Ahimsa, the principle of non-violence, is a core value in many spiritual traditions, emphasizing compassion and respect for all living beings. Practicing ahimsa promotes inner peace and fosters harmonious relationships by encouraging mindfulness in thoughts, words, and actions. Discover how embracing ahimsa can transform your life and interactions by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
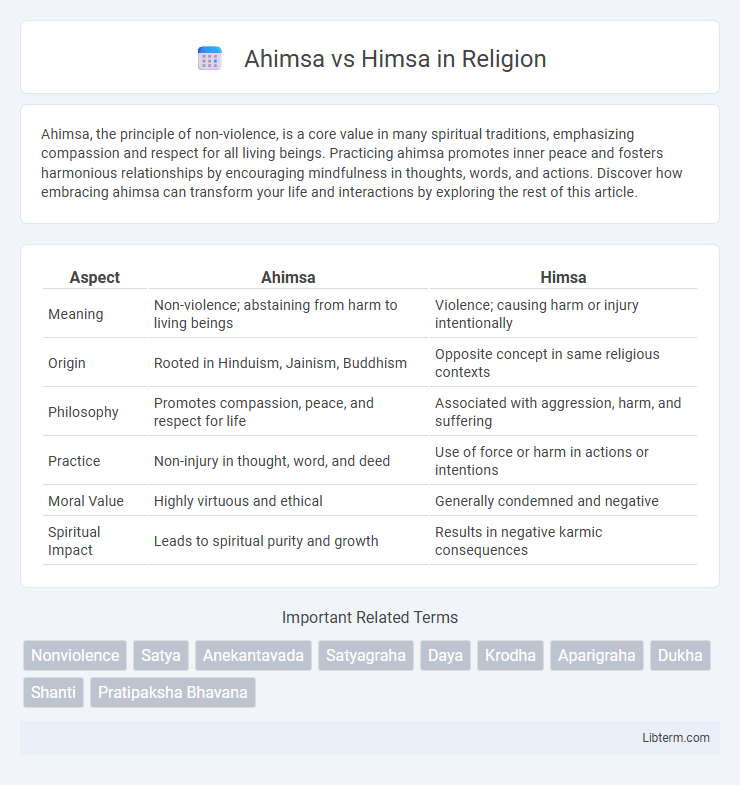
| Aspect | Ahimsa | Himsa |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Non-violence; abstaining from harm to living beings | Violence; causing harm or injury intentionally |
| Origin | Rooted in Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism | Opposite concept in same religious contexts |
| Philosophy | Promotes compassion, peace, and respect for life | Associated with aggression, harm, and suffering |
| Practice | Non-injury in thought, word, and deed | Use of force or harm in actions or intentions |
| Moral Value | Highly virtuous and ethical | Generally condemned and negative |
| Spiritual Impact | Leads to spiritual purity and growth | Results in negative karmic consequences |
Understanding Ahimsa: The Principle of Non-Violence
Ahimsa, rooted in ancient Indian philosophy, embodies the principle of non-violence by advocating harmlessness towards all living beings and promoting compassion in thought, word, and action. This ethical doctrine contrasts sharply with Himsa, which denotes violence, harm, and injury inflicted intentionally or unintentionally. Understanding Ahimsa involves recognizing its role in fostering peace, spiritual growth, and social harmony by minimizing suffering and respecting the sanctity of life.
Defining Himsa: The Nature of Violence
Himsa refers to acts of violence, harm, or injury inflicted on living beings, encompassing physical, verbal, and psychological aggression. This concept embodies destructive intentions, causing pain, suffering, or death, often linked to negative karma in various Indian philosophical traditions. Understanding Himsa involves recognizing its pervasive impact on individual well-being and social harmony, contrasting sharply with the principle of Ahimsa, which promotes non-violence and compassion.
Historical Origins of Ahimsa and Himsa
Ahimsa, rooted in ancient Indian religions such as Jainism, Hinduism, and Buddhism, originated as a principle of non-violence and respect for all living beings, emphasizing compassion and moral restraint. Himsa, by contrast, signifies violence or harm, often associated with aggression and conflict in historical contexts across civilizations. The historical origin of Ahimsa is deeply embedded in spiritual teachings that advocate for peace, whereas Himsa reflects the natural human tendencies toward conflict and dominance.
Philosophical Foundations: East vs. West Perspectives
Ahimsa, rooted in Indian philosophies like Jainism, Buddhism, and Hinduism, emphasizes non-violence as a fundamental ethical principle that promotes compassion and respect for all living beings. In contrast, Western philosophical traditions often frame concepts of violence and non-violence through legalistic or utilitarian lenses, focusing on justice, rights, and consequences rather than intrinsic moral values. The East's holistic worldview sees Ahimsa as a means to spiritual liberation and harmony, while the West commonly approaches Himsa and its avoidance through sociopolitical frameworks and individual rights.
Ahimsa in Major World Religions
Ahimsa, a foundational ethical principle emphasizing non-violence and compassion, is central to Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism, promoting respect for all living beings and encouraging peaceful coexistence. In Hinduism, Ahimsa is linked to Dharma and spiritual progress, urging followers to avoid harm in thoughts, words, and actions. Jainism elevates Ahimsa as the highest virtue, strictly avoiding harm to any life form, while Buddhism integrates Ahimsa through the Five Precepts, particularly the commitment to abstain from killing.
Himsa and Its Manifestations in Society
Himsa, rooted in violence and harm, manifests in various societal forms such as physical aggression, systemic oppression, and environmental destruction. These actions perpetuate cycles of suffering, hinder social harmony, and degrade human dignity. Recognizing the pervasive impact of Himsa is crucial for fostering justice and promoting nonviolence policies worldwide.
Psychological Impact of Practicing Ahimsa vs. Himsa
Practicing Ahimsa, or non-violence, fosters psychological well-being by reducing stress, enhancing emotional resilience, and promoting empathy towards others. In contrast, engaging in Himsa, or violence, often leads to increased anxiety, guilt, and psychological distress, impairing mental health and interpersonal relationships. Studies in positive psychology highlight how Ahimsa-based mindfulness and compassion practices contribute to improved mental health outcomes and overall life satisfaction.
Ahimsa in Modern Activism and Politics
Ahimsa, the principle of non-violence originating from ancient Indian philosophy, plays a critical role in modern activism and politics by promoting peaceful resistance and social justice. Movements led by figures such as Mahatma Gandhi and Martin Luther King Jr. demonstrate how Ahimsa effectively challenges systemic oppression without resorting to violence. Contemporary political campaigns continue to embrace Ahimsa as a strategic framework to foster dialogue, human rights, and sustainable change.
Ethical Dilemmas: Can Himsa Ever Be Justified?
The ethical dilemmas surrounding Ahimsa (non-violence) and Himsa (violence) challenge moral frameworks that prioritize harm avoidance versus justified force. Debates consider contexts such as self-defense, war, and social justice where Himsa might be argued as necessary to prevent greater harm or injustice. Philosophical and religious traditions grapple with whether absolute non-violence is feasible or if strategic violence serves a higher ethical purpose.
Choosing Ahimsa: Pathways to Personal and Social Harmony
Choosing Ahimsa fosters personal growth by promoting nonviolence, compassion, and empathy, which reduce internal conflict and enhance emotional well-being. Practicing Ahimsa in social interactions cultivates harmony, mutual respect, and peaceful coexistence, essential for resolving conflicts without aggression. Embracing Ahimsa as a lifestyle encourages sustainable societal development and supports global movements for human rights and environmental protection.
Ahimsa Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com