Revealed religion is a belief system based on divine revelation, where sacred truths are disclosed to humanity through prophets or holy texts. This form of religion contrasts with natural religion, which relies on reason and observation of the natural world. Explore the rest of the article to understand how revealed religion shapes faith and spirituality across cultures.
Table of Comparison
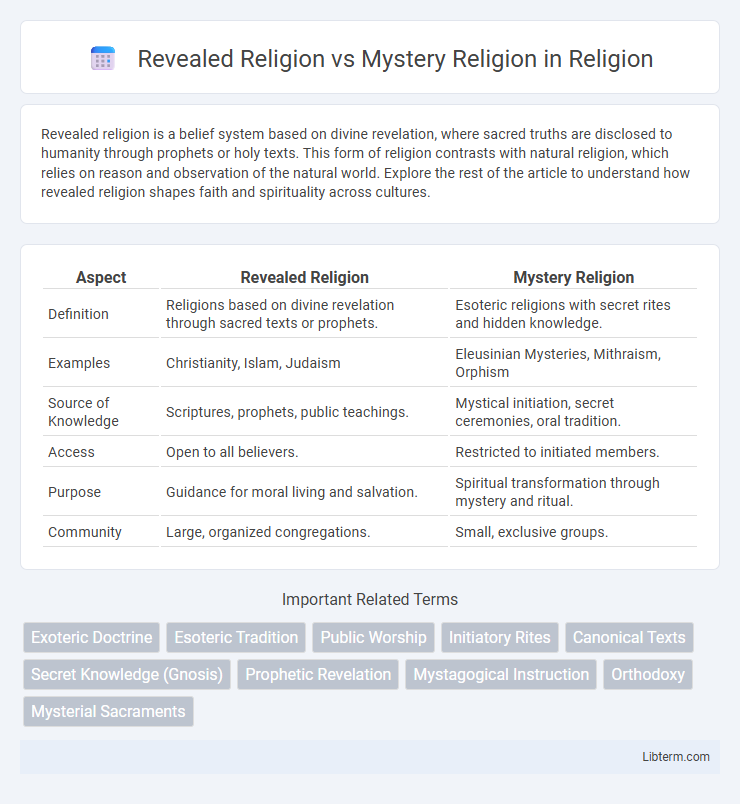
| Aspect | Revealed Religion | Mystery Religion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Religions based on divine revelation through sacred texts or prophets. | Esoteric religions with secret rites and hidden knowledge. |
| Examples | Christianity, Islam, Judaism | Eleusinian Mysteries, Mithraism, Orphism |
| Source of Knowledge | Scriptures, prophets, public teachings. | Mystical initiation, secret ceremonies, oral tradition. |
| Access | Open to all believers. | Restricted to initiated members. |
| Purpose | Guidance for moral living and salvation. | Spiritual transformation through mystery and ritual. |
| Community | Large, organized congregations. | Small, exclusive groups. |
Understanding Revealed Religion: Definition and Characteristics
Revealed religion is defined by the belief that divine truths are disclosed directly to humanity through sacred texts, prophets, or divine intervention, distinguishing it from mystery religions which rely on secret teachings and esoteric rituals. Core characteristics of revealed religion include explicit doctrines, codified scriptures, and an emphasis on faith in the revealed messages from a transcendent deity. This form of religion aims to provide clear moral guidance and universal truths accessible to all adherents, reinforcing communal worship and doctrinal consistency.
What is Mystery Religion? Key Features Explained
Mystery religions are ancient belief systems characterized by secret rites and esoteric knowledge accessible only to initiated members, contrasting with revealed religions that claim divine disclosure through sacred texts or prophets. Key features include ritual initiation, symbolic ceremonies, and a focus on personal spiritual transformation or salvation. These religions often involve myths about dying and rebirth deities, fostering a deeply experiential and mystical connection to the divine.
Historical Origins of Revealed and Mystery Religions
Revealed religions trace their origins to specific historical events where divine truths were disclosed to prophets or founders, as seen in Judaism with the covenant at Mount Sinai or Christianity with the life and teachings of Jesus. Mystery religions, prevalent in the Greco-Roman world, originated from secretive cults that emphasized esoteric knowledge and initiation rites, like the Eleusinian Mysteries and the cult of Isis. Both types shaped ancient spiritual landscapes, with revealed religions focusing on public scripture and creed, while mystery religions preserved hidden doctrines accessible only to initiated members.
Core Beliefs: Revelation versus Secret Knowledge
Revealed religion centers on divine truths disclosed publicly through sacred texts and prophets, emphasizing faith in God's open communication with humanity. Mystery religion, by contrast, relies on esoteric knowledge accessible only to initiates through secret rituals and symbolic teachings, stressing personal spiritual transformation. The core distinction lies in revealed religion's universal accessibility of doctrine versus mystery religion's exclusive, concealed wisdom for select followers.
Rituals and Practices: Public Worship vs Initiatory Rites
Revealed religions feature public worship rituals designed to be accessible to the entire community, often including prayer, sacraments, and communal gatherings that reinforce shared beliefs and moral codes. Mystery religions emphasize initiatory rites that involve secret teachings and ceremonies reserved for initiated members, aiming to provide esoteric knowledge and personal transformation. The contrast lies in the openness of revealed religion's practices versus the exclusivity and experiential focus of mystery religion rituals.
The Role of Sacred Texts in Revealed and Mystery Religions
Sacred texts in revealed religions serve as foundational authorities, providing divine laws, moral codes, and historical narratives believed to be directly communicated by a deity, exemplified by the Bible in Christianity and the Quran in Islam. Mystery religions, such as the Eleusinian Mysteries and the Cult of Isis, rely more heavily on oral traditions, secret teachings, and esoteric rituals rather than formal scriptures, emphasizing experiential knowledge and personal initiation. The contrast in the role of sacred texts highlights the structured doctrinal framework in revealed religions versus the symbolic, experiential focus in mystery religions.
Salvation and Afterlife: Divergent Doctrines Explored
Revealed religion emphasizes salvation through divine revelation and faith in a personal deity, often promising an eternal afterlife in heaven or paradise based on moral conduct and obedience. Mystery religions focus on secret rites and initiatory knowledge, offering salvation through mystical union with the divine and a transformative afterlife experience that is often symbolic and esoteric. The doctrinal divergence centers on accessible salvation through explicit teachings versus hidden, experiential knowledge leading to spiritual rebirth.
Community Structure: Clergy, Initiates, and Followers
Revealed religions feature a formal clergy that mediates sacred knowledge from divine revelation, structuring the community through set doctrines and rituals accessible to all followers. Mystery religions maintain an exclusive community, where initiates undergo secret rites and receive hidden knowledge unavailable to the general populace, often guided by specialized priests. The clear hierarchy in revealed religions contrasts with the secrecy and selective participation characterizing mystery religions' social organization.
Influence on Art, Culture, and Society
Revealed religions, such as Christianity and Islam, have significantly shaped Western art, culture, and societal norms through sacred texts, iconography, and ritual practices that reinforce communal identity and moral values. Mystery religions of the ancient world, like the Eleusinian Mysteries and Mithraism, influenced art and culture by emphasizing esoteric knowledge, secret rites, and symbolic imagery that permeated literature and architecture. Both religious forms contributed to social cohesion and cultural development, with revealed religions promoting codified ethical systems and mystery religions fostering personal spiritual experiences within communal contexts.
Modern Relevance: Lasting Impact of Both Religious Traditions
Revealed religions such as Christianity and Islam continue to shape ethical frameworks and legal systems in modern societies through codified scriptures and prophetic teachings, ensuring enduring influence on cultural norms and governance. Mystery religions like ancient Mithraism and Eleusinian Mysteries persist in scholarly interest and contemporary spiritual movements, inspiring personalized ritual practices and esoteric knowledge embracing direct divine experience. The lasting impact of both traditions manifests in the ongoing dialogue between institutionalized dogma and individualized spirituality, reflecting humanity's quest for meaning and transcendence across centuries.
Revealed Religion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com