Salvation represents the deliverance from sin and its consequences through faith, often seen as a core promise in many religious beliefs. Understanding its spiritual significance can deepen your connection to faith and life's purpose. Explore the rest of the article to uncover the profound meanings and paths to salvation.
Table of Comparison
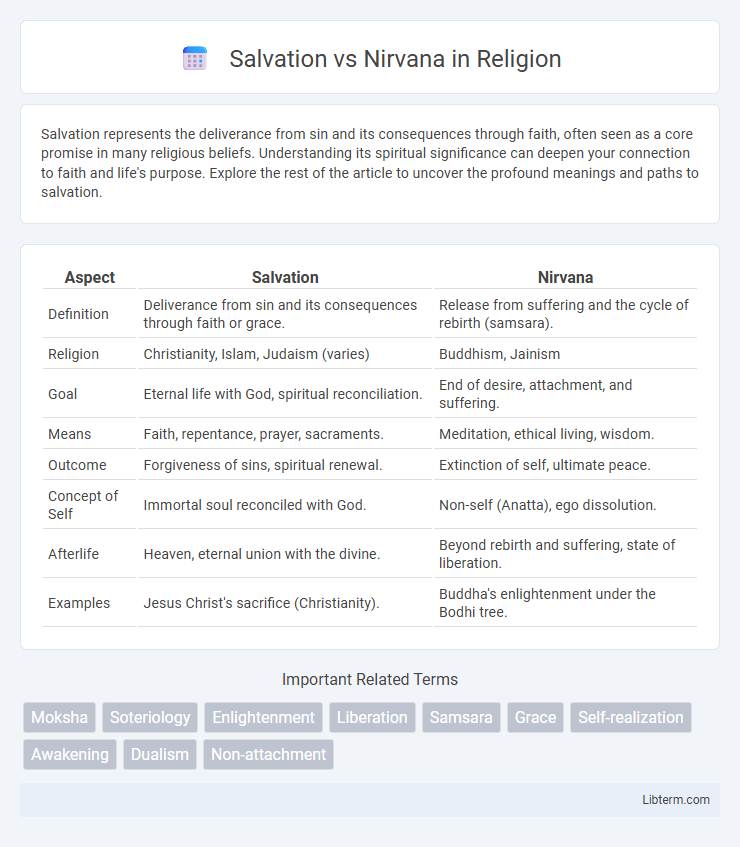
| Aspect | Salvation | Nirvana |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliverance from sin and its consequences through faith or grace. | Release from suffering and the cycle of rebirth (samsara). |
| Religion | Christianity, Islam, Judaism (varies) | Buddhism, Jainism |
| Goal | Eternal life with God, spiritual reconciliation. | End of desire, attachment, and suffering. |
| Means | Faith, repentance, prayer, sacraments. | Meditation, ethical living, wisdom. |
| Outcome | Forgiveness of sins, spiritual renewal. | Extinction of self, ultimate peace. |
| Concept of Self | Immortal soul reconciled with God. | Non-self (Anatta), ego dissolution. |
| Afterlife | Heaven, eternal union with the divine. | Beyond rebirth and suffering, state of liberation. |
| Examples | Jesus Christ's sacrifice (Christianity). | Buddha's enlightenment under the Bodhi tree. |
Understanding Salvation and Nirvana: Core Definitions
Salvation in religious contexts typically refers to the deliverance from sin and its consequences, often involving a personal relationship with a divine being and the promise of eternal life. Nirvana in Buddhist philosophy signifies the cessation of suffering and the cycle of rebirth, achieved through enlightenment and the eradication of desire and ignorance. Both concepts embody ultimate liberation but differ fundamentally in their spiritual goals, methods, and theological frameworks.
Historical Roots: Origins in Major Religions
Salvation in Christianity and Islam centers on deliverance from sin and eternal union with God, rooted in biblical and Quranic teachings emerging around 1st century CE and 7th century CE respectively. Nirvana, originating from ancient Indian traditions within Hinduism and solidified in Buddhism around the 5th century BCE, represents the cessation of suffering and liberation from the cycle of rebirth (samsara). Both concepts reflect profound metaphysical goals but differ fundamentally in their theological frameworks and historical contexts across these major religions.
Key Beliefs: Salvation in Christianity
Salvation in Christianity is the belief in deliverance from sin and its consequences through faith in Jesus Christ as Lord and Savior, emphasizing redemption and eternal life with God. Central to this doctrine is the grace of God, received through belief, repentance, and acceptance of Jesus' sacrificial death and resurrection. This transformative process restores the believer's relationship with God and offers forgiveness, healing, and spiritual renewal.
Exploring Nirvana: Foundations in Buddhism
Nirvana, a foundational concept in Buddhism, represents the ultimate liberation from the cycle of birth, death, and suffering known as samsara. It is characterized by the cessation of desire, attachment, and ignorance, leading to profound inner peace and enlightenment. Unlike Salvation in Christianity, which often implies divine intervention and eternal life in heaven, Nirvana is achieved through personal spiritual cultivation, meditation, and adherence to the Noble Eightfold Path.
The Pathways: How One Attains Salvation and Nirvana
Salvation in Christianity is attained through faith in Jesus Christ, repentance, and adherence to divine commandments, emphasizing a personal relationship with God and eternal life in heaven. Nirvana in Buddhism is achieved by following the Noble Eightfold Path, which involves ethical conduct, mental discipline, and wisdom to extinguish desire and suffering, leading to liberation from the cycle of rebirth. Both pathways require transformative inner change, yet salvation centers on divine grace, while nirvana emphasizes self-realization and enlightenment.
Role of Suffering and Liberation
Salvation in Christianity often involves enduring suffering as a path to redemption and eternal life, where suffering is viewed as a test of faith or a means to spiritual purification. Nirvana in Buddhism represents liberation from the cycle of birth, death, and suffering (samsara) by extinguishing desire and attachment, achieving a state beyond pain and existence. While salvation seeks union with God through grace, Nirvana emphasizes self-realization and the cessation of suffering through enlightenment.
The Afterlife: Contrasting Spiritual Destinations
Salvation in Christianity emphasizes eternal life in Heaven through faith and grace, where the soul experiences divine presence and everlasting joy. Nirvana in Buddhism signifies the cessation of suffering and the cycle of rebirth, leading to a state of ultimate peace and liberation from worldly desires. These contrasting spiritual destinations highlight salvation as a personal relationship with God, while Nirvana represents freedom from attachment and ego.
Ethical Implications: Morality in Salvation and Nirvana
Salvation in Abrahamic religions emphasizes moral obedience to divine commandments as a pathway to eternal life, underscoring accountability and moral judgement. Nirvana in Buddhism focuses on the cessation of suffering through ethical conduct, mental discipline, and wisdom, promoting detachment from desires to achieve liberation from the cycle of rebirth. Both concepts highlight transforming human behavior, but salvation centers on adherence to divine will, while nirvana stresses internal ethical development and enlightenment.
Influence on Daily Life and Spiritual Practices
Salvation in Christianity emphasizes a personal relationship with God through faith and grace, guiding daily life toward moral behavior, prayer, and community worship. Nirvana in Buddhism centers on liberation from suffering and the cycle of rebirth through meditation, mindfulness, and ethical living, fostering inner peace and detachment from worldly desires. Both concepts profoundly shape spiritual practices by encouraging discipline, self-reflection, and transformative life choices aimed at ultimate freedom or union with the divine.
Comparative Reflections: Similarities and Differences
Salvation in Christianity and Nirvana in Buddhism both represent ultimate spiritual goals involving liberation from suffering and the cycle of rebirth. Salvation centers on divine grace and eternal life with God through faith, while Nirvana emphasizes self-realization, extinguishing desire, and achieving non-attachment. The key difference lies in theistic salvation as a relationship with God, whereas Nirvana is a non-theistic state of profound inner peace and freedom from samsara.
Salvation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com