Sikhism emphasizes equality, devotion to one God, and selfless service, promoting a life of integrity and compassion. The teachings of Guru Nanak and the subsequent nine Gurus shape a rich spiritual and cultural tradition that continues to inspire millions worldwide. Explore the full article to understand the core principles and vibrant heritage of Sikhism.
Table of Comparison
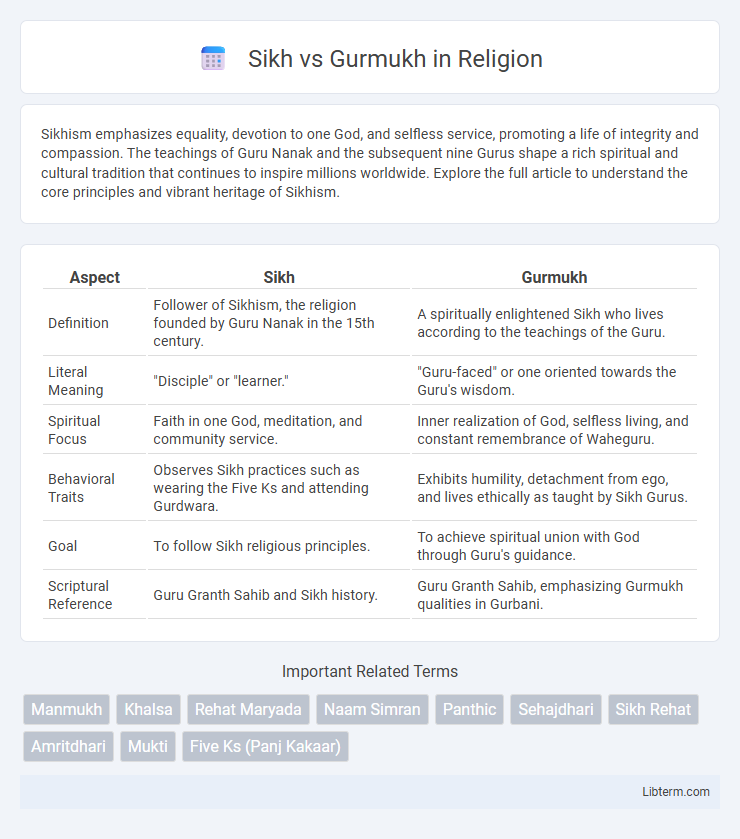
| Aspect | Sikh | Gurmukh |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Follower of Sikhism, the religion founded by Guru Nanak in the 15th century. | A spiritually enlightened Sikh who lives according to the teachings of the Guru. |
| Literal Meaning | "Disciple" or "learner." | "Guru-faced" or one oriented towards the Guru's wisdom. |
| Spiritual Focus | Faith in one God, meditation, and community service. | Inner realization of God, selfless living, and constant remembrance of Waheguru. |
| Behavioral Traits | Observes Sikh practices such as wearing the Five Ks and attending Gurdwara. | Exhibits humility, detachment from ego, and lives ethically as taught by Sikh Gurus. |
| Goal | To follow Sikh religious principles. | To achieve spiritual union with God through Guru's guidance. |
| Scriptural Reference | Guru Granth Sahib and Sikh history. | Guru Granth Sahib, emphasizing Gurmukh qualities in Gurbani. |
Understanding the Terms: Sikh and Gurmukh
The term "Sikh" refers to a follower of Sikhism, a monotheistic religion founded in the 15th century by Guru Nanak in Punjab, emphasizing devotion to God and living a truthful, ethical life. "Gurmukh," derived from Punjabi, means "one who faces the Guru," describing an individual who lives in alignment with the teachings of the Sikh Gurus, embodying spiritual discipline and selflessness. Understanding these terms highlights the distinction between identifying as a Sikh culturally or religiously and striving to be a Gurmukh, which denotes deep commitment and internalization of Sikh principles.
Historical Origins and Development
Sikhism originated in the 15th century with Guru Nanak Dev Ji, who established the foundational spiritual principles emphasizing devotion to one God, equality, and social justice. The term "Gurmukh" refers to individuals who live according to the teachings of the Gurus, embodying a lifestyle aligned with Sikh ethics and spirituality, prioritizing humility, self-discipline, and community service. Historically, while Sikhism represents the organized religion and its doctrines, being Gurmukh signifies a dedicated practitioner who internalizes and practices these principles in daily life.
Core Beliefs and Philosophies
Sikhism centers on the belief in one God, equality, and living a truthful, honest life guided by the teachings of the Ten Gurus as recorded in the Guru Granth Sahib. A Gurmukh, in Sikh philosophy, is an individual who lives according to the divine wisdom of the Guru, focusing on spiritual enlightenment, humility, and detachment from ego (haumai). Core beliefs emphasize Naam Simran (meditation on God's name), selfless service (seva), and the rejection of materialism, contrasting with worldly attachments that define the manmukh, or self-centered person.
Distinctive Practices and Lifestyles
Sikh identity centers on the teachings of Guru Nanak and adherence to the Five Ks, including uncut hair (kesh), a wooden comb (kangha), and steel bracelet (kara), which symbolize commitment to faith and equality. Gurmukh refers to individuals who live according to the Guru's teachings, embodying virtues like humility, compassion, and selflessness through meditative prayer and community service (seva). Distinctive lifestyle practices for Gurmukhs emphasize spiritual discipline, ethical living, and detachment from materialism, aligning daily actions with Sikh principles beyond ritual observance.
Role of Guru Granth Sahib
The Guru Granth Sahib serves as the eternal Guru for Sikhs, embodying the spiritual authority and teachings essential to Sikhism, whereas a Gurmukh refers to an individual who lives according to the Guru's wisdom and divine guidance. Sikh identity is deeply tied to reverence for the Guru Granth Sahib, which contains hymns and scripture central to devotion and practice. The Gurmukh's role is to internalize these teachings, aligning their thoughts and actions with the spiritual path outlined by the Guru Granth Sahib.
Spiritual Goals: Sikh vs Gurmukh Perspective
The Sikh perspective emphasizes living a disciplined life aligned with the teachings of the Guru, seeking union with Waheguru through meditation, selfless service, and honest living. The Gurmukh perspective prioritizes spiritual enlightenment by following the Guru's wisdom, focusing on detachment from ego and worldly desires to achieve a state of divine consciousness. Both views aim for spiritual growth, but Gurmukh centers on internal transformation and aligning one's will with God's will.
Community and Individual Identity
Sikh identity centers on collective belonging to the Khalsa community, emphasizing shared values, practices, and spiritual commitment. Gurmukh refers to an individual who lives according to Guru's teachings, embodying personal devotion and ethical conduct. The community-focused Sikh identity fosters unity, whereas Gurmukh highlights personal spiritual alignment within the broader Sikh tradition.
Common Misconceptions
Common misconceptions about Sikh and Gurmukh often confuse the two as synonymous terms, but Sikh refers broadly to a follower of Sikhism, while Gurmukh denotes a person who lives according to the teachings of the Guru, embodying spiritual discipline and devotion. Many incorrectly assume all Sikhs are inherently Gurmukhs, overlooking that a Gurmukh actively seeks to align actions with Gurbani and divine will. Understanding this distinction highlights the difference between cultural identity and spiritual practice within Sikhism.
Influence on Modern Sikhism
The distinction between Sikh and Gurmukh plays a crucial role in shaping modern Sikhism, emphasizing the spiritual path of the Gurmukh as one who lives according to the Guru's teachings and attunes to divine wisdom. This focus on Gurmukh ideals has profoundly influenced contemporary Sikh ethical practices, community cohesion, and personal spirituality, reinforcing core values like humility, compassion, and devotion. The Gurmukh concept continues to inspire Sikh identity by promoting a life centered on divine communion and moral integrity, thereby guiding the evolution of Sikhism in the 21st century.
Contemporary Relevance and Challenges
Sikh identity today navigates the complex balance between traditional values and modern societal demands, with Gurmukh representing those who embody spiritual discipline and community-centered living as prescribed by Guru Granth Sahib. Contemporary challenges include preserving authentic Sikh teachings amid globalization, identity dilution, and socio-political pressures, while addressing issues like youth disengagement and cultural assimilation. Emphasizing Gurmukh's path offers a counter-narrative to materialism, promoting resilience through faith, ethical conduct, and active participation in social justice.
Sikh Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com