Qiyas is a method of Islamic jurisprudence that uses analogical reasoning to derive legal rulings for new situations based on established precedents in the Quran and Hadith. It plays a crucial role in filling gaps where explicit texts do not provide direct guidance, ensuring adaptability within Islamic law. Explore the rest of the article to understand how Qiyas influences contemporary Islamic legal decision-making.
Table of Comparison
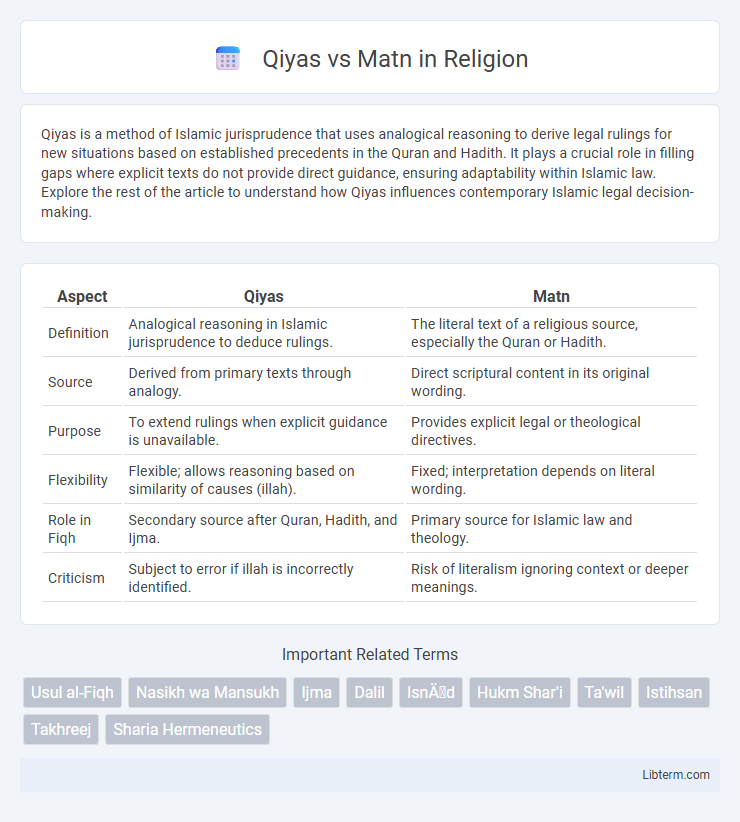
| Aspect | Qiyas | Matn |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analogical reasoning in Islamic jurisprudence to deduce rulings. | The literal text of a religious source, especially the Quran or Hadith. |
| Source | Derived from primary texts through analogy. | Direct scriptural content in its original wording. |
| Purpose | To extend rulings when explicit guidance is unavailable. | Provides explicit legal or theological directives. |
| Flexibility | Flexible; allows reasoning based on similarity of causes (illah). | Fixed; interpretation depends on literal wording. |
| Role in Fiqh | Secondary source after Quran, Hadith, and Ijma. | Primary source for Islamic law and theology. |
| Criticism | Subject to error if illah is incorrectly identified. | Risk of literalism ignoring context or deeper meanings. |
Introduction to Qiyas and Matn
Qiyas refers to analogical reasoning in Islamic jurisprudence, where rulings from the Quran or Sunnah are extended to new cases based on shared causes or characteristics. Matn denotes the actual text of a hadith, specifically the content or wording, which is critical for understanding and interpreting Islamic law. Distinguishing Qiyas from Matn is essential for accurate legal reasoning, as Qiyas involves inferential logic while Matn provides the foundational textual evidence.
Defining Qiyas: Concept and Principles
Qiyas, in Islamic jurisprudence, refers to analogical reasoning used to derive legal rulings for new situations based on established precedents from the Quran, Sunnah, and ijma (consensus). It operates on the principle of identifying a common underlying cause (illah) between the original ruling and the new case, ensuring consistency and coherence in Sharia law. This method maintains the integrity of primary texts while allowing adaptability in evolving circumstances.
Understanding Matn: Meaning and Significance
Matn refers to the core text or main body of an Islamic legal or religious document, encompassing the essential wording and content subject to interpretation. Understanding Matn is crucial for scholars to accurately derive rulings and meanings without altering the original intent embedded within the text. The significance of Matn lies in preserving the authentic message and ensuring that legal or theological conclusions remain rooted in the foundational text itself.
Historical Development of Qiyas and Matn
Qiyas, an analogical reasoning method in Islamic jurisprudence, evolved during the early Abbasid period to address new legal issues absent from the Quran and Hadith, providing dynamic adaptability to Sharia law. The matn refers to the actual text of Hadith, whose authenticity and interpretation were rigorously scrutinized through the science of Hadith criticism to ensure accurate legal derivation. The historical development of qiyas was intertwined with the codification and analysis of matn, shaping Islamic legal methodology and the maturation of fiqh principles.
Key Differences Between Qiyas and Matn
Qiyas and Matn represent distinct concepts in Islamic jurisprudence, where Qiyas refers to analogical reasoning used to derive legal rulings by comparing new cases to established precedents, while Matn denotes the literal text of the Islamic legal sources such as the Quran or Hadith. The primary key difference lies in Qiyas being a methodological tool for deduction beyond explicit texts, whereas Matn is the actual scriptural content that provides the foundational evidence. Understanding these differences is crucial for interpreting Islamic law, as Qiyas fills gaps not directly addressed by the Matn.
Role of Qiyas in Islamic Jurisprudence
Qiyas serves as a fundamental source of Islamic jurisprudence by applying analogical reasoning to derive legal rulings for new cases based on established texts (Qur'an and Sunnah). This method extends the scope of Shariah law, ensuring its relevance by addressing contemporary issues absent from primary sources. Matn, the main text of hadith, is analyzed critically during Qiyas to extract legal principles, making Qiyas essential for interpreting Islamic law within evolving contexts.
Importance of Matn in Hadith Studies
Matn holds paramount importance in Hadith studies as it encompasses the precise wording and content of the Prophet's sayings, which directly affect interpretation and application of Islamic teachings. Unlike Qiyas, which involves analogical reasoning to derive rulings, Matn ensures the authenticity and clarity of the original message, safeguarding the integrity of legal and theological analysis. Accurate examination of Matn is essential for verifying chains of transmission and contextual understanding within Hadith scholarship.
Examples Illustrating Qiyas and Matn
Qiyas refers to analogical reasoning in Islamic jurisprudence where rulings are derived by comparing a new case to an established precedent based on a common effective cause, such as deriving prohibition of smoking by analogy to alcohol due to health harm. Matn, the actual text of a Hadith, forms the foundational source used for qiyas, exemplified in the Hadith text forbidding alcohol consumption that serves as the basis for extending rulings to intoxicants like drugs. Examples illustrating qiyas demonstrate how jurists extrapolate rulings from matn by identifying underlying causes, thus enabling Islamic law to address new issues systematically.
Debates and Criticisms: Qiyas vs Matn
Scholars have raised significant debates criticizing Qiyas for its reliance on analogical reasoning, which some argue introduces subjectivity and potential error in Islamic jurisprudence. Matn, as the textual content of hadith, faces scrutiny over its authenticity and transmission, complicating legal rulings based solely on its text. The tension between Qiyas and Matn centers on balancing reasoned inference with strict adherence to textual evidence, a critical issue in formulating Islamic law.
Conclusion: Integrating Qiyas and Matn in Islamic Scholarship
Integrating Qiyas (analogical reasoning) and Matn (textual content) enhances Islamic jurisprudence by balancing dynamic legal interpretation with scriptural authenticity. This approach ensures that legal rulings remain relevant to contemporary issues while rooted firmly in foundational texts, preserving both flexibility and doctrinal integrity. The synergy between Qiyas and Matn fosters a comprehensive methodology that strengthens the adaptability and coherence of Shariah law.
Qiyas Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com