Forgiveness is a powerful tool that frees your mind from the burden of resentment and anger, promoting emotional healing and personal growth. Letting go of past hurts can improve mental well-being and foster healthier relationships with yourself and others. Explore this article to understand the profound benefits of forgiveness and how to practice it effectively.
Table of Comparison
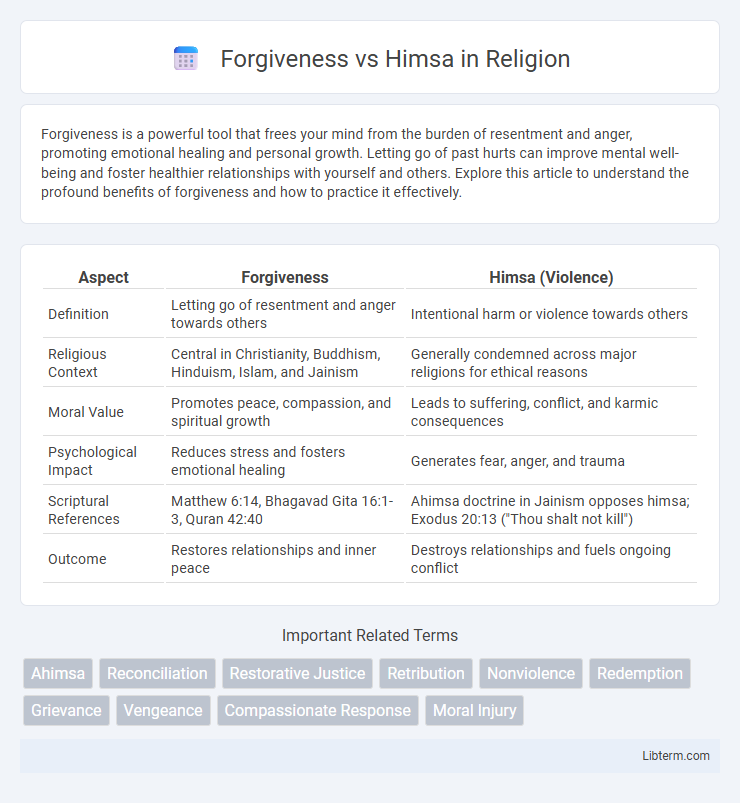
| Aspect | Forgiveness | Himsa (Violence) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Letting go of resentment and anger towards others | Intentional harm or violence towards others |
| Religious Context | Central in Christianity, Buddhism, Hinduism, Islam, and Jainism | Generally condemned across major religions for ethical reasons |
| Moral Value | Promotes peace, compassion, and spiritual growth | Leads to suffering, conflict, and karmic consequences |
| Psychological Impact | Reduces stress and fosters emotional healing | Generates fear, anger, and trauma |
| Scriptural References | Matthew 6:14, Bhagavad Gita 16:1-3, Quran 42:40 | Ahimsa doctrine in Jainism opposes himsa; Exodus 20:13 ("Thou shalt not kill") |
| Outcome | Restores relationships and inner peace | Destroys relationships and fuels ongoing conflict |
Understanding Forgiveness: Definition and Importance
Forgiveness is the intentional process of releasing resentment and anger toward someone who has caused harm, fostering emotional healing and personal peace. This concept contrasts sharply with himsa, a Sanskrit term meaning violence or harm, which perpetuates suffering and conflict. Understanding forgiveness is crucial for reducing negative emotions, improving mental health, and promoting reconciliation in interpersonal relationships.
Exploring the Concept of Himsa (Violence)
Himsa, derived from Sanskrit, signifies violence or harm inflicted on others, encompassing physical, mental, and emotional forms of aggression. This concept deeply contrasts with forgiveness, which promotes healing, reconciliation, and the cessation of hostile actions. Exploring Himsa reveals its root in ego and ignorance, perpetuating cycles of suffering and conflict within individuals and societies.
Historical Perspectives on Forgiveness and Himsa
Historical perspectives on forgiveness and himsa reveal contrasting approaches to conflict resolution across cultures and religions; forgiveness, rooted in compassion and reconciliation, has been central in traditions like Buddhism, Christianity, and Jainism, promoting non-violence and inner peace. Himsa, meaning violence or harm, has often been associated with war, punishment, and societal control in various ancient legal and philosophical systems, including Hindu dharma and early legal codes. The juxtaposition of forgiveness and himsa reflects enduring human tensions between peace-building and retributive justice throughout history.
Psychological Impacts of Forgiveness vs Himsa
Forgiveness promotes psychological well-being by reducing stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms, fostering emotional healing and resilience. In contrast, himsa, or violence, exacerbates trauma, heightens fear responses, and can lead to long-term mental health disorders such as PTSD. Embracing forgiveness facilitates positive neuroplasticity and emotional regulation, whereas himsa reinforces negative cognitive patterns and emotional dysregulation.
Cultural Interpretations of Forgiveness and Violence
Cultural interpretations of forgiveness and himsa (violence) reveal diverse value systems where forgiveness is often seen as a path to social harmony and personal healing, while himsa represents disruption and moral failure. In many Eastern traditions, forgiveness is tied to spiritual growth and karma, contrasting with the acceptance of himsa as a necessary but controlled response to injustice. Western cultures frequently emphasize forgiveness as an ethical choice promoting reconciliation, whereas violence is portrayed as a breakdown of civility with legal and social repercussions.
Forgiveness and Himsa in Religious Teachings
Forgiveness is central to many religious teachings, emphasizing compassion, mercy, and spiritual liberation, as seen in Christianity's teachings on turning the other cheek and Buddhism's focus on releasing anger to achieve inner peace. Himsa, often translated as violence or harm, is condemned in Hinduism, Jainism, and Buddhism, where it is believed to generate negative karma and obstruct spiritual growth. Religious doctrines advocate forgiveness as a moral virtue that counters the destructive consequences of himsa by promoting reconciliation and non-violence.
The Role of Empathy in Resolving Himsa
Empathy plays a crucial role in resolving himsa by fostering understanding and emotional connection between conflicting parties, which reduces animosity and promotes forgiveness. Recognizing the pain and suffering of others through empathy enables individuals to move beyond retaliation and violence, encouraging peaceful reconciliation. Cultivating empathy supports transforming destructive behaviors into compassionate responses, ultimately breaking the cycle of himsa.
Practical Steps: Moving from Himsa to Forgiveness
Practicing mindfulness and self-awareness helps recognize and reduce Himsa, fostering emotional regulation and empathy. Engaging in active listening and open communication promotes understanding and reconciliation, replacing anger with compassion. Consistent reflection on personal values and seeking supportive communities enhances resilience, guiding the transition toward genuine forgiveness and healing.
Benefits of Choosing Forgiveness Over Violence
Choosing forgiveness over himsa (violence) fosters emotional healing by reducing stress and promoting mental clarity. Forgiveness encourages empathy and restores relationships, leading to stronger social bonds and community cohesion. This approach also diminishes cycles of retaliation, thereby supporting long-term peace and societal stability.
Building a Forgiving Society: Reducing Himsa for Peace
Building a forgiving society significantly reduces himsa by promoting empathy, understanding, and reconciliation among individuals and communities. Forgiveness acts as a powerful catalyst for healing social wounds, breaking cycles of violence, and fostering a culture of non-violence that prioritizes peace and harmony. Emphasizing restorative justice practices and community dialogue enhances forgiveness, which in turn diminishes aggressive behaviors and contributes to sustainable peace.
Forgiveness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com