A diocese is a district under the pastoral care of a bishop in the Christian Church, serving as a vital administrative and spiritual unit. It organizes local parishes to support community worship, religious education, and various outreach programs. Discover how your diocese influences faith and community by exploring the details in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
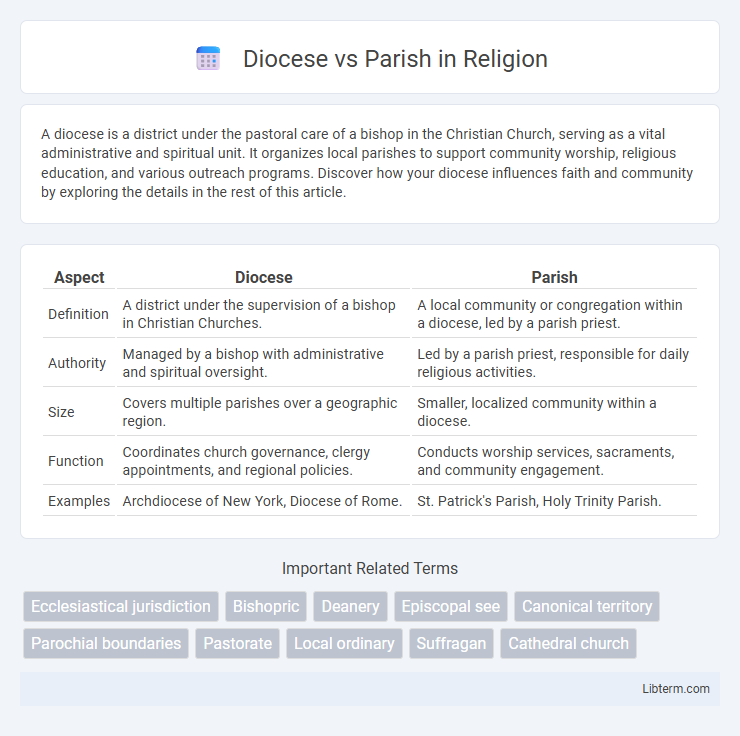
| Aspect | Diocese | Parish |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A district under the supervision of a bishop in Christian Churches. | A local community or congregation within a diocese, led by a parish priest. |
| Authority | Managed by a bishop with administrative and spiritual oversight. | Led by a parish priest, responsible for daily religious activities. |
| Size | Covers multiple parishes over a geographic region. | Smaller, localized community within a diocese. |
| Function | Coordinates church governance, clergy appointments, and regional policies. | Conducts worship services, sacraments, and community engagement. |
| Examples | Archdiocese of New York, Diocese of Rome. | St. Patrick's Parish, Holy Trinity Parish. |
Introduction to Dioceses and Parishes
A diocese is a geographic administrative unit of the Catholic Church overseen by a bishop, encompassing multiple parishes within its territory. A parish is the local community or congregation within a diocese, led by a parish priest, and serves as the primary place of worship and pastoral care for Catholics. Understanding the distinction highlights the hierarchical structure where dioceses govern broad regions while parishes focus on localized religious activities and community support.
Defining a Diocese: Structure and Leadership
A diocese is a district under the pastoral care of a bishop in the Christian Church, serving as the primary administrative unit that oversees multiple parishes within a defined geographical region. The bishop, as the chief ecclesiastical leader, exercises spiritual and organizational authority, guiding the clergy and laity in religious matters and sacramental duties. Dioceses are structured with a hierarchical framework including auxiliary bishops, archdeacons, and various church offices to ensure effective governance and coordination of activities across all parishes.
What Is a Parish? Roles and Responsibilities
A parish is a local community within a diocese, led by a parish priest responsible for conducting religious services, administering sacraments, and providing pastoral care to members. It serves as the primary place of worship and spiritual guidance for parishioners, organizing activities such as education, charity, and community outreach. The parish acts as the frontline of church engagement, fostering faith development and social support within its geographical area.
Historical Origins: Diocese and Parish Development
The historical origins of dioceses trace back to the administrative divisions of the Roman Empire, serving as territorial jurisdictions led by bishops to oversee multiple congregations. Parishes emerged later as smaller, localized communities within dioceses, centered around individual churches and led by parish priests to address the spiritual needs of specific populations. This hierarchical development reflects the Church's expansion strategy, balancing broad ecclesiastical governance with intimate community care.
Key Differences: Diocese vs Parish
A diocese is a large ecclesiastical territory overseen by a bishop and comprises multiple parishes, which are smaller local communities headed by a priest. Key differences include governance scope, with the diocese managing regional church activities, clergy assignments, and broader administrative duties, while a parish focuses on direct pastoral care, worship services, and community engagement for its local members. The diocese serves as the primary organizational unit in the church hierarchy, whereas a parish functions as the foundational unit for individual congregants' spiritual needs.
Governance: Who Leads a Diocese vs a Parish?
A diocese is governed by a bishop who holds ecclesiastical authority over all parishes within the diocesan territory, coordinating clergy and overseeing administrative, pastoral, and doctrinal matters. A parish is led by a parish priest or pastor responsible for the day-to-day spiritual guidance and operational management of a single local church community. The bishop's governance encompasses multiple parishes, ensuring unity in teaching and discipline throughout the diocese.
Territorial Organization: Boundaries and Scope
A diocese is a large ecclesiastical territory overseen by a bishop, encompassing multiple parishes within defined geographic boundaries. Parishes are smaller local communities within a diocese, each managed by a parish priest and serving a specific neighborhood or town. The territorial organization ensures clear jurisdictional scope, with dioceses coordinating regional church activities while parishes address local worship and pastoral care.
Functions and Services Provided
A diocese is an administrative region overseen by a bishop, responsible for coordinating multiple parishes, managing clergy assignments, and facilitating diocesan-wide programs such as education, charitable outreach, and sacramental guidelines. Parishes function as localized worship communities led by priests, providing regular Mass services, sacraments like baptism and marriage, faith formation, and pastoral care to parishioners. While the diocese sets overarching policies and supports large-scale initiatives, parishes implement these services directly, serving as the primary point of contact for individual members.
Relationship Between Dioceses and Parishes
A diocese is a regional ecclesiastical jurisdiction overseen by a bishop, encompassing multiple parishes, which are local communities led by parish priests. Parishes function as the fundamental units within the diocese, providing localized pastoral care, sacraments, and community services directly to congregants. The diocesan authority coordinates broader administrative, spiritual, and doctrinal guidance, ensuring consistency and unity across all parishes under its jurisdiction.
Importance in Modern Church Administration
A diocese serves as a regional administrative unit led by a bishop, overseeing multiple parishes and coordinating church activities on a larger scale. Parishes function as local communities under the diocese's guidance, providing direct pastoral care, worship services, and community engagement for congregants. Effective modern church administration relies on the structured relationship between dioceses and parishes to ensure cohesive governance, resource allocation, and spiritual support across diverse populations.
Diocese Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com