Mindfulness meditation enhances mental clarity by training your mind to stay present and focused, reducing stress and promoting emotional balance. Practicing regularly can improve concentration, increase self-awareness, and boost overall well-being. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical techniques and benefits that can transform your daily routine.
Table of Comparison
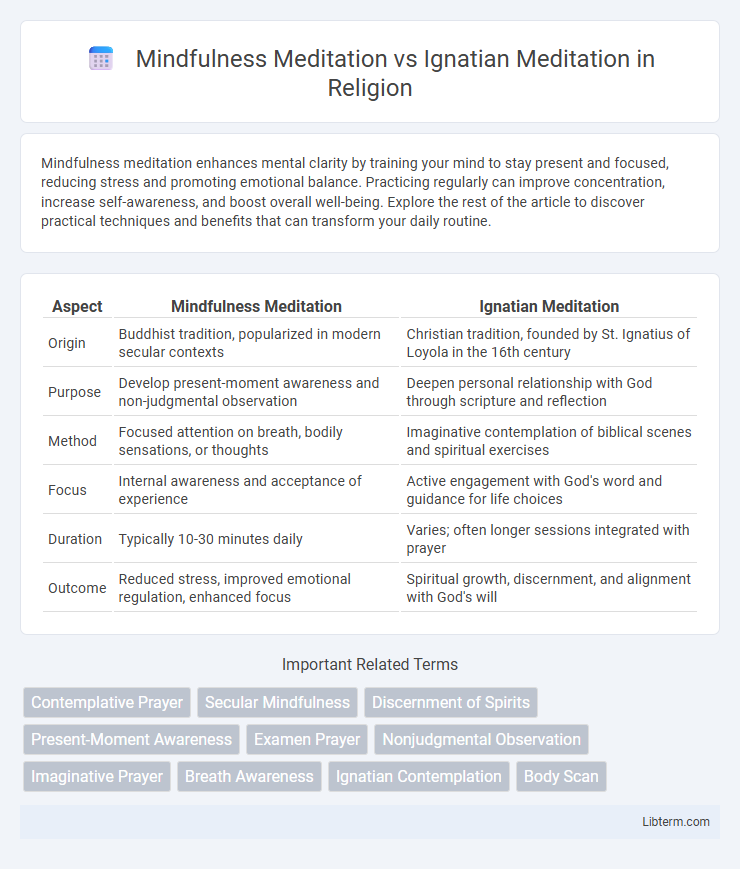
| Aspect | Mindfulness Meditation | Ignatian Meditation |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Buddhist tradition, popularized in modern secular contexts | Christian tradition, founded by St. Ignatius of Loyola in the 16th century |
| Purpose | Develop present-moment awareness and non-judgmental observation | Deepen personal relationship with God through scripture and reflection |
| Method | Focused attention on breath, bodily sensations, or thoughts | Imaginative contemplation of biblical scenes and spiritual exercises |
| Focus | Internal awareness and acceptance of experience | Active engagement with God's word and guidance for life choices |
| Duration | Typically 10-30 minutes daily | Varies; often longer sessions integrated with prayer |
| Outcome | Reduced stress, improved emotional regulation, enhanced focus | Spiritual growth, discernment, and alignment with God's will |
Introduction to Mindfulness and Ignatian Meditation
Mindfulness meditation centers on cultivating present-moment awareness through focused breathing and sensory observation, promoting mental clarity and emotional balance. Ignatian meditation, rooted in the Spiritual Exercises of St. Ignatius Loyola, involves imaginative contemplation of biblical scenes to deepen spiritual connection and discernment. Both practices enhance self-awareness but differ in approach: mindfulness emphasizes non-judgmental presence, while Ignatian meditation integrates active reflection and spiritual dialogue.
Historical Origins and Foundations
Mindfulness meditation originates from ancient Buddhist practices dating back over 2,500 years, emphasizing present-moment awareness and non-judgmental observation. Ignatian meditation, rooted in the Spiritual Exercises of St. Ignatius of Loyola in the 16th century, focuses on guided reflection and imaginative engagement with biblical scenes to deepen spiritual connection. Both traditions offer distinct historical foundations where mindfulness centers on personal awareness while Ignatian meditation integrates scriptural contemplation.
Core Principles of Mindfulness Meditation
Mindfulness meditation centers on cultivating present-moment awareness, non-judgmental observation, and acceptance of thoughts and feelings to enhance mental clarity and reduce stress. Core principles include focused breathing, sensory awareness, and open monitoring that foster emotional regulation and cognitive resilience. This practice contrasts with Ignatian meditation, which emphasizes imaginative contemplation and reflective prayer rooted in Christian spirituality.
Core Principles of Ignatian Meditation
Ignatian Meditation centers on the imaginative contemplation of biblical scenes, encouraging deep engagement with Scripture through sensory and emotional involvement, which distinguishes it from the passive awareness emphasized in mindfulness meditation. Its core principles include the use of the "composition of place" to vividly visualize Gospel events, the application of the "examen" for self-reflection on one's spiritual life, and the pursuit of discernment to align personal will with God's purpose. These elements foster an active, prayerful dialogue with Christ, contrasting with mindfulness meditation's secular focus on present-moment awareness and nonjudgmental observation.
Meditation Techniques: Practices and Approaches
Mindfulness meditation emphasizes non-judgmental awareness of the present moment through focused breathing and sensory observation, cultivating deep mental clarity and emotional regulation. Ignatian meditation adopts a guided imaginative approach, encouraging practitioners to engage with scripture or spiritual narratives by visualizing scenes and reflecting on personal responses to foster a relational connection with the divine. These distinct techniques highlight mindfulness as a secular self-awareness practice, whereas Ignatian meditation integrates contemplative dialogue rooted in Christian spirituality.
Purpose and Spiritual Goals
Mindfulness meditation centers on cultivating present-moment awareness and nonjudgmental observation to reduce stress and enhance mental clarity, serving primarily secular well-being and personal insight. Ignatian meditation, rooted in the Spiritual Exercises of St. Ignatius of Loyola, focuses on engaging the imagination to deepen a personal relationship with God and discern spiritual truths, aiming at moral transformation and alignment with divine will. The spiritual goal of mindfulness emphasizes inner peace and cognitive balance, whereas Ignatian meditation seeks active spiritual growth and guided discernment within a Christian framework.
Benefits and Outcomes for Practitioners
Mindfulness meditation enhances present-moment awareness, reducing stress and improving emotional regulation through focused breathing and sensory observation. Ignatian meditation engages reflective prayer and imaginative contemplation of scripture, fostering spiritual growth, moral insight, and a deeper personal relationship with God. Practitioners of mindfulness often report increased cognitive clarity and reduced anxiety, while Ignatian meditators experience heightened spiritual discernment and ethical decision-making.
Common Challenges and Misconceptions
Mindfulness meditation often faces challenges such as difficulty maintaining focus and misconceptions equating it solely with relaxation or stress reduction, whereas Ignatian meditation encounters struggles in understanding its narrative prayer structure and the misconception that it requires extensive theological knowledge. Both practices demand consistent discipline and an openness to experiential learning, yet many practitioners mistakenly expect immediate results or a purely passive experience. Recognizing these common challenges and clarifying misconceptions can enhance the effectiveness and accessibility of both meditation forms.
Choosing Between Mindfulness and Ignatian Meditation
Choosing between mindfulness meditation and Ignatian meditation depends on individual spiritual goals and preferences. Mindfulness meditation emphasizes present-moment awareness and stress reduction through non-judgmental observation, while Ignatian meditation involves reflective prayer rooted in Christian spirituality, focusing on biblical narratives and personal relationship with God. Evaluating whether one seeks secular mental clarity or faith-based contemplative practice guides the decision towards mindfulness or Ignatian meditation respectively.
Integrating Both Practices for Holistic Wellbeing
Integrating Mindfulness Meditation and Ignatian Meditation enhances holistic wellbeing by combining present-moment awareness with reflective spiritual discernment. Mindfulness Meditation cultivates nonjudgmental attention to thoughts and sensations, improving mental clarity and emotional balance, while Ignatian Meditation engages imagination and contemplation on scripture or life experiences to foster deeper spiritual insight and purposeful action. This integrative approach promotes a balanced state of mental calm and spiritual growth, supporting overall health and inner harmony.
Mindfulness Meditation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com