties without attachment to outcomes, which cultivates discipline and social responsibility in daily life. Jnana focuses on self-inquiry and wisdom, helping individuals develop clarity and insight to overcome ignorance and make conscious decisions. Integrating Karma and Jnana promotes balanced living by combining purposeful action with reflective understanding, enhancing personal growth and harmonious relationships.
Integrating Karma and Jnana for Holistic Growth
Integrating Karma (selfless action) and Jnana (knowledge and wisdom) fosters holistic growth by balancing practical engagement with deep understanding. This synergy encourages individuals to act ethically while cultivating insight, leading to spiritual maturity and purposeful living. Emphasizing both paths simultaneously enhances personal development and aligns actions with higher consciousness.
Choosing Your Path: Which Suits You?
Karma Yoga emphasizes selfless action and service as a path to spiritual growth, ideal for those inclined toward active engagement and practical duties. Jnana Yoga centers on knowledge, self-inquiry, and insight, suited for individuals drawn to philosophical study and contemplation. Assessing your temperament and life circumstances can help determine whether the dynamic practice of Karma or the reflective pursuit of Jnana aligns best with your spiritual journey.
Karma Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com