Sharia is a comprehensive legal and ethical framework derived from the Quran and Hadith, guiding many aspects of Muslim life including worship, finance, and personal conduct. Its principles emphasize justice, compassion, and social welfare, influencing laws in various Islamic countries. Explore the rest of the article to understand how Sharia impacts contemporary society and your perspective on cultural practices.
Table of Comparison
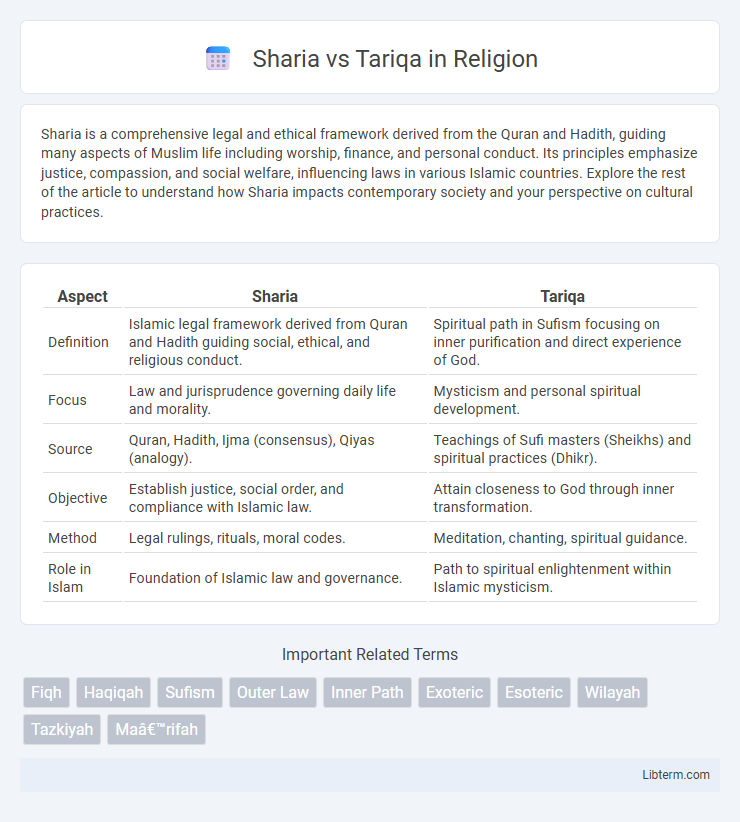
| Aspect | Sharia | Tariqa |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Islamic legal framework derived from Quran and Hadith guiding social, ethical, and religious conduct. | Spiritual path in Sufism focusing on inner purification and direct experience of God. |
| Focus | Law and jurisprudence governing daily life and morality. | Mysticism and personal spiritual development. |
| Source | Quran, Hadith, Ijma (consensus), Qiyas (analogy). | Teachings of Sufi masters (Sheikhs) and spiritual practices (Dhikr). |
| Objective | Establish justice, social order, and compliance with Islamic law. | Attain closeness to God through inner transformation. |
| Method | Legal rulings, rituals, moral codes. | Meditation, chanting, spiritual guidance. |
| Role in Islam | Foundation of Islamic law and governance. | Path to spiritual enlightenment within Islamic mysticism. |
Understanding Sharia: Definition and Foundations
Sharia, derived from the Quran and Hadith, constitutes the comprehensive Islamic legal framework governing rituals, morality, and social conduct. Its foundations rest on the Quran as the primary source, supplemented by Sunnah, Ijma (consensus), and Qiyas (analogical reasoning), ensuring adherence to divine law. Understanding Sharia requires recognizing its role in structuring ethical guidelines and jurisprudence within Muslim communities.
Tariqa Explained: The Sufi Path
Tariqa refers to the spiritual path in Sufism focused on inner purification and direct experience of the Divine, guided by a spiritual master or Sheikh. Unlike Sharia, which constitutes Islamic law governing external conduct, Tariqa emphasizes personal transformation through practices such as dhikr (remembrance of God), meditation, and asceticism. This mystical approach aims to transcend the ego and achieve spiritual union with God, central to Sufi philosophy and devotional life.
Historical Origins of Sharia and Tariqa
Sharia, rooted in the Quran and Hadith, emerged in the 7th century as Islamic law guiding ethical, social, and legal aspects of Muslim life. Tariqa developed later as a mystical path within Sufism, emphasizing spiritual practices and direct experience of the divine. Historically, Sharia forms the legal and moral framework, while Tariqa represents the esoteric, experiential dimension of Islam.
Key Differences Between Sharia and Tariqa
Sharia represents the Islamic legal framework derived from the Quran and Hadith, governing laws, ethics, and social conduct, while Tariqa refers to spiritual paths or Sufi orders emphasizing inner purification and mystical experience. Sharia prescribes external compliance with religious duties and societal rules, whereas Tariqa focuses on personal spiritual development through practices like dhikr and meditation. The key difference lies in Sharia's legalistic nature contrasted with Tariqa's esoteric, experiential approach to Islam.
The Role of Sharia in Islamic Society
Sharia serves as the foundational legal and ethical framework in Islamic society, governing aspects of daily life, justice, and worship through divine law derived from the Quran and Hadith. Its role ensures social order, moral conduct, and communal responsibility by enforcing rituals, economic rules, and family law. Unlike Tariqa, which focuses on spiritual purification through mystical practices, Sharia provides the structured, codified guidelines essential for societal governance and cohesion.
Spiritual Focus of Tariqa in Sufism
Tariqa in Sufism emphasizes the internal spiritual journey aimed at achieving direct experiential knowledge of the divine, contrasting with Sharia's focus on outward legalistic observance of Islamic law. The spiritual focus of Tariqa involves disciplined practices such as dhikr (remembrance of God), meditation, and guidance under a spiritual master to purify the heart and attain mystical union with God. This transformative path prioritizes inner realization and awakening beyond the formal rituals prescribed by Sharia.
Sharia: Law, Ethics, and Daily Practice
Sharia represents the comprehensive Islamic legal framework derived from the Quran and Hadith, governing ethics, rituals, and social conduct. It encompasses detailed laws on personal behavior, financial transactions, criminal justice, and family matters, aiming to align individual actions with divine principles. Daily practice under Sharia involves adherence to prescribed moral standards, prayer routines, dietary restrictions, and social responsibilities that shape a Muslim's spiritual and communal life.
Tariqa: Inner Transformation and Mystical Experience
Tariqa represents the inner spiritual path within Sufism, emphasizing personal transformation through mystical experience and direct communion with the Divine. This journey involves practices such as dhikr (remembrance), meditation, and guidance from a spiritual master (sheikh) to purify the heart and transcend the ego. Unlike Sharia, which governs external legal and ethical conduct, Tariqa focuses on the esoteric reality of faith, seeking profound inner awakening and unity with God.
Interrelationship Between Sharia and Tariqa
Sharia represents the legal framework and ethical guidelines derived from the Quran and Hadith, outlining the outward duties and moral conduct for Muslims. Tariqa encompasses the spiritual path and inner purification practices aimed at achieving closeness to God through Sufi orders. The interrelationship between Sharia and Tariqa lies in Sharia providing the structural foundation of Islamic law, while Tariqa deepens the heart's connection, with both essential for holistic Islamic spiritual and practical life.
Contemporary Relevance of Sharia and Tariqa
Sharia, as the legal framework derived from Islamic jurisprudence, continues to shape governance, social justice, and ethical conduct in many Muslim-majority countries, influencing contemporary debates on human rights and legal reform. Tariqa, representing the spiritual path within Sufism, maintains its relevance by fostering inner transformation, personal discipline, and communal harmony in modern societies seeking spiritual depth beyond formal religious practice. The interplay between Sharia's external legal structures and Tariqa's internal spiritual guidance addresses the holistic needs of contemporary Muslim communities navigating both worldly and mystical dimensions.
Sharia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com