Mercy embodies compassion and forgiveness, offering relief from judgment and fostering healing in difficult situations. It transforms relationships by replacing resentment with understanding and kindness. Discover how embracing mercy can profoundly impact your life in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
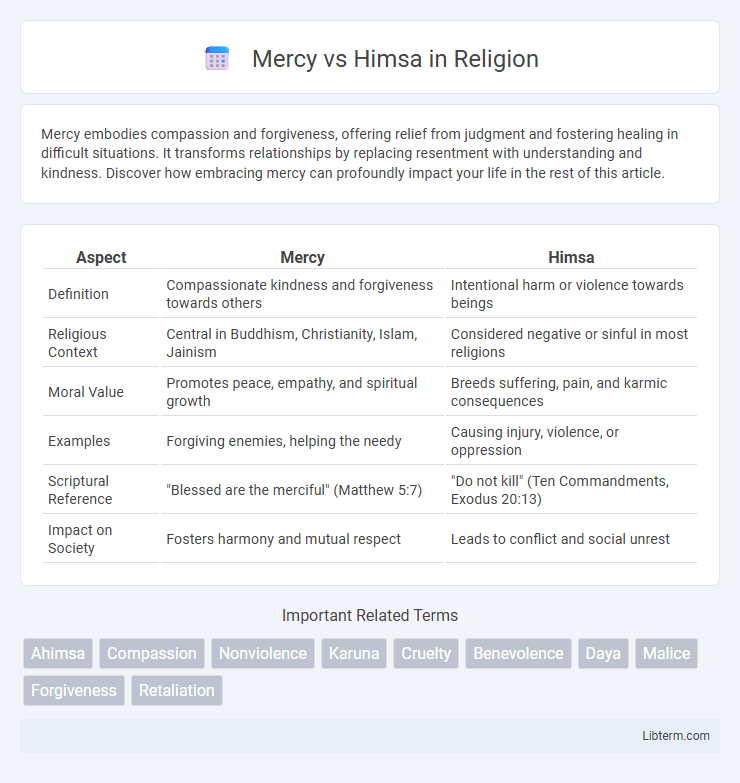
| Aspect | Mercy | Himsa |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Compassionate kindness and forgiveness towards others | Intentional harm or violence towards beings |
| Religious Context | Central in Buddhism, Christianity, Islam, Jainism | Considered negative or sinful in most religions |
| Moral Value | Promotes peace, empathy, and spiritual growth | Breeds suffering, pain, and karmic consequences |
| Examples | Forgiving enemies, helping the needy | Causing injury, violence, or oppression |
| Scriptural Reference | "Blessed are the merciful" (Matthew 5:7) | "Do not kill" (Ten Commandments, Exodus 20:13) |
| Impact on Society | Fosters harmony and mutual respect | Leads to conflict and social unrest |
Understanding the Concepts: Mercy and Himsa
Mercy is the compassionate and forgiving attitude that seeks to alleviate suffering and promote kindness, often leading to acts of forgiveness and care. Himsa, rooted in Sanskrit, refers to violence or harm inflicted intentionally, encompassing physical, mental, or emotional damage. Understanding these concepts is crucial for fostering ethical behavior, as mercy encourages peace and reconciliation, while recognizing himsa highlights the impact and consequences of harmful actions.
Historical Perspectives on Mercy and Himsa
Historical perspectives on mercy and himsa reveal foundational contrasts in ethical and religious teachings across cultures. Mercy, often emphasized in Abrahamic faiths like Christianity and Islam, is portrayed as compassion and forgiveness that foster social harmony and moral growth. Himsa, rooted in Indian traditions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism, denotes violence and harm, with strict doctrines advocating non-violence (ahimsa) to promote spiritual purity and reduce suffering.
The Philosophical Roots of Mercy
Mercy, deeply rooted in philosophical traditions such as Stoicism and Christian ethics, emphasizes compassion and forgiveness as foundational virtues guiding human behavior. This concept contrasts sharply with Himsa, derived from ancient Indian philosophies like Hinduism and Buddhism, where it represents intentional harm or violence, directly opposing non-violence (Ahimsa). Understanding mercy through its philosophical roots highlights a commitment to empathy and moral responsibility that challenges the destructive impulses central to Himsa.
The Nature and Impact of Himsa
Himsa, often defined as intentional violence or harm, fundamentally disrupts social harmony and individual well-being, leading to physical injury, psychological trauma, and long-term societal instability. Its manifestations range from physical assault to systemic oppression, each inflicting profound damage on victims and communities by perpetuating fear and mistrust. The impact of Himsa extends beyond immediate suffering, eroding ethical values and hindering collective progress towards peace and justice.
Mercy in World Religions and Cultures
Mercy is a central tenet in many world religions, embodying compassion, forgiveness, and kindness towards others. In Christianity, mercy is exemplified through Jesus' teachings of love and forgiveness, while in Islam, it is a fundamental attribute of Allah known as "Ar-Rahman" (The Most Merciful). Hinduism emphasizes mercy through the principles of ahimsa (non-violence) and compassion, promoting harmony and empathy within communities.
Himsa: Causes, Consequences, and Manifestations
Himsa, rooted in aggression and harm, causes physical injury, emotional trauma, and societal unrest by promoting violence and intolerance. Consequences of Himsa include increased conflict, mental health issues, and disruption of social harmony, often manifesting in domestic abuse, warfare, and systemic oppression. Manifestations of Himsa appear through acts of cruelty, verbal abuse, and destructive behaviors that perpetuate suffering and inhibit community well-being.
Mercy as a Force for Social Harmony
Mercy acts as a powerful catalyst for social harmony by fostering compassion and forgiveness within communities, reducing conflicts and promoting peaceful coexistence. Emphasizing empathy and understanding, mercy encourages individuals to address grievances through dialogue rather than violence, contrasting sharply with Himsa, or violence, which perpetuates division and unrest. Cultivating mercy nurtures trust and cooperation, essential elements for building resilient and inclusive societies.
Overcoming Himsa: Strategies and Solutions
Overcoming Himsa involves implementing nonviolent communication, promoting conflict resolution through dialogue, and fostering empathy in communities. Educational programs aimed at raising awareness about the consequences of violence play a critical role in reducing Himsa. Legal frameworks combined with social support systems ensure accountability and provide rehabilitation for those affected by violent behavior.
Case Studies: Mercy Triumphs Over Himsa
Case studies reveal Mercy's effectiveness in resolving conflicts compared to Himsa by promoting forgiveness and reconciliation, which reduces cycles of violence and fosters lasting peace. Instances such as post-conflict community rebuilding in Rwanda demonstrate how mercy-based approaches support healing and social cohesion more sustainably than punitive measures. Data from restorative justice programs highlight significant drops in recidivism rates where mercy is prioritized over Himsa, emphasizing mercy's role in achieving long-term conflict resolution.
Fostering Mercy in Modern Society
Fostering mercy in modern society encourages empathy, compassion, and restorative justice, counteracting the aggression embodied by Himsa. Emphasizing mercy reduces social tensions and promotes conflict resolution through understanding and forgiveness rather than violence. Integrating mercy-driven policies in education, criminal justice, and community initiatives cultivates a more harmonious and resilient society.
Mercy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com