Allamah is a title given to scholars recognized for their deep knowledge and expertise in Islamic theology, philosophy, and jurisprudence. This honorific signifies a high level of scholarship and intellectual contribution, often associated with individuals who have mastered multiple disciplines within Islamic studies. Discover how the profound insights of an Allamah can enrich Your understanding of Islamic thought in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
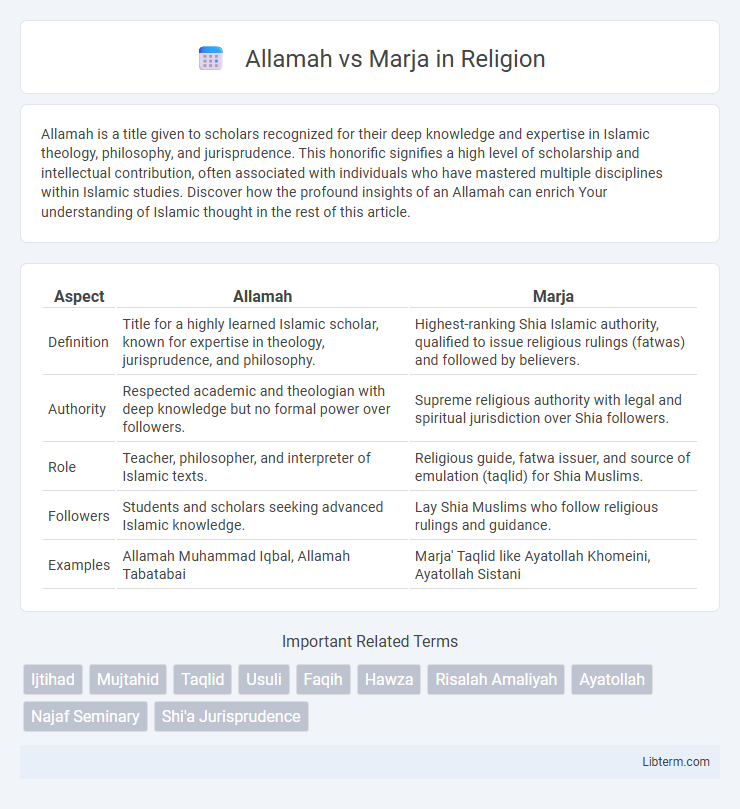
| Aspect | Allamah | Marja |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Title for a highly learned Islamic scholar, known for expertise in theology, jurisprudence, and philosophy. | Highest-ranking Shia Islamic authority, qualified to issue religious rulings (fatwas) and followed by believers. |
| Authority | Respected academic and theologian with deep knowledge but no formal power over followers. | Supreme religious authority with legal and spiritual jurisdiction over Shia followers. |
| Role | Teacher, philosopher, and interpreter of Islamic texts. | Religious guide, fatwa issuer, and source of emulation (taqlid) for Shia Muslims. |
| Followers | Students and scholars seeking advanced Islamic knowledge. | Lay Shia Muslims who follow religious rulings and guidance. |
| Examples | Allamah Muhammad Iqbal, Allamah Tabatabai | Marja' Taqlid like Ayatollah Khomeini, Ayatollah Sistani |
Introduction to Islamic Titles: Allamah and Marja
Allamah is a prestigious Islamic title awarded to scholars recognized for their vast knowledge across multiple fields of Islamic studies, including theology, jurisprudence, and philosophy, showcasing expertise and intellectual depth. Marja, short for Marja' taqlid, refers to the highest-ranking Shia authority qualified to issue religious rulings and guidance, serving as a source of emulation for followers in matters of Islamic law and practice. The distinction lies in Allamah emphasizing broad scholarly excellence, while Marja signifies a definitive religious authority with jurisdiction to interpret and legislate Shariah for the community.
Defining Allamah: Meaning and Significance
Allamah refers to a highly learned scholar in Islamic studies, recognized for profound expertise in theology, jurisprudence, philosophy, and Quranic exegesis. This title signifies exceptional intellectual accomplishment and deep scholarly contributions, often attributed to individuals with comprehensive knowledge across various Islamic sciences. Unlike Marja, whose role centers on religious authority and issuing legal rulings for Shia Muslims, an Allamah's significance lies primarily in academic mastery and theological insight.
Understanding the Role of a Marja
A Marja, or Marja' taqlid, is a high-ranking Shia religious authority who provides guidance on Islamic jurisprudence and issues fatwas for followers. Unlike Allamah, a title denoting a learned scholar with vast knowledge in Islamic sciences, a Marja holds the exclusive role of being a source of emulation for practical religious decisions. The authority of a Marja is central to Shia Islam, as believers rely on their interpretations to navigate religious obligations in daily life.
Historical Evolution of Allamah and Marja
The historical evolution of Allamah and Marja reflects distinct scholarly statuses within Islamic tradition, particularly in Shia Islam. The title Allamah, historically attributed to polymath scholars such as Allamah Tabatabai, denotes profound expertise across various Islamic sciences, philosophy, and mysticism, emerging prominently during the Islamic Golden Age. In contrast, the Marja' al-Taqlid developed as the highest religious authority governing jurisprudential rulings and legal emulation, solidifying in the 18th and 19th centuries with figures like Ayatollah Muhammad Baqir al-Sadr, marking a codified leadership role in Shia jurisprudence.
Key Differences between Allamah and Marja
Allamah is a title given to highly knowledgeable Islamic scholars recognized for their vast expertise in various fields such as theology, philosophy, and jurisprudence, whereas Marja specifically refers to a Shia Islamic authority or source of emulation who provides religious guidance and legal rulings for followers. The key difference lies in their roles: Allamah denotes a broad scholarly eminence, while Marja holds a formal religious leadership position authorized to issue fatwas and interpret Sharia law. Marjas possess the authority to be followed in practical religious matters, unlike Allamahs, whose recognition is primarily academic and intellectual.
Qualifications Required for Allamah and Marja
Allamah is a title awarded to Islamic scholars who demonstrate extensive knowledge in various religious sciences, including Quranic exegesis, Hadith, jurisprudence, and theology, typically requiring years of dedicated study and mastery of multiple disciplines. A Marja, or Marja' al-Taqlid, must possess advanced expertise in Islamic jurisprudence (Fiqh) and legal theory (Usul al-Fiqh), enabling them to issue authoritative religious rulings (fatwas) and guide followers in practical religious matters. While an Allamah is recognized for scholarly depth across a broad spectrum of Islamic knowledge, a Marja is distinguished by their juridical authority and recognized capacity to serve as the highest source of emulation within the Shia community.
Influential Figures: Prominent Allamahs vs. Maraji
Prominent Allamahs, such as Allamah Tabatabai and Allamah Majlisi, are celebrated for their profound scholarly contributions in Islamic philosophy, theology, and exegesis, shaping intellectual discourse across generations. Maraji, including figures like Ayatollah Sistani and Ayatollah Khamenei, hold significant religious authority as sources of emulation, influencing religious practice and legal rulings within Shia communities worldwide. The distinction lies in Allamahs' roles as scholars and thinkers, versus Maraji's function as living juristic authorities guiding contemporary Shia adherents.
Jurisprudential Authority: Marja’s Unique Position
A Marja holds the highest level of jurisprudential authority in Shia Islam, serving as a source of emulation for followers in deriving religious rulings and fatwas. Unlike an Allamah, who is recognized primarily for profound scholarship and expertise in Islamic knowledge, a Marja possesses the distinct qualification to issue binding legal opinions (ijtihad) that guide daily religious practice. This unique position grants the Marja an authoritative role in interpreting Sharia law, overseeing the religious obligations of their followers within the framework of Islamic jurisprudence.
Scholarly Influence: Allamah’s Contribution to Islamic Knowledge
Allamah refers to a scholar with profound expertise across various Islamic sciences, often recognized for pioneering original contributions and vast intellectual influence. Marja, or Marja' Taqlid, holds authority primarily in jurisprudence, authorizing religious rulings and guiding followers in legal and spiritual matters. Allamahs significantly shape Islamic knowledge through interdisciplinary scholarship, blending philosophy, theology, jurisprudence, and mysticism, thereby enriching the intellectual tradition beyond the legalistic focus of Maraji'.
Choosing Guidance: Why the Distinction Matters
Choosing between Allamah and Marja matters because an Allamah is a distinguished scholar known for vast knowledge in Islamic sciences, while a Marja holds the highest authority in religious jurisprudence, providing direct guidance on everyday legal and ethical matters. Followers seek a Marja for practical fatwas and spiritual leadership, ensuring adherence to Sharia in personal and communal life. Understanding this distinction empowers believers to align their religious decisions with authoritative expertise and maintain authentic Shia Islamic practice.
Allamah Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com