Ijma represents the consensus of Islamic scholars on religious matters, serving as a vital source of Islamic jurisprudence alongside the Quran and Sunnah. It helps ensure consistency in interpretations and legal rulings across the Muslim community, reinforcing unity and preserving the faith's principles. Explore the full article to understand how Ijma influences your spiritual and legal understanding in Islam.
Table of Comparison
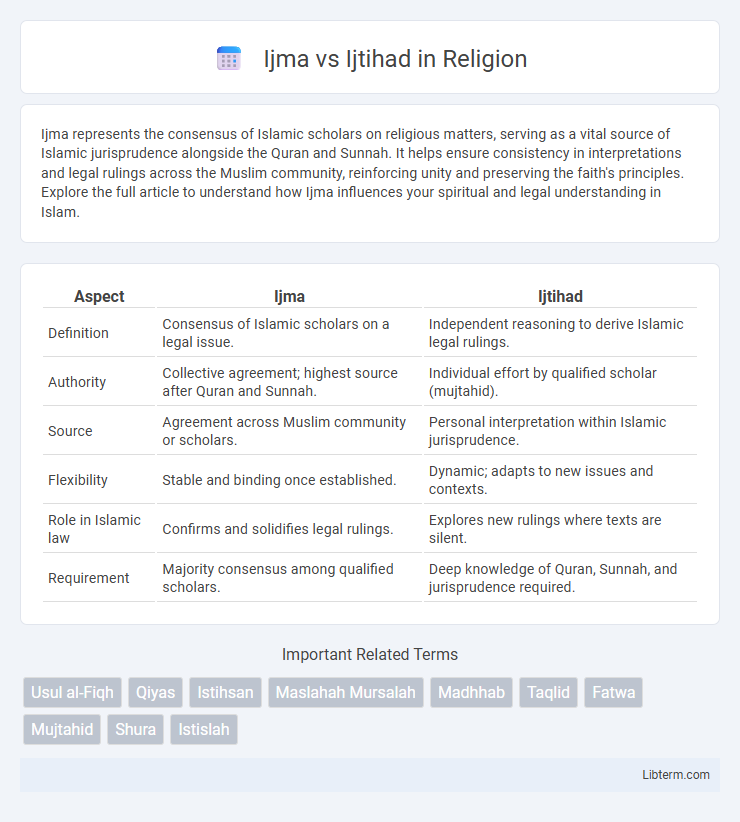
| Aspect | Ijma | Ijtihad |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consensus of Islamic scholars on a legal issue. | Independent reasoning to derive Islamic legal rulings. |
| Authority | Collective agreement; highest source after Quran and Sunnah. | Individual effort by qualified scholar (mujtahid). |
| Source | Agreement across Muslim community or scholars. | Personal interpretation within Islamic jurisprudence. |
| Flexibility | Stable and binding once established. | Dynamic; adapts to new issues and contexts. |
| Role in Islamic law | Confirms and solidifies legal rulings. | Explores new rulings where texts are silent. |
| Requirement | Majority consensus among qualified scholars. | Deep knowledge of Quran, Sunnah, and jurisprudence required. |
Understanding Ijma: Definition and Importance
Ijma refers to the consensus of Islamic scholars on a legal or religious issue, serving as a crucial source of Islamic jurisprudence after the Quran and Sunnah. It embodies collective agreement, ensuring continuity and unity within Islamic law, thus preserving the integrity of Sharia through generations. The importance of Ijma lies in its role in addressing new or complex issues by providing authoritative guidance grounded in scholarly agreement.
What is Ijtihad? An Overview
Ijtihad is an Islamic legal term referring to independent reasoning or the thorough exertion of a jurist's intellectual effort to deduce legal rulings from the Quran and Sunnah when clear texts are absent. It serves as a dynamic source of Islamic law, enabling scholars to address new issues and adapt jurisprudence to changing circumstances. Unlike Ijma, which represents consensus among scholars, Ijtihad emphasizes individual interpretation and analytical reasoning in Islamic jurisprudence.
Historical Origins of Ijma and Ijtihad
Ijma, rooted in the early Islamic community, originated as a collective consensus among the Prophet Muhammad's companions to address new legal and theological issues, establishing a foundation for unified interpretation of Sharia. Ijtihad emerged as an independent legal reasoning process, empowering qualified jurists to derive rulings through personal effort and analogy (qiyas) when explicit Quranic or Hadith texts were absent. Both concepts evolved during the classical Islamic period, shaping the dynamic interplay between communal agreement and individual jurisprudential interpretation in Islamic law.
Key Differences between Ijma and Ijtihad
Ijma refers to the unanimous consensus of Islamic scholars on a particular legal issue, serving as a collective agreement that solidifies religious rulings and ensures community-wide acceptance. Ijtihad, on the other hand, is the individual or scholarly effort to interpret and apply Islamic principles to new or complex situations through independent reasoning. The key difference lies in Ijma's basis on communal consensus versus Ijtihad's reliance on personal scholarly judgment to derive laws in the absence of clear scriptural guidance.
The Role of Ijma in Islamic Jurisprudence
Ijma, the consensus of Islamic scholars, serves as a critical source of law in Islamic jurisprudence, ensuring collective agreement on legal rulings when explicit Quranic or Hadith guidance is absent. It reinforces the unity and stability of Shariah by validating norms accepted by the Muslim community across generations. The authority of Ijma bridges gaps in legislation, allowing dynamic adaptation while preserving core Islamic principles.
The Function of Ijtihad in Islamic Law
Ijtihad serves as a critical mechanism in Islamic law, enabling qualified scholars to interpret and apply Sharia principles to novel issues not explicitly addressed in foundational texts. This process ensures the adaptability and relevance of Islamic jurisprudence by allowing reasoned judgment and contextual analysis in legal rulings. Unlike Ijma, which represents unanimous consensus among scholars, Ijtihad provides dynamic legal insight through independent reasoning, thus playing a pivotal role in the evolution and practical application of Islamic law.
Notable Scholars and Contributions to Ijma and Ijtihad
Notable scholars such as Imam Abu Hanifa and Imam Malik significantly advanced Ijtihad through rigorous interpretation of Islamic law, emphasizing personal reasoning in the absence of explicit texts. In contrast, scholars like Imam Al-Shafi'i systematized Ijma by consolidating consensus among Muslim jurists as a binding source of Sharia. Their contributions helped delineate Ijtihad as dynamic legal reasoning while establishing Ijma as collective scholarly agreement, both crucial for Islamic jurisprudence development.
Contemporary Relevance of Ijma and Ijtihad
Ijma, the consensus of Islamic scholars, serves as a foundational tool for ensuring unity and continuity in religious rulings, while Ijtihad, the independent reasoning by qualified scholars, allows for dynamic interpretation of Islamic law in response to contemporary issues. In modern contexts, Ijtihad plays a crucial role in addressing novel challenges such as bioethics, digital finance, and human rights, enabling Islam to remain relevant and adaptable across diverse societies. Meanwhile, Ijma provides a collective authority that helps stabilize and legitimize evolving interpretations, balancing innovation with tradition in Islamic jurisprudence.
Modern Debates: Reinterpreting Ijma and Ijtihad
Modern debates on Ijma emphasize its dynamic reinterpretation to address contemporary Islamic law challenges, highlighting the need for collective scholarly consensus that adapts to global contexts. Ijtihad is increasingly viewed as a vital tool for independent reasoning that facilitates innovative solutions within Sharia, allowing adaptability in issues like bioethics and finance. Scholars advocate integrating both Ijma and Ijtihad to balance tradition with modernity, ensuring Islamic jurisprudence remains relevant amid evolving societal norms.
Future of Islamic Legal Thought: Balancing Ijma and Ijtihad
Future Islamic legal thought will increasingly balance Ijma, the consensus of scholars, with Ijtihad, independent reasoning, to address contemporary challenges. This dynamic equilibrium allows adaptation to modern issues while maintaining continuity with classical jurisprudence. Emphasizing both collective agreement and individual interpretative efforts ensures resilience and relevance in evolving socio-legal contexts.
Ijma Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com