Unilineal descent traces lineage through either the paternal (patrilineal) or maternal (matrilineal) line, shaping social identity and inheritance patterns within many cultures. This system influences kinship, property rights, and group membership, impacting how communities organize themselves and maintain traditions. Discover how unilineal descent affects societal structures and your understanding of ancestry in the full article.
Table of Comparison
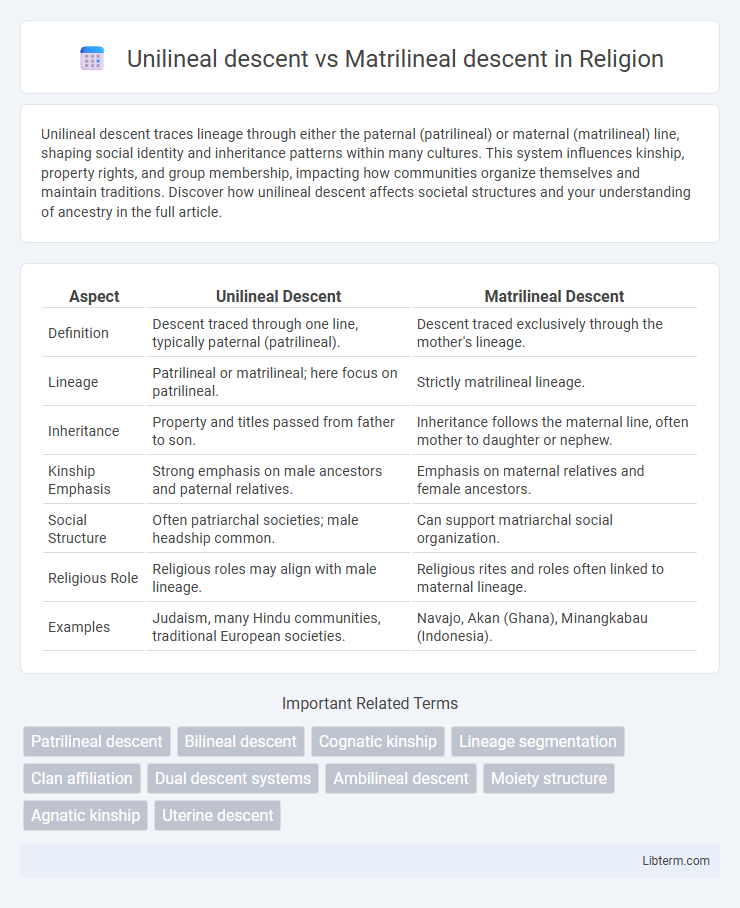
| Aspect | Unilineal Descent | Matrilineal Descent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Descent traced through one line, typically paternal (patrilineal). | Descent traced exclusively through the mother's lineage. |
| Lineage | Patrilineal or matrilineal; here focus on patrilineal. | Strictly matrilineal lineage. |
| Inheritance | Property and titles passed from father to son. | Inheritance follows the maternal line, often mother to daughter or nephew. |
| Kinship Emphasis | Strong emphasis on male ancestors and paternal relatives. | Emphasis on maternal relatives and female ancestors. |
| Social Structure | Often patriarchal societies; male headship common. | Can support matriarchal social organization. |
| Religious Role | Religious roles may align with male lineage. | Religious rites and roles often linked to maternal lineage. |
| Examples | Judaism, many Hindu communities, traditional European societies. | Navajo, Akan (Ghana), Minangkabau (Indonesia). |
Introduction to Descent Systems
Unilineal descent systems trace lineage through a single line, either paternal (patrilineal) or maternal (matrilineal), determining inheritance and social identity. Matrilineal descent specifically emphasizes lineage through the mother's side, influencing property rights, clan membership, and familial responsibilities within societies. These descent systems shape kinship structures and cultural norms by defining group membership based on one ancestral line rather than both.
Defining Unilineal Descent
Unilineal descent traces lineage exclusively through one gender line, either paternal (patrilineal) or maternal (matrilineal), establishing clear inheritance, kinship, and social identity pathways. Matrilineal descent specifically follows the mother's lineage, influencing property rights, clan membership, and familial roles within societies. Understanding unilineal descent systems is crucial for analyzing cultural norms, inheritance laws, and social structure dynamics across various ethnic groups.
Understanding Matrilineal Descent
Matrilineal descent traces lineage and inheritance through the mother's line, emphasizing the maternal connection in defining family relationships and social roles. This system often shapes property rights, clan membership, and succession by prioritizing female ancestors and their descendants. Understanding matrilineal descent reveals how cultural norms and kinship structures vary, influencing social organization and identity in many societies worldwide.
Key Differences Between Unilineal and Matrilineal Descent
Unilineal descent traces lineage exclusively through either the paternal or maternal line, whereas matrilineal descent specifically follows the maternal line for inheritance and social identity. In unilineal systems, inheritance rights, clan membership, and succession are determined by one parent's lineage, often emphasizing patrilineal descent globally, while matrilineal descent centers on the mother's lineage for these purposes. Key differences include the direction of lineage tracing--unilineal being either paternal or maternal and matrilineal strictly maternal--and the cultural roles assigned to kinship and inheritance within societies.
Social Structure Influences of Descent Systems
Unilineal descent systems, including matrilineal descent, shape social structure by establishing clear lineage-based kinship groups that influence inheritance, residence, and social roles. Matrilineal descent traces lineage through the mother's line, often granting women significant authority within the clan and affecting property rights and leadership roles. These descent systems reinforce group identity, regulate marriage alliances, and stabilize social organization by defining membership and obligations within extended families.
Inheritance Patterns and Lineage
Unilineal descent systems trace lineage exclusively through one gender, with patrilineal descent following the male line and matrilineal descent tracing lineage through females, significantly impacting inheritance patterns. In matrilineal descent, inheritance and family property pass through the maternal line, often granting children access to their mother's family wealth and status, whereas unilineal systems emphasize inheritance rights strictly along the designated gender line. These distinct lineage frameworks shape social organization, property rights, and kinship responsibilities in diverse cultures worldwide.
Gender Roles in Unilineal and Matrilineal Societies
Gender roles in unilineal descent systems often reflect patrilineal or matrilineal inheritance patterns, influencing social responsibilities and power dynamics within the group. In matrilineal descent societies, women typically hold significant authority over lineage, property, and family decisions, while men may have roles centered around maternal kin. Contrastly, patrilineal unilineal systems emphasize male lineage continuity and often assign leadership and inheritance predominantly to men, reinforcing patriarchal structures.
Case Studies: Cultures Practicing Each Descent System
The Nuer of South Sudan exemplify unilineal descent through their patrilineal lineage, tracing ancestry and inheritance exclusively via male lines, which shapes their social organization and kinship roles. The Minangkabau of West Sumatra represent matrilineal descent, passing property, family name, and social status through the female line, resulting in women's centrality in family and community structure. These case studies highlight the profound impact of unilineal descent systems on inheritance patterns, social responsibilities, and cultural identity in diverse societies.
Modern Implications of Descent Systems
Unilineal descent systems, including patrilineal and matrilineal descent, play a significant role in shaping inheritance, property rights, and social identity in modern societies. Matrilineal descent emphasizes lineage and succession through the mother's side, often influencing gender roles and the transmission of wealth and cultural heritage. Understanding these descent systems is crucial for addressing legal frameworks, family dynamics, and cultural preservation in contemporary multicultural contexts.
Conclusion: Significance of Descent Systems in Anthropology
Unilineal descent systems, including patrilineal and matrilineal descent, play a crucial role in structuring kinship, inheritance, and social organization across cultures. Matrilineal descent emphasizes lineage traced through the mother's side, often influencing property rights and familial authority, while patrilineal descent follows the father's line, typically shaping political power and clan membership. Understanding these descent systems helps anthropologists decode cultural norms, social cohesion, and identity formation within diverse societies worldwide.
Unilineal descent Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com