Sharia, rooted in Islamic law, governs aspects of daily life, morality, and justice based on the Quran and Hadith. Its principles influence legal systems and ethical conduct in many Muslim-majority countries, balancing religious guidance with contemporary societal needs. Explore this article to understand how Sharia shapes cultures and legal frameworks around the world.
Table of Comparison
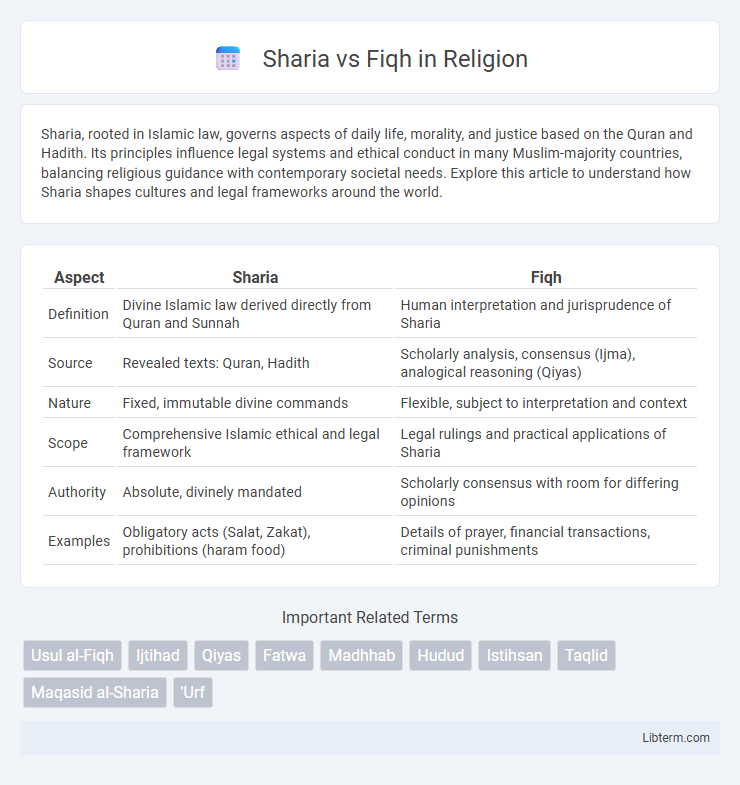
| Aspect | Sharia | Fiqh |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Divine Islamic law derived directly from Quran and Sunnah | Human interpretation and jurisprudence of Sharia |
| Source | Revealed texts: Quran, Hadith | Scholarly analysis, consensus (Ijma), analogical reasoning (Qiyas) |
| Nature | Fixed, immutable divine commands | Flexible, subject to interpretation and context |
| Scope | Comprehensive Islamic ethical and legal framework | Legal rulings and practical applications of Sharia |
| Authority | Absolute, divinely mandated | Scholarly consensus with room for differing opinions |
| Examples | Obligatory acts (Salat, Zakat), prohibitions (haram food) | Details of prayer, financial transactions, criminal punishments |
Introduction to Sharia and Fiqh
Sharia represents the divine law derived from the Quran and Sunnah, guiding all aspects of a Muslim's life with principles rooted in Islamic theology. Fiqh is the human understanding and interpretation of Sharia, developed by Islamic jurists to apply these divine laws to specific legal and ethical issues. The distinction highlights Sharia as the ideal divine framework, while Fiqh serves as the practical legal system shaped by scholarly reasoning.
Defining Sharia: Divine Law in Islam
Sharia represents the divine law in Islam, derived directly from the Quran and the Sunnah, prescribing the ethical and legal framework for Muslim life. It encompasses mandatory duties, prohibitions, and guidelines that define the relationship between humans, God, and society. Sharia serves as the ultimate source of authority, intended to ensure justice, morality, and well-being within the Islamic community.
Understanding Fiqh: Human Interpretation of Law
Fiqh represents the human interpretation and application of Sharia, encompassing Islamic jurisprudence that addresses practical legal rulings derived from the Quran and Hadith. It involves scholars' efforts to reconcile religious texts with contemporary contexts, allowing for adaptability and legal reasoning (ijtihad) within Islamic law. This dynamic process highlights the distinction between divine, immutable Sharia and the evolving, context-sensitive framework of Fiqh.
Historical Development of Sharia and Fiqh
Sharia, derived from the Quran and Hadith, represents the divine Islamic law guiding moral and legal principles since Islam's inception in the 7th century. Fiqh emerged as the human interpretation and jurisprudential understanding of Sharia, evolving through scholarly debates and methodologies like ijtihad and qiyas during the Abbasid era. This distinction highlights Sharia as immutable divine law, while Fiqh reflects contextual and adaptive legal frameworks developed by Muslim jurists over centuries.
Key Differences Between Sharia and Fiqh
Sharia represents the divine, immutable law derived from the Quran and Hadith, serving as the foundational legal and ethical framework in Islam. Fiqh, in contrast, is the human interpretation and jurisprudence of Sharia, adapting its principles to varying contexts through scholarly reasoning and consensus. While Sharia is considered sacred and perfect, Fiqh evolves over time to address practical issues and changing societal needs.
Sources of Sharia and Fiqh
Sharia is derived directly from primary sources including the Quran, Sunnah, Ijma (consensus), and Qiyas (analogical reasoning), serving as the divine law framework in Islam. Fiqh, on the other hand, is the human interpretation and jurisprudence developed by Islamic scholars to apply Sharia principles to practical matters, utilizing these same sources alongside secondary tools like Ijtihad (independent reasoning). The distinction between Sharia and Fiqh lies in Sharia's divine origin and immutable character, whereas Fiqh is adaptive, reflecting contextual understanding and scholarly opinions.
The Role of Scholars in Sharia and Fiqh
Scholars play a pivotal role in both Sharia and Fiqh by interpreting and expounding Islamic principles to guide Muslim communities. In Sharia, scholars help articulate divine law derived from the Quran and Sunnah, while in Fiqh, they engage in juristic deliberation to address practical issues through ijtihad. Their expertise ensures that legal rulings remain relevant, contextual, and aligned with the core tenets of Islam.
Application of Sharia vs. Fiqh in Modern Contexts
Sharia represents the divine, immutable Islamic law derived from the Quran and Hadith, while Fiqh is the human interpretation and application of Sharia principles, allowing for flexibility in various cultural and temporal contexts. In modern societies, Sharia provides the foundational ethical and legal framework, whereas Fiqh adapts these guidelines to contemporary issues such as finance, human rights, and technology. The dynamic nature of Fiqh enables Muslim jurists to address evolving social realities while maintaining fidelity to core Sharia values.
Common Misconceptions about Sharia and Fiqh
Sharia and Fiqh are often confused, but Sharia refers to the divine law derived from the Quran and Sunnah, while Fiqh is the human interpretation and application of Sharia through scholarly reasoning. Common misconceptions include viewing Sharia as a rigid, punitive legal code, whereas it encompasses ethical, spiritual, and social guidelines aimed at justice and welfare. Fiqh varies across different Islamic schools of thought, reflecting cultural and contextual adaptations rather than a single, fixed system.
Conclusion: The Dynamic Relationship Between Sharia and Fiqh
Sharia represents the divine, immutable principles derived from the Quran and Sunnah, while fiqh embodies the human interpretation and application of these principles through jurisprudential reasoning. This dynamic relationship allows fiqh to adapt sharia's eternal values to diverse cultural, social, and temporal contexts, ensuring relevance and practical guidance for Muslim communities. Consequently, fiqh serves as a vital mechanism for the evolution and contextualization of sharia within the framework of Islamic law.
Sharia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com