Incarnation refers to the embodiment of a deity or spirit in a physical form, often central to various religious and philosophical beliefs. This concept explores how divine essence manifests in human or earthly existence, influencing theological interpretations and spiritual practices. Discover how the idea of incarnation shapes understanding across different cultures and religions in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
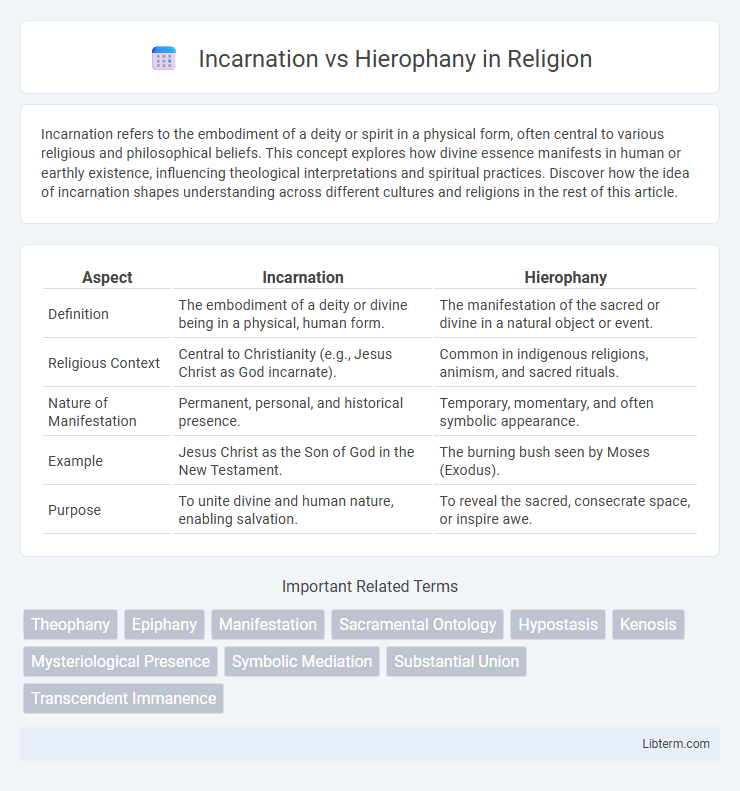
| Aspect | Incarnation | Hierophany |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The embodiment of a deity or divine being in a physical, human form. | The manifestation of the sacred or divine in a natural object or event. |
| Religious Context | Central to Christianity (e.g., Jesus Christ as God incarnate). | Common in indigenous religions, animism, and sacred rituals. |
| Nature of Manifestation | Permanent, personal, and historical presence. | Temporary, momentary, and often symbolic appearance. |
| Example | Jesus Christ as the Son of God in the New Testament. | The burning bush seen by Moses (Exodus). |
| Purpose | To unite divine and human nature, enabling salvation. | To reveal the sacred, consecrate space, or inspire awe. |
Understanding Incarnation: Definition and Origins
Incarnation refers to the theological concept where a divine being takes on a physical, human form, most notably seen in Christian doctrine with the belief that God became flesh in the person of Jesus Christ. Its origins trace back to ancient religious traditions emphasizing the union of the divine and material realms, evolving through early Christian thought and scripture interpretation. This concept contrasts with hierophany, which signifies a manifestation of the sacred or divine in the world without assuming a full human embodiment.
Exploring Hierophany: Meaning and Historical Context
Hierophany, derived from the Greek words "hieros" (sacred) and "phainein" (to reveal), signifies the manifestation of the sacred in the ordinary world, often through symbols, rituals, or natural phenomena. Historically, Mircea Eliade's studies emphasized hierophany as central to religious experience, where the sacred interrupts the profane, providing a connection between humans and the divine. Unlike incarnation, which specifically refers to a deity embodying a human form, hierophany encompasses a broader spectrum of sacred revelations across diverse cultures and spiritual traditions.
Key Differences Between Incarnation and Hierophany
Incarnation refers to the embodiment of a divine being in a physical form, often human, as seen in religious contexts like Christianity where God becomes flesh in Jesus Christ. Hierophany denotes the manifestation of the sacred or divine in any form, which can be natural objects, rituals, or symbols, without necessarily taking a physical body. The key difference lies in incarnation being a specific, personal embodiment of divinity, while hierophany represents a broader, often impersonal or symbolic, revelation of the sacred.
Theological Significance of Incarnation
The theological significance of the Incarnation centers on the belief that God became fully human in the person of Jesus Christ, bridging the infinite gap between divinity and humanity to enable salvation. Unlike hierophany, which represents divine manifestation in various forms or sacred symbols, the Incarnation uniquely embodies God's presence in a tangible, historical individual. This doctrine underscores the intimate union of God and man, emphasizing God's active participation in human experience and the transformative power of divine grace.
Symbolism and Function of Hierophany in Religion
Hierophany represents the manifestation of the sacred in the physical world, symbolizing the intersection between the divine and the mundane in religious contexts. It functions as a conduit through which believers experience and recognize the presence of the sacred, often embodied in rituals, sacred objects, or natural phenomena. This symbolization establishes a tangible connection that reinforces faith, communal identity, and the transmission of spiritual truths within religious traditions.
Incarnation in Major World Religions
Incarnation in major world religions such as Christianity, Hinduism, and Buddhism represents the manifestation of the divine in human or earthly form, emphasizing God's or celestial beings' presence within the material world. In Christianity, the incarnation of Jesus Christ is central, signifying God becoming flesh to provide salvation. Hinduism describes incarnation through avatars of deities like Vishnu, who descend to restore dharma, while certain Buddhist traditions refer to tulkus as reincarnated spiritual masters embodying enlightened consciousness.
Hierophany Across Cultures: Comparative Perspectives
Hierophany, the manifestation of the sacred in the physical world, appears across diverse cultures as a pivotal concept in understanding religious experience and symbolism. In Indigenous Australian traditions, hierophanies are often expressed through sacred sites and ancestral beings, while in Hinduism, manifestations such as avatars serve as hierophanic events revealing divine presence. Compared to the incarnation, which specifically denotes the embodiment of the divine in human form, hierophany encompasses a broader range of sacred manifestations, including objects, rituals, and natural phenomena, highlighting its cross-cultural significance.
Impact on Religious Experience and Practice
Incarnation emphasizes the divine presence embodied in a specific figure, typically shaping religious experience through personal devotion and ritual centered on that incarnation. Hierophany involves the manifestation of the sacred in ordinary objects or events, broadening spiritual practice by highlighting the transcendence within everyday life and nature. This distinction influences religious communities by directing worship either toward an anthropomorphic deity or sacred symbols perceived as gateways to the divine.
Incarnation vs Hierophany: Contemporary Interpretations
Incarnation vs Hierophany in contemporary interpretations highlights differing expressions of the divine entering the human realm versus sacred manifestations within the world. The Incarnation is often viewed as a unique, historical event where divinity takes on human form, central to Christian theology, emphasizing both transcendence and immanence. Hierophany, broadly defined in religious studies, refers to any appearance of the sacred in ordinary reality, allowing modern scholars to explore diverse cultural rituals and spiritual experiences as expressions of universal sacred presence.
Conclusion: Bridging Incarnation and Hierophany
Bridging incarnation and hierophany reveals a profound connection where divine presence manifests within both human form and sacred phenomena, emphasizing the multifaceted nature of spiritual revelation. Understanding incarnation as the embodiment of divine essence and hierophany as the manifestation of the sacred in material reality highlights their interplay in religious experience. This synthesis underscores the importance of recognizing both personal embodiment and symbolic manifestation in comprehending the full scope of the divine-human relationship.
Incarnation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com