A priest plays a vital role in spiritual leadership, guiding communities through worship, rituals, and personal counsel. Their responsibilities often include conducting ceremonies, offering pastoral care, and interpreting sacred texts to foster faith and moral growth. Discover how a priest's dedication can enrich your spiritual journey by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
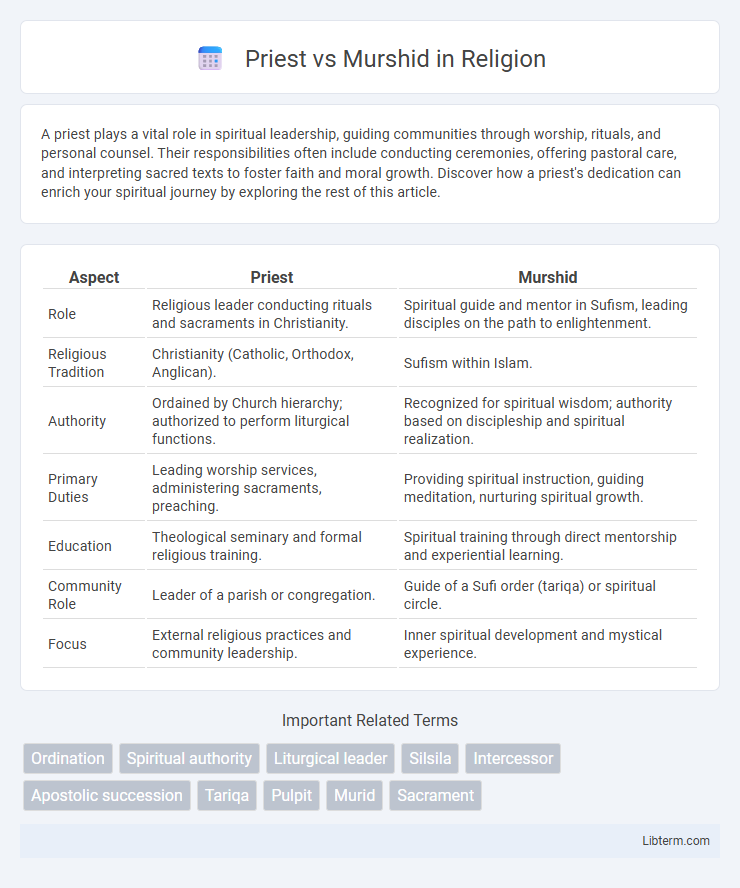
| Aspect | Priest | Murshid |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Religious leader conducting rituals and sacraments in Christianity. | Spiritual guide and mentor in Sufism, leading disciples on the path to enlightenment. |
| Religious Tradition | Christianity (Catholic, Orthodox, Anglican). | Sufism within Islam. |
| Authority | Ordained by Church hierarchy; authorized to perform liturgical functions. | Recognized for spiritual wisdom; authority based on discipleship and spiritual realization. |
| Primary Duties | Leading worship services, administering sacraments, preaching. | Providing spiritual instruction, guiding meditation, nurturing spiritual growth. |
| Education | Theological seminary and formal religious training. | Spiritual training through direct mentorship and experiential learning. |
| Community Role | Leader of a parish or congregation. | Guide of a Sufi order (tariqa) or spiritual circle. |
| Focus | External religious practices and community leadership. | Inner spiritual development and mystical experience. |
Understanding the Roles: Priest vs Murshid
Priests serve as ordained religious leaders primarily in Christian traditions, performing rituals, administering sacraments, and offering spiritual guidance to congregants. Murshids, in Sufi Islam, act as spiritual guides who lead disciples through personalized teachings and mystical practices aimed at inner enlightenment and union with the Divine. Understanding the roles of Priest and Murshid highlights the differing structures of authority and spiritual focus within Christianity and Sufism, emphasizing ritual duties versus individualized spiritual mentorship.
Historical Background of Priests and Murshids
Priests have historically served as intermediaries between humans and deities in various religious traditions, with roles deeply embedded in ancient rituals, temple ceremonies, and structured hierarchies dating back to civilizations like Mesopotamia and Egypt. Murshids, in contrast, are spiritual guides in Sufism, emerging in the Islamic medieval period as mentors who direct disciples on mystical paths toward divine knowledge and inner purification. Both roles reflect distinct cultural and religious contexts--priests often performing formalized, public rites, while murshids emphasize personal spiritual development within Sufi brotherhoods.
Core Beliefs and Teachings
Priests in Christianity serve as intermediaries between God and believers, administering sacraments like the Eucharist and emphasizing doctrines such as salvation through faith and the sanctity of scripture. Murshids, Islamic spiritual guides in Sufism, focus on inner purification, guiding disciples (murids) on a mystical path toward union with Allah through practices like dhikr (remembrance) and adherence to the Shariah. Core teachings of priests center on communal worship and doctrinal orthodoxy, while murshids emphasize personal spiritual transformation and direct experiential knowledge of the Divine.
Duties and Responsibilities
A priest primarily conducts religious ceremonies, offers spiritual guidance, and oversees the administration of sacraments within a church or temple, focusing on ritualistic duties and community worship. A murshid serves as a spiritual guide in Sufism, providing personalized mentorship, teaching esoteric knowledge, and leading disciples on the path of inner purification and enlightenment. Both roles emphasize spiritual leadership but differ in approach, with priests maintaining formal religious structures and murshids fostering intimate, experiential learning.
Spiritual Leadership Comparison
A Priest typically serves as a formal religious leader within structured institutions, performing rituals and guiding congregations based on codified doctrines. A Murshid, prominent in Sufi traditions, functions as a spiritual guide who offers personalized mentorship aimed at inner purification and direct experiential knowledge of the Divine. The Priest emphasizes external worship and community rites, while the Murshid prioritizes intimate spiritual development and mystical insight.
Training and Qualifications
Priests typically undergo formal theological education at seminaries, completing rigorous programs that include philosophy, theology, pastoral care, and liturgy, often culminating in ordination by a recognized religious authority. Murshids, within Sufi traditions, receive extensive spiritual training under a qualified spiritual guide, focusing on inner purification, mystical knowledge, and transmission of esoteric teachings through personal mentorship rather than formal academic institutions. The qualifications for priests emphasize structured doctrinal understanding and sacramental responsibilities, while Murshid qualifications prioritize experiential wisdom, spiritual insight, and ongoing guidance in the spiritual path.
Rituals and Practices
Priests typically follow structured rituals centered on sacraments and liturgical ceremonies within institutionalized religions like Christianity, emphasizing formal rites such as Mass or Eucharist. Murshids, spiritual guides in Sufism, focus on personalized practices involving dhikr (remembrance of God), meditation, and spiritual mentorship to cultivate inner purification and closeness to the divine. While priests perform public rituals for community worship, Murshids engage in intimate, experiential teachings aimed at the disciple's direct spiritual experience.
Influence in Communities
Priests often hold significant influence in their communities by leading religious ceremonies, providing spiritual guidance, and serving as moral authorities within organized religions such as Christianity. Murshids, in Sufi Islam, shape communities through personalized mentorship, fostering spiritual growth and inner transformation among disciples, which creates deep, intimate bonds. The communal impact of a Murshid often emphasizes mystical and ethical development, contrasting with the Priest's role in doctrinal teaching and formal ritual leadership.
Challenges Faced by Priests and Murshids
Priests often struggle with maintaining congregational attendance amid growing secularism and addressing diverse spiritual needs within rigid institutional frameworks. Murshids face challenges in preserving the authenticity of Sufi teachings while adapting to modern followers' expectations and combating misconceptions about mysticism. Both roles require balancing tradition with contemporary relevance to sustain their spiritual authority and community impact.
Modern-Day Relevance and Evolution
The terms "Priest" and "Murshid" represent distinct spiritual leadership roles, with priests primarily serving in Christian religious traditions and murshids acting as guides in Sufi Islam, each adapting to modern contexts through evolving practices and community engagement. In contemporary society, priests often integrate technology for virtual worship and community outreach, while murshids emphasize personalized spiritual mentorship and cultural preservation within increasingly globalized Muslim communities. The evolution of both roles highlights a shift toward inclusivity and interfaith dialogue, reflecting broader trends in religious experience and leadership today.
Priest Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com