The Synod is a council of church leaders who gather to discuss and decide on important matters of doctrine, governance, and practice within a Christian denomination. It plays a crucial role in shaping religious teachings and policies that affect the faith community. Explore the rest of the article to understand how synods influence your spiritual journey and church life.
Table of Comparison
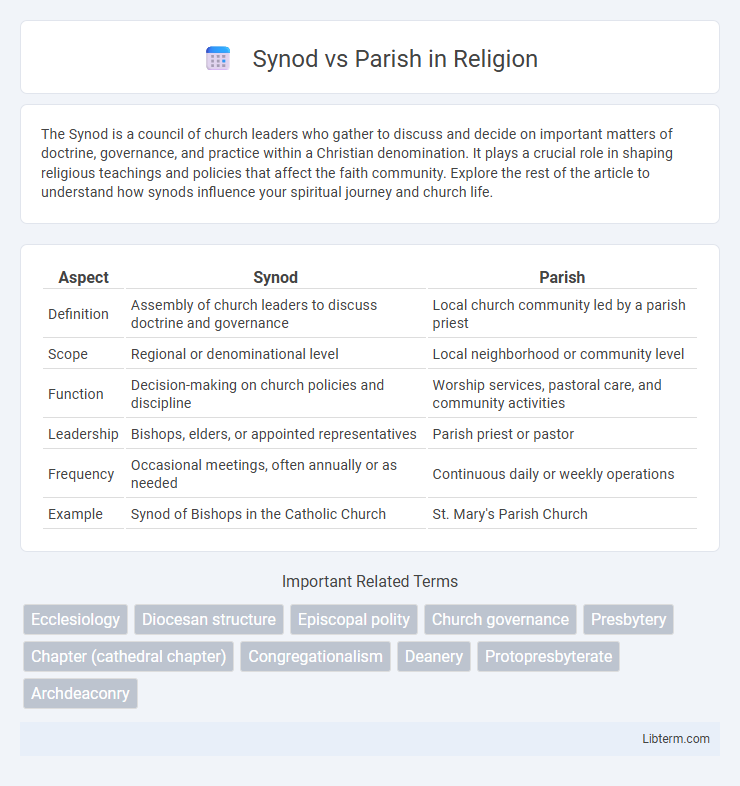
| Aspect | Synod | Parish |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assembly of church leaders to discuss doctrine and governance | Local church community led by a parish priest |
| Scope | Regional or denominational level | Local neighborhood or community level |
| Function | Decision-making on church policies and discipline | Worship services, pastoral care, and community activities |
| Leadership | Bishops, elders, or appointed representatives | Parish priest or pastor |
| Frequency | Occasional meetings, often annually or as needed | Continuous daily or weekly operations |
| Example | Synod of Bishops in the Catholic Church | St. Mary's Parish Church |
Introduction to Synod and Parish
A synod is a council or assembly of church officials and sometimes laity that governs or advises on ecclesiastical matters within a particular Christian denomination, often at regional or national levels. A parish is a local church community led by a parish priest or pastor, serving as the basic organizational unit for worship, pastoral care, and community activities. Synods play a crucial role in decision-making and policy formation, while parishes focus on the daily spiritual needs and engagement of their congregants.
Defining a Synod: Structure and Purpose
A synod is a governing body within certain Christian denominations, consisting of bishops, clergy, and sometimes lay representatives, tasked with overseeing church doctrine, administration, and discipline across multiple parishes. Unlike a parish, which is a local community or congregation led by a priest or pastor, a synod functions at a regional or national level, providing guidance and coordination among various parishes. Synods facilitate unified decision-making, doctrinal consistency, and strategic planning within the broader church hierarchy.
Understanding the Parish: Role and Organization
A parish represents the smallest local ecclesiastical community within the Christian Church, functioning as the primary unit for pastoral care and worship. It is led by a parish priest or pastor who administers sacraments, organizes religious education, and fosters community engagement among parishioners. The organizational structure of a parish often includes councils or committees that assist in managing resources, planning activities, and supporting the parish mission.
Key Differences Between Synod and Parish
A synod is a governing council or assembly within certain Christian denominations that oversees multiple parishes, making decisions on doctrine, administration, and policies across a regional or national level. A parish is a local community or congregation led by a parish priest or pastor, providing regular worship services, pastoral care, and community activities at the neighborhood level. Key differences include scope, as synods operate over several parishes, and function, with synods focusing on governance and parishes on localized ministry and worship.
Authority and Governance Comparison
A synod serves as a higher ecclesiastical authority, often comprising clergy and lay representatives tasked with decision-making on doctrinal, administrative, and policy matters within a denomination. In contrast, a parish operates as the local community unit led by a parish priest or pastor responsible for the day-to-day spiritual care, worship services, and pastoral activities of its congregation. Governance in a synod involves collective deliberation and jurisdiction over multiple parishes, whereas parish governance focuses on direct pastoral leadership and local church management.
Functions and Responsibilities
A Synod functions as a governing council that oversees multiple parishes, responsible for setting doctrinal guidelines, church policies, and administrative decisions within a specific denomination or geographic region. Parishes focus on local community worship, pastoral care, and the administration of sacraments, directly serving the spiritual needs of their congregants. Synods coordinate large-scale church initiatives and represent collective interests, while parishes implement these directives through everyday religious activities and local engagement.
Historical Development of Synods and Parishes
Synods emerged in the early Christian Church as regional councils to discuss doctrine and church discipline, tracing back to the New Testament era and gaining prominence during the fourth century. Parishes developed later as localized ecclesiastical jurisdictions governed by a parish priest, originating in the early medieval period to address pastoral care and community organization. The historical development of synods reflects collective decision-making at broader ecclesiastical levels, while parishes evolved to serve the spiritual and administrative needs of individual congregations.
Interaction Between Synod and Parish
Synods provide strategic oversight and resource allocation to individual parishes, shaping their mission and governance through canonical directives and pastoral guidelines. Parishes serve as the local embodiment of the church's mission, implementing synodal decisions in community worship, outreach, and administration. This interaction fosters a dynamic relationship where synods guide doctrinal consistency while parishes offer feedback and real-world insights to the synodal leadership.
Impact on Local Church Communities
Synods facilitate broader decision-making and doctrinal guidance that influence multiple parishes within a region, fostering unity and consistency in church teachings and practices. Parishes serve as the primary local community hubs where individual members engage in worship, sacraments, and community support, directly impacting daily spiritual life. The interaction between synods and parishes ensures that local needs are addressed while maintaining alignment with the wider church's mission and governance.
Synod vs Parish: Which is More Influential?
A Synod holds greater influence than a Parish due to its broader ecclesiastical authority, often governing multiple parishes and setting doctrinal standards within a denomination. Parishes operate at the local level, focusing on community worship and pastoral care without the administrative or legislative power that Synods possess. The Synod's role in decision-making and church governance significantly shapes religious practices beyond individual congregations, amplifying its impact within the church hierarchy.
Synod Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com