Lamas are domesticated South American camelids known for their gentle nature and valuable wool, commonly used in textiles. They thrive in high-altitude environments and have been integral to Andean cultures for centuries, serving as pack animals and companions. Discover more fascinating facts about lamas and their unique role in the ecosystem by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
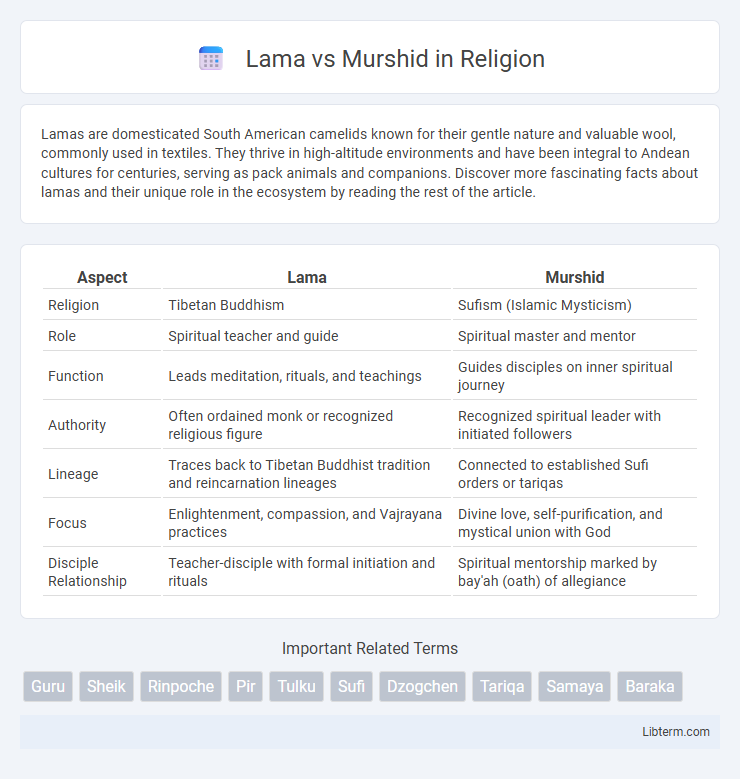
| Aspect | Lama | Murshid |
|---|---|---|
| Religion | Tibetan Buddhism | Sufism (Islamic Mysticism) |
| Role | Spiritual teacher and guide | Spiritual master and mentor |
| Function | Leads meditation, rituals, and teachings | Guides disciples on inner spiritual journey |
| Authority | Often ordained monk or recognized religious figure | Recognized spiritual leader with initiated followers |
| Lineage | Traces back to Tibetan Buddhist tradition and reincarnation lineages | Connected to established Sufi orders or tariqas |
| Focus | Enlightenment, compassion, and Vajrayana practices | Divine love, self-purification, and mystical union with God |
| Disciple Relationship | Teacher-disciple with formal initiation and rituals | Spiritual mentorship marked by bay'ah (oath) of allegiance |
Introduction to Spiritual Leadership: Lama vs Murshid
Lama and Murshid both serve as spiritual leaders guiding disciples on paths of enlightenment within Tibetan Buddhism and Sufism, respectively. The Lama emphasizes monastic discipline, meditation, and ritual practice, while the Murshid centers on direct personal connection, spiritual wisdom, and mystical teachings. Understanding their distinct roles provides insight into diverse traditions of spiritual mentorship and leadership.
Historical Origins of Lama and Murshid Traditions
The historical origins of the Lama tradition trace back to Tibetan Buddhism, where Lamas serve as spiritual teachers and leaders instrumental in preserving the Vajrayana lineage. In contrast, the Murshid tradition stems from Sufi Islam, evolving as a guide or spiritual master who leads disciples (murids) on the path toward divine enlightenment. Both roles embody deep-rooted cultural and religious systems but differ fundamentally in spiritual practices, geographic origins, and doctrinal frameworks.
Core Philosophies: Tibetan Buddhism vs Sufism
Lamas in Tibetan Buddhism serve as spiritual guides who embody the path to enlightenment through meditation, ritual, and the transmission of esoteric knowledge rooted in Mahayana and Vajrayana traditions. Murshids in Sufism function as spiritual mentors guiding disciples toward divine love and unity with God via practices emphasizing dhikr (remembrance), spiritual purification, and the inner realization of Tawhid (oneness of God). The core philosophical distinction lies in Tibetan Buddhism's focus on overcoming samsara through wisdom and compassion to attain Buddhahood, while Sufism centers on dissolving the ego and achieving mystical union with the divine essence.
Roles and Responsibilities of Lamas
Lamas serve as spiritual teachers and leaders within Tibetan Buddhism, guiding disciples through rituals, meditation practices, and doctrinal study to advance on the path to enlightenment. Their responsibilities include conducting religious ceremonies, offering personal spiritual advice, and preserving sacred teachings and texts. Unlike Murshids, who primarily provide direct guidance in Sufi mysticism, Lamas often hold institutional authority in monastic settings and emphasize the transmission of Vajrayana Buddhist teachings.
Roles and Responsibilities of Murshids
Murshids serve as spiritual guides in Sufism, responsible for leading disciples along the path of self-realization and divine connection through personalized teachings and practices. Their roles include nurturing ethical conduct, facilitating spiritual transmission (Tariqa), and providing mentorship tailored to each disciple's spiritual needs. Unlike Lamas, who often function as institutional monks and ritual leaders in Tibetan Buddhism, Murshids emphasize direct experiential knowledge and inner transformation.
Spiritual Training and Lineage in Both Traditions
Lamas and Murshids both serve as spiritual guides, but Lamas are specifically rooted in Tibetan Buddhism where they provide teachings based on a well-documented lineage tracing back to the Buddha through successive incarnations or recognized masters. Murshids function within Sufi Islam, offering personalized spiritual training through a tariqa (spiritual path) that emphasizes direct transmission of knowledge from master to disciple, often preserving a chain or silsila linking back to the Prophet Muhammad. The spiritual training under both traditions involves disciplined practices, meditation or dhikr, and ethical guidance aimed at spiritual enlightenment and inner transformation.
Methods of Teaching: Lama and Murshid Approaches
Lama teaching methods emphasize ritualistic practices, meditation techniques, and oral transmission of esoteric knowledge rooted in Tibetan Buddhism. Murshid approaches prioritize personalized guidance, spiritual mentorship, and direct experiential learning within Sufi traditions. Both rely on a deep teacher-student relationship but differ in pedagogical focus and cultural contexts.
Rituals and Practices: Comparisons and Contrasts
Lamas in Tibetan Buddhism perform intricate rituals involving mandalas, mantra recitations, and elaborate ceremonies aimed at spiritual enlightenment and guiding disciples through tantric practices. Murshids in Sufism emphasize devotional practices such as dhikr (remembrance of God), prayer, and spiritual guidance within a tariqa, focusing on the purification of the heart and the experiential realization of divine love. While both serve as spiritual teachers, lamas engage in ritualistic, symbolic ceremonies linked to monastic traditions, whereas murshids prioritize intimate, often informal practices of spiritual mentorship and inner transformation.
Influence on Followers and Spiritual Communities
A Lama holds a pivotal role in Tibetan Buddhism by offering direct spiritual guidance and rituals that shape the religious experiences of followers, fostering a deep communal identity through teachings and meditation practices. A Murshid in Sufism serves as a spiritual master who leads disciples on the path to divine truth, emphasizing personal transformation and bonding through zikr and mystical insight. Both figures significantly influence their spiritual communities by cultivating discipline, ethical conduct, and a shared aspirational vision, promoting a cohesive sense of belonging and spiritual growth among adherents.
Contemporary Relevance: Lama and Murshid Today
Lamas and Murshids today play essential roles in guiding spiritual growth within Tibetan Buddhism and Sufism, respectively, adapting ancient teachings to modern contexts. Contemporary Lamas integrate traditional Buddhist practices with psychological insights to address mental health and personal development, while Murshids offer spiritual mentorship emphasizing inner peace and ethical living amidst global challenges. Both figures remain vital sources of wisdom, fostering community cohesion and individual transformation in increasingly secular societies.
Lama Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com