Tafsir is the detailed explanation and interpretation of the Quran, providing context and clarity to its verses. It helps you understand the deeper meanings, historical background, and linguistic nuances of the sacred text. Explore this article to unlock the profound insights offered by tafsir.
Table of Comparison
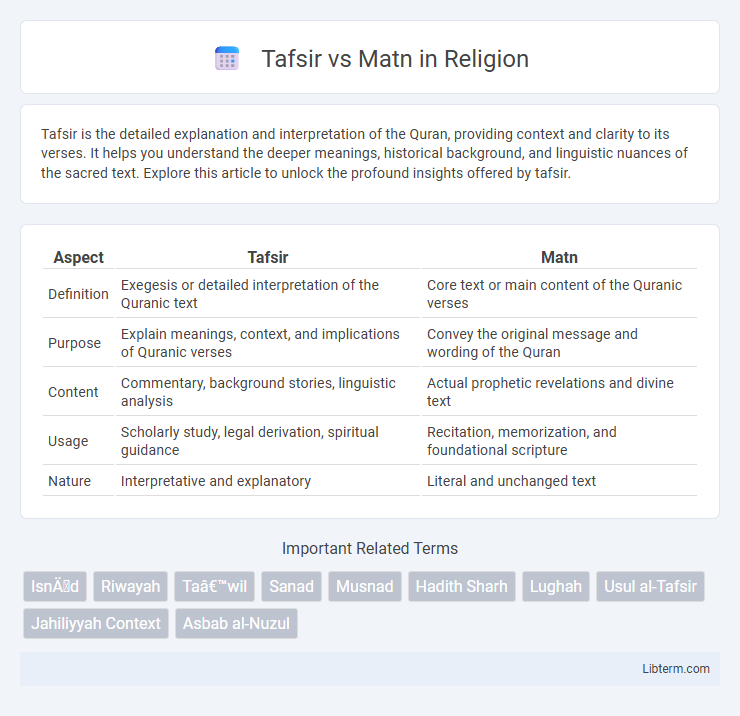
| Aspect | Tafsir | Matn |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exegesis or detailed interpretation of the Quranic text | Core text or main content of the Quranic verses |
| Purpose | Explain meanings, context, and implications of Quranic verses | Convey the original message and wording of the Quran |
| Content | Commentary, background stories, linguistic analysis | Actual prophetic revelations and divine text |
| Usage | Scholarly study, legal derivation, spiritual guidance | Recitation, memorization, and foundational scripture |
| Nature | Interpretative and explanatory | Literal and unchanged text |
Introduction to Tafsir and Matn
Tafsir refers to the exegesis or interpretation of the Quran, aiming to explain the context, meanings, and linguistic nuances of the divine text. Matn is the actual text of the Quran or Hadith itself, representing the core scriptural content without commentary. Understanding Tafsir is essential to grasp the deeper implications of Matn, bridging the literal verses with theological, jurisprudential, and historical perspectives.
Defining Tafsir: Meaning and Purpose
Tafsir refers to the detailed exegesis and interpretation of the Quran, aiming to clarify its linguistic, legal, and theological meanings for readers. It serves to explain the context, occasions of revelation (Asbab al-Nuzul), and the linguistic nuances embedded in the Quranic verses. The primary purpose of Tafsir is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the Quran, facilitating correct application and avoiding misinterpretation of the Matn, the actual text or content of the scripture.
Understanding Matn: Core Concept
Matn refers to the main text of a Hadith or Quranic verse, representing the core content that conveys the intended message or teaching. Understanding Matn is crucial for accurate interpretation, as it forms the primary source of religious knowledge without the influence of external commentary or explanation. Tafsir, in contrast, involves detailed exegesis and analysis of the Matn to uncover deeper meanings, linguistic nuances, and contextual relevance.
Historical Origins of Tafsir and Matn
Tafsir, rooted in early Islamic scholarship, originated as a scholarly effort to interpret and explain the Qur'anic text (Matn) within its historical, linguistic, and theological contexts. Matn refers specifically to the original Qur'anic text, which has remained unchanged since its revelation to Prophet Muhammad in the 7th century, serving as the foundational source for Islamic theology and law. Historical origins of Tafsir highlight its evolution through various classical schools, including the Kufan, Basran, and Baghdad traditions, emphasizing linguistic analysis, prophetic traditions (Hadith), and juristic principles to elucidate the Matn.
Methodological Differences
Tafsir involves exegesis of the Quran, focusing on explaining, interpreting, and contextualizing the divine text through linguistic, theological, and historical analyses. Matn criticism centers on verifying the authenticity and integrity of the Quranic text itself by examining manuscripts, variants, and transmission chains. While Tafsir prioritizes meaning and contextual understanding, Matn criticism emphasizes textual preservation and philological scrutiny.
Role in Islamic Scholarship
Tafsir serves as the comprehensive exegesis of the Quran, analyzing linguistic, theological, and historical contexts to elucidate its meanings, while Matn refers to the Quranic text itself, whose precise language forms the basis for legal and doctrinal rulings in Islamic jurisprudence. Islamic scholarship relies on Tafsir to interpret the Matn, enabling scholars to derive applicable guidance in varied contexts. The interplay between Tafsir and Matn underpins the development of Islamic law, theology, and ethical teachings across centuries.
Tafsir: Interpretive Approaches
Tafsir involves the detailed exegesis of the Quran, employing various interpretive approaches such as linguistic analysis, contextual understanding, and jurisprudential insights to uncover the intended meanings behind the text. Scholars utilize traditional methods like tafsir bi'l-ma'thur (exegesis based on transmitted reports) and tafsir bi'r-ra'y (independent reasoning) to address complexities and ambiguities. This interpretive process integrates historical context, linguistic nuances, and theological principles to provide comprehensive explanations that guide religious understanding and practice.
Importance of Matn in Hadith Sciences
Matn, the main textual content of a hadith, is crucial for authentic interpretation and application within Hadith sciences, providing the core message conveyed by the Prophet Muhammad (PBUH). Tafsir, or exegesis, complements the understanding of Matn by offering contextual analysis and clarifying ambiguous terms, yet without precise knowledge of the Matn, interpretations risk deviation from authentic meanings. Scholars prioritize the Matn to ensure accurate transmission, assessment of authenticity, and correct legal and theological rulings derived from Hadith texts.
Comparative Analysis: Tafsir vs Matn
Tafsir provides detailed exegesis and contextual interpretation of the Quranic text, focusing on linguistic, historical, and theological aspects, whereas Matn refers to the primary textual content of the Quran itself. Comparative analysis highlights Tafsir's role in elucidating ambiguous verses and exploring jurisprudential rulings, while Matn remains the fixed scriptural text that serves as the foundation for Islamic doctrine and law. Tafsir bridges the understanding gap by offering comprehensive commentary that complements the literal and spiritual meanings embedded within the Matn.
Contemporary Relevance and Challenges
Tafsir provides essential contextual understanding of Quranic verses, addressing contemporary issues such as technological advancements and social justice, while Matn represents the primary scriptural text requiring interpretation. Modern challenges involve reconciling traditional Tafsir with evolving societal norms and scientific knowledge, ensuring relevance without compromising theological integrity. Effective engagement with both Tafsir and Matn enables dynamic application of Islamic principles in modern contexts, bridging historical wisdom and present-day realities.
Tafsir Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com