Dualism divides reality into two fundamental substances: mind and matter, emphasizing their distinct nature and interaction. This philosophical concept has profound implications for understanding consciousness, identity, and the nature of existence. Explore the rest of this article to discover how dualism shapes modern thought and your perception of reality.
Table of Comparison
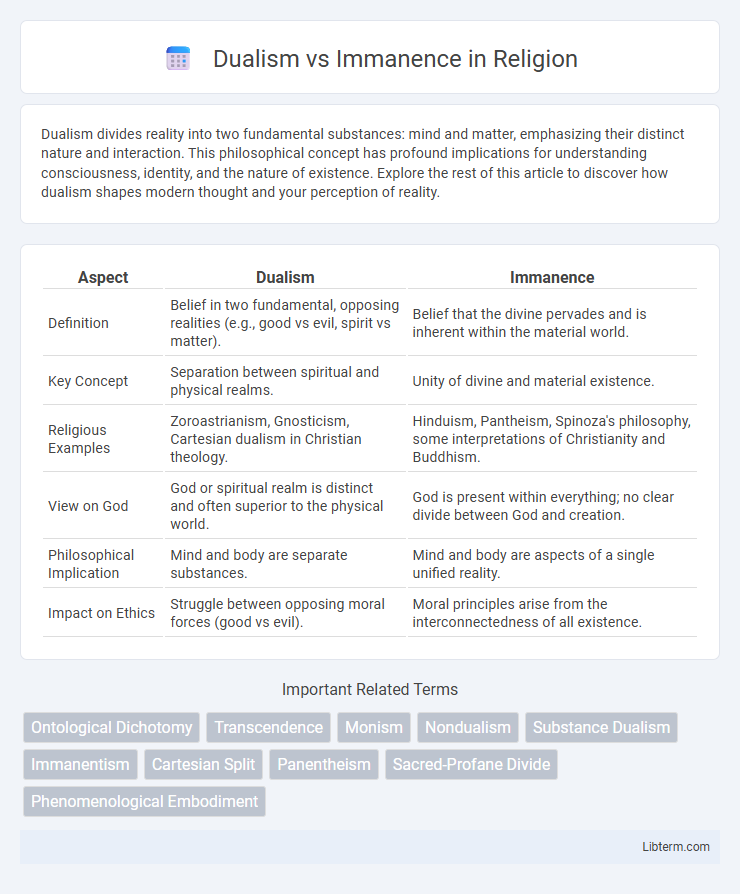
| Aspect | Dualism | Immanence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief in two fundamental, opposing realities (e.g., good vs evil, spirit vs matter). | Belief that the divine pervades and is inherent within the material world. |
| Key Concept | Separation between spiritual and physical realms. | Unity of divine and material existence. |
| Religious Examples | Zoroastrianism, Gnosticism, Cartesian dualism in Christian theology. | Hinduism, Pantheism, Spinoza's philosophy, some interpretations of Christianity and Buddhism. |
| View on God | God or spiritual realm is distinct and often superior to the physical world. | God is present within everything; no clear divide between God and creation. |
| Philosophical Implication | Mind and body are separate substances. | Mind and body are aspects of a single unified reality. |
| Impact on Ethics | Struggle between opposing moral forces (good vs evil). | Moral principles arise from the interconnectedness of all existence. |
Understanding Dualism: Core Principles
Dualism posits the existence of two fundamentally distinct substances or realities, often identified as mind and body, or spirit and matter, which interact yet remain separate. This philosophical framework emphasizes the independent and irreducible nature of mental states in contrast to physical entities, influencing debates in metaphysics, philosophy of mind, and theology. Understanding dualism's core principles involves exploring the mind-body problem, the nature of consciousness, and the implications of non-material existence on identity and causality.
Defining Immanence: A Philosophical Overview
Immanence refers to the inherent presence of the divine or the fundamental essence within the material world, contrasting with dualism's strict separation of mind and body or spirit and matter. Philosophers such as Spinoza and Deleuze emphasize immanence as a continuous, indwelling force that negates transcendence, situating meaning and existence within the natural order itself. This concept challenges traditional dualistic paradigms by positing that reality and consciousness are unified through an internal, self-sustaining process rather than an external, separate realm.
Historical Roots of Dualism
The historical roots of dualism trace back to ancient Greek philosophy, particularly in the works of Plato, who posited a fundamental distinction between the material body and the immaterial soul. This ontological separation was further developed by Rene Descartes in the 17th century, emphasizing mind-body dualism as two distinct substances. Dualism contrasts sharply with immanence, which rejects this divide and asserts that the divine or consciousness is inherently present within the material world itself.
The Evolution of Immanent Thought
The evolution of immanent thought traces a philosophical shift from Dualism's division of mind and body towards the emphasis on internal, self-contained reality within material existence. Immanence posits that consciousness, spirit, and value arise intrinsically from the physical world rather than an external, transcendent realm. This perspective underlies modern metaphysics, influencing existentialism, process philosophy, and contemporary debates on the mind-body problem.
Dualism in Religion and Spirituality
Dualism in religion and spirituality refers to the belief in two fundamental, opposing forces or realities, often characterized as good versus evil or mind versus body. This concept is prominent in traditions like Zoroastrianism, which posits a cosmic battle between Ahura Mazda (truth) and Angra Mainyu (destruction), as well as in certain interpretations of Christianity that distinguish between the material and spiritual realms. Dualism shapes religious narratives and ethical frameworks by emphasizing the contrast and interaction between spiritual divinity and earthly existence.
Immanence in Modern Philosophy
Immanence in modern philosophy emphasizes the inherent presence of the divine or ultimate reality within the material world, rejecting the separation posited by dualism between mind and body or spirit and matter. Philosophers like Spinoza and Deleuze argue that all existence is interconnected through a single substance or plane of reality, where consciousness and nature are not distinct but expressions of the same immanent force. This perspective challenges traditional metaphysical frameworks by prioritizing experience, embodiment, and the continuous unfolding of reality without transcendent intervention.
Key Differences: Dualism vs Immanence
Dualism asserts a fundamental separation between mind and body, emphasizing two distinct substances or realms of existence, typically the physical and the non-physical. Immanence denies any transcendent division, proposing that the divine or ultimate reality is fully present and active within the material world. The key difference lies in Dualism's emphasis on separation versus Immanence's focus on inherent unity and presence within the same plane of existence.
Contemporary Debates and Perspectives
Contemporary debates on Dualism versus Immanence center on ontological distinctions between mind and matter, with dualists asserting the existence of two fundamentally different substances, while proponents of immanence emphasize the inherent presence of consciousness within physical reality. Recent philosophical perspectives challenge Cartesian dualism by integrating neuroscientific findings that support immanent frameworks like physicalism and panpsychism, which propose that mental states arise from or are intrinsic to material processes. These discourses critically impact fields such as cognitive science and metaphysics, where interpretations of consciousness shape ethical and existential theories.
Dualism and Immanence in Science
Dualism in science posits the existence of two fundamentally distinct substances or realities, such as mind and matter, influencing fields like neuroscience and quantum mechanics by exploring consciousness separate from physical processes. Immanence emphasizes the presence of meaning, mind, or spirit inherent within the physical universe, promoting holistic approaches in ecological studies and systems biology where life and consciousness emerge from material interactions. Debates between dualism and immanence shape scientific theories on the nature of consciousness, causality, and the relationship between mind and body.
Implications for Ethics and Society
Dualism, which posits a separation between mind and body or spirit and matter, often leads to ethical frameworks emphasizing transcendent values and moral absolutism, shaping societies that prioritize spiritual or ideological purity over material conditions. Immanence, emphasizing the inherent interconnectedness and material basis of existence, fosters ethical systems grounded in relationality, social equity, and environmental stewardship, encouraging communities to focus on collective well-being and practical responsibility. These philosophical perspectives significantly influence legal structures, educational priorities, and social policies by determining whether morality is viewed as externally imposed or intrinsically developed within human experience.
Dualism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com