Prayer serves as a powerful tool for connecting with inner peace and spiritual guidance, offering profound emotional support during challenging times. Regular practice can enhance your mental clarity and foster a deeper sense of gratitude and mindfulness. Explore the rest of this article to discover how prayer can transform your daily life and well-being.
Table of Comparison
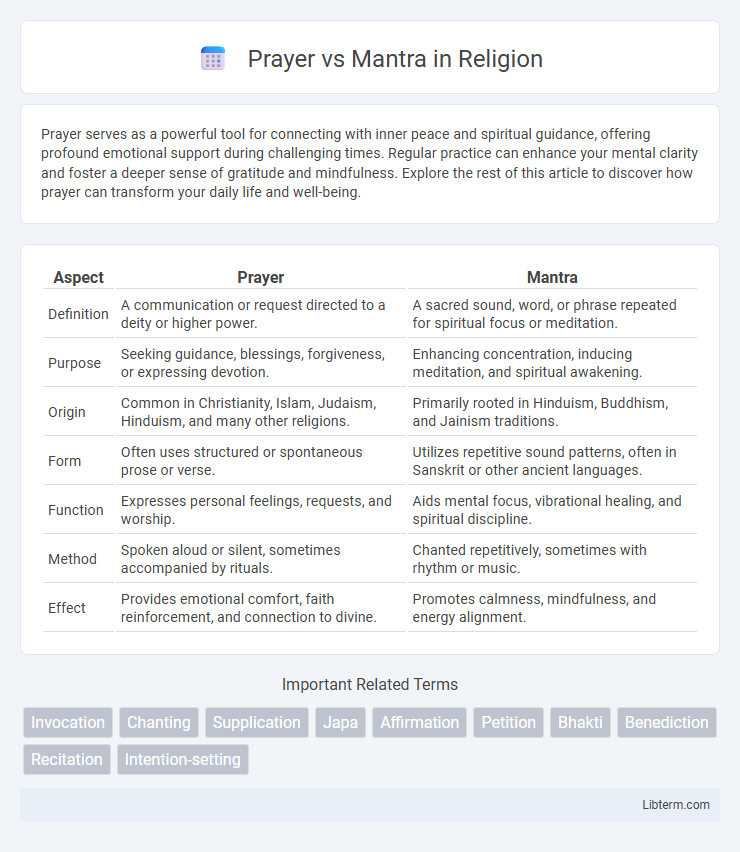
| Aspect | Prayer | Mantra |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A communication or request directed to a deity or higher power. | A sacred sound, word, or phrase repeated for spiritual focus or meditation. |
| Purpose | Seeking guidance, blessings, forgiveness, or expressing devotion. | Enhancing concentration, inducing meditation, and spiritual awakening. |
| Origin | Common in Christianity, Islam, Judaism, Hinduism, and many other religions. | Primarily rooted in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism traditions. |
| Form | Often uses structured or spontaneous prose or verse. | Utilizes repetitive sound patterns, often in Sanskrit or other ancient languages. |
| Function | Expresses personal feelings, requests, and worship. | Aids mental focus, vibrational healing, and spiritual discipline. |
| Method | Spoken aloud or silent, sometimes accompanied by rituals. | Chanted repetitively, sometimes with rhythm or music. |
| Effect | Provides emotional comfort, faith reinforcement, and connection to divine. | Promotes calmness, mindfulness, and energy alignment. |
Understanding Prayer and Mantra
Prayer involves communicating with a divine entity using words or thoughts to express devotion, request guidance, or seek blessings, often rooted in specific religious traditions. A mantra is a sacred sound, phrase, or word repeated rhythmically during meditation or spiritual practice to focus the mind, invoke spiritual energy, or achieve a higher state of consciousness. Both prayer and mantra serve as spiritual tools but differ in structure: prayer is typically dialogic and petitionary, while mantra emphasizes repetition and sound vibrations for mental clarity and inner peace.
Historical Origins of Prayer and Mantra
Prayer originated in ancient religious traditions as a form of communication between humans and deities, evident in early Mesopotamian, Egyptian, and Vedic cultures where ritualistic prayers sought divine intervention. Mantras trace back to the Vedic period in India, serving as sacred sounds or phrases believed to possess spiritual power and used primarily in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism for meditation and ritual purposes. Both practices share roots in early spiritual expressions but diverged in form, with prayer emphasizing direct supplication and mantra focusing on vibrational resonance and repetition.
Key Differences Between Prayer and Mantra
Prayer involves direct communication with a deity or higher power, expressing requests, gratitude, or devotion, often structured around religious traditions and scriptures. Mantra consists of repetitive sounds, words, or phrases chanted to invoke spiritual energy, aid meditation, or focus the mind, independent of specific requests or direct communication. While prayer emphasizes relational dialogue and intention, mantras prioritize vibrational resonance and mental discipline.
Spiritual Significance of Prayer
Prayer serves as a profound spiritual practice that fosters a direct connection with a higher power, enabling believers to express devotion, seek guidance, and find comfort in times of distress. Unlike mantras, which primarily emphasize repetitive sound vibrations for meditation and mental focus, prayer often involves personal communication that strengthens faith and promotes spiritual growth. This dynamic interaction with the divine cultivates a sense of hope, peace, and divine presence in the lives of practitioners.
Spiritual Significance of Mantra
Mantras hold profound spiritual significance as ancient sacred sounds or phrases that facilitate deep meditation and connection with divine energies, enhancing inner peace and spiritual awakening. Unlike general prayers that often involve requests or expressions of faith, mantras are repetitive vibrations believed to transform consciousness and align the practitioner with universal truths. The continuous chanting of mantras stimulates positive energy flow, purifies the mind, and strengthens the spiritual practice by fostering a direct experience of the divine.
Methods of Practice: Prayer vs Mantra
Prayer typically involves direct communication with a deity or higher power through spoken words, petitions, or expressions of gratitude, often performed individually or in group settings. Mantra practice centers on the repetitive chanting or silent recitation of specific sounds or phrases, believed to carry spiritual energy and aid in concentration or meditation. Both methods use vocalization and mental focus but differ in intent, with prayer emphasizing dialogue and mantra prioritizing vibration and mindfulness.
Psychological Effects of Prayer and Mantra
Prayer and mantra both influence the brain's neural pathways, promoting relaxation and emotional regulation through repeated verbal or mental focus. Prayer often engages personal and relational aspects of spirituality, fostering feelings of connection, hope, and emotional support, which can reduce stress and anxiety. Mantra repetition triggers a meditative state, enhancing cognitive control and mindfulness, resulting in improved concentration and decreased symptoms of depression and PTSD.
Cultural Contexts: East Meets West
Prayer in Western contexts often involves direct communication with a deity, rooted in Abrahamic religions like Christianity and Islam, emphasizing faith, supplication, and worship. Mantras in Eastern traditions, particularly within Hinduism and Buddhism, utilize repetitive sacred sounds or phrases to focus the mind and invoke spiritual power. The cultural intersection reveals prayer as a personal dialogue, while mantra functions as a meditative tool, illustrating diverse spiritual practices shaped by historical and religious frameworks.
Scientific Studies on Prayer and Mantra
Scientific studies on prayer and mantra reveal distinct neurological and psychological effects; prayer often engages brain regions linked to emotion and empathy, while mantra repetition activates areas associated with attention and relaxation. Research published in journals like NeuroImage and the Journal of Behavioral Medicine indicates that both practices reduce stress and enhance mental well-being, but mantras exhibit stronger influence on autonomic nervous system regulation. Evidence also suggests that mantra meditation produces significant decreases in cortisol levels and promotes sustained alpha brainwave activity, supporting improved cognitive function and emotional stability.
Choosing Between Prayer and Mantra: Which Is Right for You?
Choosing between prayer and mantra depends on your spiritual goals and personal preferences. Prayer typically involves communicating with a higher power for guidance or support, fostering a relational connection and emotional release. Mantra repetition promotes focused meditation and mental clarity through rhythmic sound, ideal for enhancing concentration and inner peace.
Prayer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com