Salvation represents the profound deliverance from sin and its consequences, offering eternal peace and reconciliation with the divine. It is a cornerstone of many religious beliefs, emphasizing grace, faith, and redemption through a higher power. Explore the rest of this article to understand how salvation can transform your spiritual journey and life perspective.
Table of Comparison
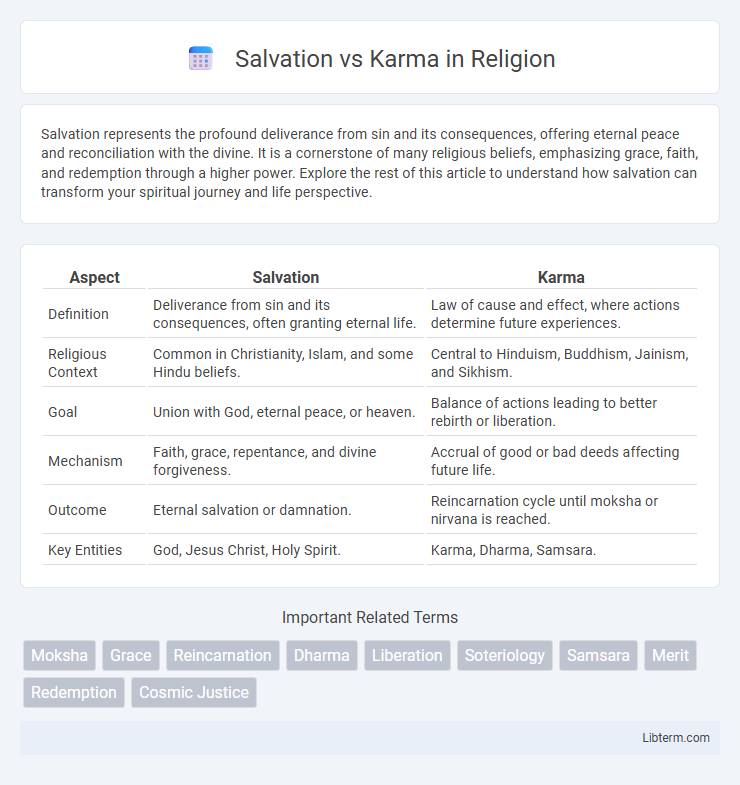
| Aspect | Salvation | Karma |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliverance from sin and its consequences, often granting eternal life. | Law of cause and effect, where actions determine future experiences. |
| Religious Context | Common in Christianity, Islam, and some Hindu beliefs. | Central to Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. |
| Goal | Union with God, eternal peace, or heaven. | Balance of actions leading to better rebirth or liberation. |
| Mechanism | Faith, grace, repentance, and divine forgiveness. | Accrual of good or bad deeds affecting future life. |
| Outcome | Eternal salvation or damnation. | Reincarnation cycle until moksha or nirvana is reached. |
| Key Entities | God, Jesus Christ, Holy Spirit. | Karma, Dharma, Samsara. |
Understanding Salvation: Core Concepts
Salvation, central to many religious traditions like Christianity and Islam, represents deliverance from sin and its consequences, offering eternal life or unity with the divine. It often involves grace, faith, and divine intervention, contrasting with karma's principle of cause and effect rooted in Hinduism and Buddhism. Understanding salvation requires grasping its emphasis on forgiveness, redemption, and transcendence beyond earthly existence.
Defining Karma: Origins and Meaning
Karma originates from ancient Indian philosophies, primarily Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism, where it signifies the law of cause and effect governing moral actions. It implies that every deed, thought, or intention influences future experiences, creating a cycle of rebirth and consequences. This concept emphasizes ethical behavior and personal responsibility as fundamental to spiritual growth and liberation.
Historical Roots: Salvation in Major Religions
Salvation in major religions such as Christianity, Islam, and Hinduism historically centers on liberation from sin, suffering, or the cycle of rebirth. Christianity emphasizes salvation through faith in Jesus Christ as a path to eternal life, while Islam teaches salvation through submission to Allah's will and righteous deeds. Hinduism interprets salvation (moksha) as liberation from karma and samsara, achieved through spiritual knowledge, devotion, and ethical living.
Philosophical Foundations of Karma
Karma, rooted in Indian philosophy, emphasizes the law of cause and effect, where every action influences future experiences and spiritual progression. This principle underlines ethical responsibility and the belief that moral deeds lead to positive outcomes, while negative actions result in suffering. Unlike the concept of salvation, which often involves divine grace or liberation, Karma operates autonomously within the cosmic order to maintain moral balance and personal growth.
Salvation and Karma: Key Differences
Salvation in many religions refers to the deliverance from sin and its consequences, often achieved through faith, grace, or divine intervention, while karma is a principle of cause and effect where one's actions determine future experiences. Salvation typically offers a path to eternal peace or union with the divine, whereas karma emphasizes moral accountability and the shaping of one's destiny through ethical living. The key difference lies in salvation being a state or gift of spiritual freedom, while karma functions as an ongoing process of moral cause and consequence.
The Role of Personal Responsibility
Personal responsibility plays a crucial role in both salvation and karma, shaping the outcomes of individual actions. In salvation, personal accountability often involves moral choices and faith leading to spiritual redemption or eternal life. Karma emphasizes cause and effect, where every intentional deed influences future circumstances, reinforcing the importance of ethical behavior and self-awareness.
Moral Implications: Justice and Forgiveness
Salvation emphasizes divine justice and forgiveness, offering redemption through faith and grace regardless of past actions, which fosters moral accountability and hope for transformation. Karma operates on a principle of moral cause and effect, where every action inevitably results in corresponding consequences, promoting personal responsibility and ethical behavior. The moral implications highlight a contrast: salvation centers on mercy and grace beyond human merit, while karma underscores impartial justice based on individual deeds.
Pathways to Redemption: Works vs. Grace
Salvation emphasizes grace as the unmerited favor granted by a divine power, offering redemption through faith rather than human deeds. Karma operates on the principle of cause and effect, where redemption and spiritual progress result directly from one's actions and ethical living. This fundamental difference highlights salvation's reliance on divine mercy compared to karma's emphasis on personal responsibility and moral accountability.
Salvation and Karma in Contemporary Spirituality
Salvation in contemporary spirituality often emphasizes personal liberation and transcendence from worldly suffering through inner transformation or divine grace. Karma is understood as the law of cause and effect, shaping one's present and future experiences based on past actions, encouraging ethical behavior and spiritual growth. Both concepts converge in modern practices that integrate self-awareness, moral responsibility, and the pursuit of enlightenment.
Reconciling Salvation and Karma: Can They Coexist?
Salvation and karma represent distinct spiritual concepts often perceived as opposing paths: salvation emphasizes divine grace and liberation from the cycle of rebirth, while karma entails ethical causality influencing future experiences. Reconciling salvation and karma involves understanding that karmic law governs moral consequences, but salvation offers transcendence by divine intervention or enlightenment beyond karmic debts. Many philosophical traditions propose that practicing righteous actions (karma) aligns with spiritual growth, making salvation a culmination of karmic purification rather than contradiction.
Salvation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com