Iman is a Nigerian-American supermodel, entrepreneur, and philanthropist known for revolutionizing the fashion industry with her striking beauty and business acumen. Her work has paved the way for greater diversity and representation in modeling, while her cosmetics line empowers individuals to embrace their unique skin tones. Discover how Iman's legacy continues to inspire and shape the world of fashion by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
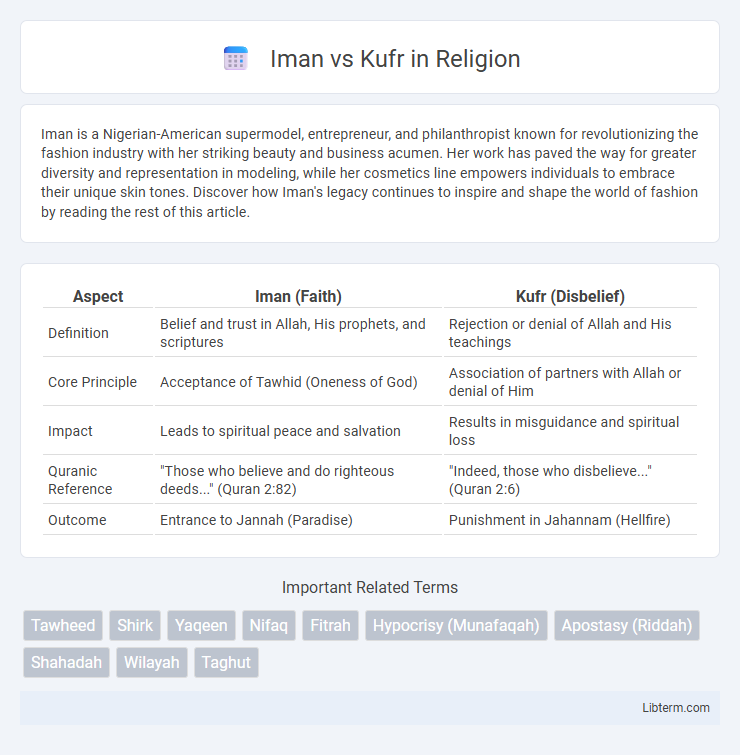
| Aspect | Iman (Faith) | Kufr (Disbelief) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief and trust in Allah, His prophets, and scriptures | Rejection or denial of Allah and His teachings |
| Core Principle | Acceptance of Tawhid (Oneness of God) | Association of partners with Allah or denial of Him |
| Impact | Leads to spiritual peace and salvation | Results in misguidance and spiritual loss |
| Quranic Reference | "Those who believe and do righteous deeds..." (Quran 2:82) | "Indeed, those who disbelieve..." (Quran 2:6) |
| Outcome | Entrance to Jannah (Paradise) | Punishment in Jahannam (Hellfire) |
Understanding the Concepts: Iman and Kufr
Iman and Kufr represent fundamental opposites in Islamic theology, where Iman denotes faith or belief in Allah, His prophets, and the core tenets of Islam, while Kufr signifies disbelief or rejection of these principles. Iman encompasses conviction in the unseen, acceptance of divine guidance, and submission to God's will, forming the foundation of a Muslim's spiritual and moral framework. Kufr, on the other hand, involves denial or opposition to Islamic teachings, which can manifest in various forms such as atheism, idolatry, or hypocrisy, ultimately affecting one's relationship with Allah and afterlife destiny.
The Core Beliefs of Iman in Islam
The core beliefs of Iman in Islam include the conviction in the oneness of Allah (Tawhid), belief in the angels, the revealed books including the Quran, the prophets with Muhammad as the final messenger, the Day of Judgment, and Qadar (divine predestination). Iman signifies unwavering faith and acceptance of these principles, fundamentally opposing Kufr, which represents disbelief or rejection of these tenets. Understanding Iman is essential to recognizing the spiritual and theological foundation that distinguishes a Muslim from a non-believer in Islamic teachings.
Characteristics and Types of Kufr
Kufr, in Islamic theology, refers to the rejection or denial of faith (Iman) and manifests in various forms such as Kufr al-Takdhib (denial), Kufr al-Istibdal (replacement of divine laws), and Kufr al-Kibr (pride leading to disbelief). These types of Kufr directly oppose the pillars of Iman, which encompass belief in Allah, His angels, scriptures, prophets, the Day of Judgment, and divine decree. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for recognizing how disbelief disrupts the spiritual and doctrinal framework established by Iman in a Muslim's faith journey.
Signs and Fruits of True Iman
True Iman, or faith, manifests through sincere belief in the oneness of Allah, His prophets, angels, and the Day of Judgment, accompanied by heartfelt submission and righteous deeds. Its signs include unwavering trust in Allah's wisdom, consistent performance of obligatory prayers, and sincere repentance from sins, reflecting an inner transformation. Fruits of genuine Iman appear as increased patience, humility, generosity, and a commitment to justice, highlighting a profound spiritual and ethical renewal.
The Consequences of Kufr in the Hereafter
Kufr, or disbelief in the core tenets of Islam, leads to severe consequences in the Hereafter, including eternal punishment and separation from Allah's mercy. The Qur'an emphasizes that those who reject faith will face the Fire of Hell, where suffering is both physical and spiritual, reflecting their denial of divine guidance. Contrastingly, iman (faith) grants forgiveness, entry into Paradise, and closeness to Allah, highlighting the stark divergence in posthumous outcomes based on belief.
Pathways to Strengthening Iman
Consistent daily prayers, sincere repentance, and regular Quranic recitation serve as primary pathways to strengthening Iman, fostering a deeper connection with Allah. Engaging in Dhikr (remembrance of Allah) and seeking knowledge from authentic Islamic sources enriches faith while diminishing the influence of Kufr. Surrounding oneself with a supportive community of believers further reinforces spiritual resilience and commitment to monotheism.
The Dangers and Manifestations of Kufr
Kufr, defined as disbelief or rejection of faith, manifests through behaviors such as denial of God's existence, rejection of religious obligations, and propagation of atheistic or polytheistic ideologies. The dangers of kufr include spiritual loss, alienation from the Muslim community, and exposure to moral corruption and societal decay. Persisting in kufr leads to eternal consequences in the afterlife, emphasizing the critical need for iman (faith) as protection and salvation.
Distinguishing Between Weak Iman and Kufr
Distinguishing between weak iman (faith) and kufr (disbelief) involves understanding that weak iman reflects fluctuations in spiritual strength without outright rejection of core Islamic beliefs, whereas kufr signifies denial or apostasy from fundamental tenets such as belief in Allah, His prophets, or the afterlife. Scholars emphasize signs like persistent doubt, neglect of obligatory acts, or loss of conviction as indicators of weak iman, which can be revived through sincere repentance and increased adherence to faith practices. Clear kufr manifests in explicit denial, blasphemy, or atheism, necessitating formal separation from Islam according to classical jurisprudence and theologians.
Quranic Verses on Iman and Kufr
The Quran emphasizes the contrast between Iman (faith) and Kufr (disbelief) in numerous verses, highlighting their spiritual and moral consequences. Surah Al-Baqarah (2:256) states, "There is no compulsion in religion; truly the right way has become clearly distinct from error," underscoring the importance of sincere Iman. Surah Al-Kafirun (109:1-6) explicitly rejects Kufr while affirming monotheistic belief, illustrating the Quranic stance on faith and rejection of disbelief.
Preserving Iman in a Modern World
Preserving Iman in a modern world requires steadfast commitment to core Islamic beliefs amid pervasive secular influences and moral relativism. Strengthening spiritual practices such as regular prayer, Quranic study, and community engagement enhances resilience against doubts and distractions that challenge faith. Embracing technology for Islamic education and fostering supportive networks ensures that believers maintain a strong connection to Iman despite societal pressures toward Kufr.
Iman Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com