Compassion involves recognizing the suffering of others and responding with empathy and kindness, fostering deeper human connections. Practicing compassion enhances emotional well-being and promotes a supportive community environment. Discover how cultivating compassion can transform your relationships and daily life by reading the rest of the article.
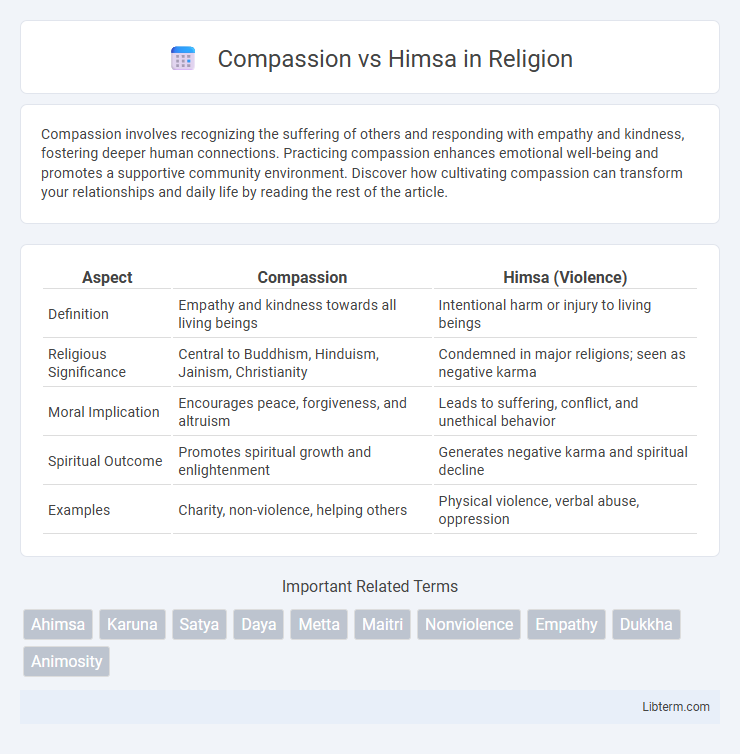
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Compassion | Himsa (Violence) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Empathy and kindness towards all living beings | Intentional harm or injury to living beings |
| Religious Significance | Central to Buddhism, Hinduism, Jainism, Christianity | Condemned in major religions; seen as negative karma |
| Moral Implication | Encourages peace, forgiveness, and altruism | Leads to suffering, conflict, and unethical behavior |
| Spiritual Outcome | Promotes spiritual growth and enlightenment | Generates negative karma and spiritual decline |
| Examples | Charity, non-violence, helping others | Physical violence, verbal abuse, oppression |
Understanding Compassion: A Core Human Value
Compassion, a fundamental human value, involves recognizing and empathizing with the suffering of others, promoting kindness and altruism. In contrast, Himsa, rooted in harm or violence, disrupts social harmony and fosters fear and suffering. Emphasizing compassion cultivates emotional intelligence and ethical behavior, essential for individual and collective well-being.
Defining Himsa: The Nature of Harm and Violence
Himsa, rooted in Sanskrit, refers to deliberate harm or violence inflicted upon living beings, encompassing physical injury, mental anguish, and ethical transgressions. This concept highlights the intentional disruption of peace and well-being, contrasting with compassion's emphasis on empathy and non-violence. Understanding himsa involves recognizing actions that cause suffering, whether through physical force, verbal abuse, or neglect, and its detrimental impact on both individuals and society.
Historical Perspectives: Compassion and Himsa in World Religions
Historical perspectives on compassion and himsa reveal profound divergences across world religions, with Hinduism emphasizing ahimsa as non-violence central to Dharma, while Buddhism highlights metta (loving-kindness) as a path to enlightenment opposing all forms of himsa. Jainism elevates ahimsa to the highest ethical principle, advocating for strict non-violence in thought, word, and deed. In contrast, some interpretations of ancient texts in Christianity and Islam acknowledge justified himsa in the context of divine justice or self-defense, reflecting complex moral frameworks.
Psychological Impact: How Compassion Heals, How Himsa Hurts
Compassion fosters psychological healing by reducing stress, enhancing emotional resilience, and promoting neural pathways associated with empathy and trust. Himsa, or violence, triggers chronic stress responses, increasing cortisol levels that damage brain regions responsible for emotional regulation and cognitive function. Empirical studies show that environments rich in compassion significantly lower anxiety and depression rates, while exposure to himsa correlates strongly with post-traumatic stress disorder and impaired social functioning.
Compassion vs Himsa in Daily Life Choices
Choosing compassion over himsa in daily life involves consciously opting for kindness and empathy rather than harm or aggression in interactions. Practicing compassion promotes harmonious relationships, mental well-being, and social cohesion, while himsa often leads to conflict, stress, and societal breakdown. Decisions such as speaking gently, offering help, and considering others' feelings reflect compassion, contrasting with actions like verbal abuse, negligence, or violence that embody himsa.
Social Consequences: Building Communities with Compassion or Himsa
Compassion fosters social cohesion by promoting empathy, trust, and mutual support, which strengthens community resilience and cooperation. In contrast, Himsa, or violence, often leads to distrust, fear, and social fragmentation, undermining communal stability and increasing conflict. Communities built on compassion experience enhanced social well-being and collective growth, while those dominated by Himsa face persistent cycles of harm and division.
Cultural Narratives: Stories that Illustrate Compassion Over Himsa
Cultural narratives across various societies often highlight compassion as a superior value to himsa (violence) through tales that emphasize empathy, forgiveness, and non-violence. For instance, the ancient Indian epic Mahabharata showcases characters like Bhishma and Arjuna who embody compassion amidst conflict, promoting dharma over destructive behavior. These stories serve as moral frameworks encouraging societies to resolve disputes peacefully and uphold humanitarian principles.
Compassion in Action: Strategies for Reducing Himsa
Compassion in action involves practical strategies such as community engagement, conflict resolution, and restorative justice to reduce himsa (violence). Programs promoting empathy and social support effectively address the root causes of aggressive behavior, fostering nonviolent communication and cooperation. Implementing education on emotional intelligence and providing mental health resources play crucial roles in transforming violent tendencies into compassionate responses.
The Role of Empathy in Overcoming Himsa
Empathy acts as a crucial bridge in overcoming Himsa by fostering a deep emotional understanding of others' suffering, which motivates compassionate actions that counteract violence. Neuroscientific studies reveal that empathic engagement activates brain regions associated with pain processing, enabling individuals to resonate with others' distress and choose non-violent responses. Cultivating empathy through mindfulness and social-emotional learning programs significantly reduces aggressive behaviors and promotes reconciliation in conflict zones.
Moving Forward: Cultivating a Culture of Compassion Over Himsa
Cultivating a culture of compassion over himsa demands intentional practices that prioritize empathy, active listening, and non-violent communication in communities and organizations. Implementing restorative justice programs reduces cycles of harm by encouraging accountability and healing instead of punishment and fear. Embedding compassion in education, workplace policies, and leadership models fosters resilience and social cohesion, counteracting the destructive patterns associated with himsa.
Compassion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com