Henotheism embraces the worship of one primary deity while acknowledging the existence of other gods, distinguishing it from strict monotheism. This belief system offers a flexible approach, allowing Your spiritual focus to center on a single god without denying other divine beings. Discover deeper insights into henotheism and its cultural significance by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
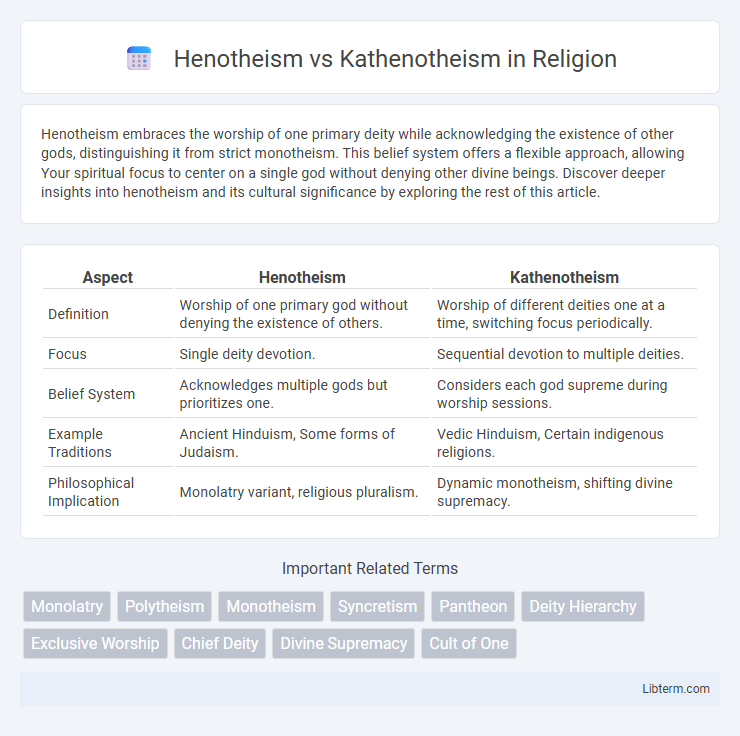
| Aspect | Henotheism | Kathenotheism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Worship of one primary god without denying the existence of others. | Worship of different deities one at a time, switching focus periodically. |
| Focus | Single deity devotion. | Sequential devotion to multiple deities. |
| Belief System | Acknowledges multiple gods but prioritizes one. | Considers each god supreme during worship sessions. |
| Example Traditions | Ancient Hinduism, Some forms of Judaism. | Vedic Hinduism, Certain indigenous religions. |
| Philosophical Implication | Monolatry variant, religious pluralism. | Dynamic monotheism, shifting divine supremacy. |
Understanding Henotheism: Definition and Origins
Henotheism is the belief in and worship of one primary deity while accepting the existence or possible worship of other gods, commonly observed in early Vedic religion and some ancient Near Eastern cultures. Originating in religious traditions where multiple gods were recognized, henotheism maintains exclusive devotion to a singular god without denying other deities' existence or power. This concept contrasts with polytheism by emphasizing loyalty to one god at a time and serves as a foundational step in the development of monotheistic beliefs.
Exploring Kathenotheism: Meaning and Historical Context
Kathenotheism refers to the worship of one god at a time while acknowledging the existence of multiple deities, often seen in ancient Hindu and early Vedic traditions where each god is revered as supreme in turn. This concept contrasts with henotheism, which entails devotion to a single deity without denying others but does not necessarily involve sequential worship. Historically, kathenotheism reflects a dynamic theological approach allowing devotees to honor multiple gods individually, highlighting a complex polytheistic belief system.
Key Similarities Between Henotheism and Kathenotheism
Henotheism and Kathenotheism both involve the worship of a single god while acknowledging the existence of others, reflecting a monolatristic framework rather than strict monotheism. Both belief systems emphasize devotion to one deity at a time, though Kathenotheism often shifts this devotion to different gods sequentially. This approach allows followers to recognize multiple gods' legitimacy without polytheistic worship of all simultaneously.
Fundamental Differences Explained
Henotheism centers on the devotion to one god while acknowledging the existence of other deities in a broader pantheon, without denying their validity. Kathenotheism, on the other hand, involves worshiping one god at a time as supreme, with the worshipper shifting focus to different gods on different occasions. The fundamental difference lies in henotheism's persistent allegiance to a single deity alongside others and kathenotheism's sequential elevation of multiple gods to the highest status.
Philosophical Implications of Both Concepts
Henotheism posits the worship of one primary deity while acknowledging the existence of others, emphasizing a hierarchical yet exclusive devotion that influences philosophical discussions on religious pluralism and the nature of divine supremacy. Kathenotheism involves the worship of different deities one at a time, reflecting a dynamic approach to divinity that challenges fixed theological boundaries and encourages a fluid understanding of sacred authority. Both concepts invite deep philosophical inquiry into the relationship between monotheism and polytheism, the conception of divine unity, and the evolution of religious consciousness.
Henotheism in Ancient Religions
Henotheism, prevalent in many ancient religions such as Vedic Hinduism and early Semitic traditions, involves the worship of one primary deity without denying the existence of others. This religious practice emphasizes devotion to a single god while acknowledging a pantheon of divine beings, distinguishing it from kathenotheism, where worship shifts sequentially from one god to another. Ancient henotheistic beliefs shaped theological frameworks by integrating monotheistic tendencies with polytheistic worship, influencing religious development across Mesopotamian, Egyptian, and early Indian cultures.
Kathenotheism in Vedic Traditions
Kathenotheism in Vedic traditions involves the worship of a single deity at a time while acknowledging the existence of multiple gods, contrasting with henotheism which prioritizes one god without denying others. Vedic hymns frequently illustrate kathenotheistic practices by praising individual deities like Agni, Indra, or Varuna in succession as supreme. This fluid devotion reflects the dynamic and inclusive nature of Vedic spirituality, emphasizing the singular greatness of each god in different contexts.
Modern Interpretations and Applications
Henotheism in modern interpretations emphasizes the worship of one primary deity while acknowledging the existence of others, often seen in contemporary spiritual practices that blend traditional belief systems. Kathenotheism, contrastingly, involves the worship of one god at a time, with the focus shifting among multiple deities, a concept reflected in certain modern polytheistic and eclectic religious movements. Both frameworks influence current theological discussions by highlighting the fluidity and diversity of divine reverence across various cultural contexts.
Criticisms and Controversies
Henotheism faces criticism for its perceived ambiguity in acknowledging multiple deities while privileging one, often viewed as a compromise between monotheism and polytheism that lacks theological consistency. Kathenotheism is controversial for its sequential worship of different deities as supreme, raising debates about the coherence of exclusive divine authority and the practicality of shifting devotional focus. Both concepts challenge traditional religious frameworks, provoking scholarly debate on their implications for understanding divine hierarchy and exclusivity in ancient and contemporary faith systems.
Conclusion: Comparing Henotheism and Kathenotheism
Henotheism involves devotion to one primary deity while acknowledging the existence of others, whereas kathenotheism entails worshiping different gods one at a time as supreme. Both concepts highlight the complexity of religious belief systems that do not adhere strictly to monotheism or polytheism. Understanding these distinctions clarifies how ancient and modern faiths navigate divine hierarchy and worship practices.
Henotheism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com