Haram refers to anything that is prohibited or forbidden under Islamic law, including specific foods, behaviors, and actions considered sinful. Observing what is haram helps maintain spiritual purity and a moral lifestyle aligned with Islamic teachings. Discover more about the concepts of halal and haram and how they impact daily life in the following article.
Table of Comparison
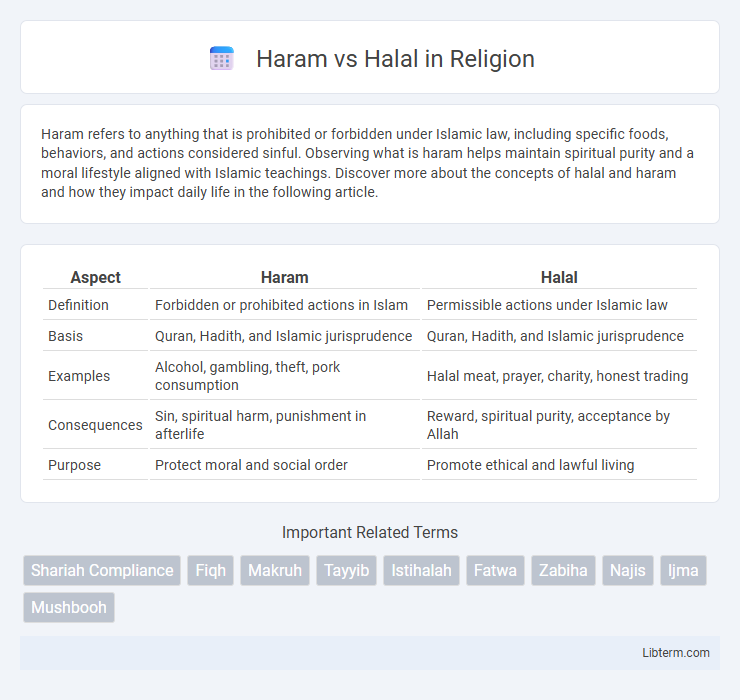
| Aspect | Haram | Halal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Forbidden or prohibited actions in Islam | Permissible actions under Islamic law |
| Basis | Quran, Hadith, and Islamic jurisprudence | Quran, Hadith, and Islamic jurisprudence |
| Examples | Alcohol, gambling, theft, pork consumption | Halal meat, prayer, charity, honest trading |
| Consequences | Sin, spiritual harm, punishment in afterlife | Reward, spiritual purity, acceptance by Allah |
| Purpose | Protect moral and social order | Promote ethical and lawful living |
Understanding the Concepts: Haram vs Halal
Haram and Halal are key Islamic terms defining what is forbidden and permitted, respectively, according to Islamic law (Sharia). Haram activities or foods are explicitly prohibited due to their harmful or unethical nature, while Halal covers all actions and consumables allowed for Muslims, ensuring purity and compliance with divine guidelines. Understanding these concepts is essential for practicing Muslims to maintain spiritual cleanliness and ethical living across daily activities, including diet, finance, and behavior.
Historical Origins of Halal and Haram
Halal and Haram concepts originate from Islamic jurisprudence rooted in the Quran and Hadith, defining permissible and forbidden actions. Historically, these classifications guided Muslims in dietary laws, social conduct, and ethical behavior as Islam spread across diverse cultures. The terms gained significance through early Islamic scholars who systematically interpreted religious texts to establish legal frameworks for everyday life.
Key Differences Between Halal and Haram
Halal and Haram are Islamic dietary laws that distinguish permissible (Halal) from forbidden (Haram) actions and foods based on Quranic teachings and Hadith. Key differences include the consumption of meat slaughtered according to Islamic rites (Halal) versus pork and intoxicants, which are strictly prohibited (Haram). Halal encompasses not only food but all lawful practices, while Haram denotes actions or items forbidden by Islamic law, impacting lifestyle choices and religious compliance.
Common Examples of Haram Practices
Consuming pork and its by-products is strictly haram in Islamic dietary laws, as is the consumption of alcohol and intoxicants that impair judgment. Engaging in gambling and usury (riba), which exploit financial transactions for unfair profit, are also widely recognized as haram practices. Other common examples include dishonest behavior, such as theft and fraud, which violate Islamic ethical guidelines.
Everyday Halal Choices in Modern Life
Everyday halal choices in modern life encompass food, personal care products, and financial transactions that comply with Islamic dietary laws and ethical principles. Consuming halal-certified foods, using halal cosmetics free from forbidden ingredients like alcohol or pork derivatives, and engaging in Sharia-compliant banking ensures adherence to Islamic guidance. The growing availability of halal options in supermarkets, restaurants, and online platforms facilitates maintaining a halal lifestyle amidst contemporary conveniences.
Religious Significance in Islam
Haram and Halal are central concepts in Islamic law (Sharia), distinguishing actions as forbidden or permissible based on Quranic injunctions and Hadiths. Haram activities, such as consuming pork or engaging in usury, violate divine commands and harm spiritual purity, while Halal practices ensure obedience to Allah's guidance and promote ethical living. Observing these distinctions shapes a Muslim's daily conduct, reflecting faithfulness to Islamic teachings and fostering a sense of religious identity and community.
Halal Certification and Global Standards
Halal certification ensures that products comply with Islamic dietary laws, verified through rigorous inspections aligned with global halal standards such as those set by the Islamic Food and Nutrition Council of America (IFANCA) and the Halal Food Authority (HFA). This certification guarantees that food, beverages, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals are free from haram (forbidden) elements like pork, alcohol, and non-halal slaughtering methods. Growing international demand for halal-certified products underscores the importance of standardized certification processes to maintain consumer trust and facilitate global trade.
Consequences of Consuming Haram
Consuming Haram substances can lead to spiritual consequences such as loss of divine blessings and increased guilt or remorse in one's conscience. Health risks may arise from prohibited foods or items, potentially causing physical harm or illness. Socially, engaging in Haram consumption can damage relationships, community trust, and personal integrity within Islamic contexts.
Contemporary Challenges in Defining Halal and Haram
Contemporary challenges in defining halal and haram often arise from the globalization of food markets and evolving dietary practices, leading to discrepancies in interpretation across Islamic scholars and communities. Technological advancements in food processing and biotechnology create complexities in determining compliance with Shariah principles, especially regarding genetically modified organisms and synthetic additives. The diversity of cultural contexts further complicates consensus on halal certification standards, necessitating ongoing dialogue and adaptive regulatory frameworks.
Navigating Halal and Haram in a Multicultural Society
Navigating halal and haram in a multicultural society requires understanding diverse religious dietary laws and cultural practices integral to Muslim communities worldwide. Businesses and institutions should implement clear labeling and inclusive food policies that respect halal certification standards while accommodating various cultural sensitivities. Promoting awareness and education about halal dietary requirements helps foster mutual respect and enables smoother social integration among diverse populations.
Haram Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com