Non-hierarchical structures promote collaboration by eliminating traditional top-down management, fostering equal participation and shared decision-making. This approach enhances creativity and agility within teams, enabling faster problem-solving and innovation. Explore the article to discover how non-hierarchical models can transform your organization's dynamics.
Table of Comparison
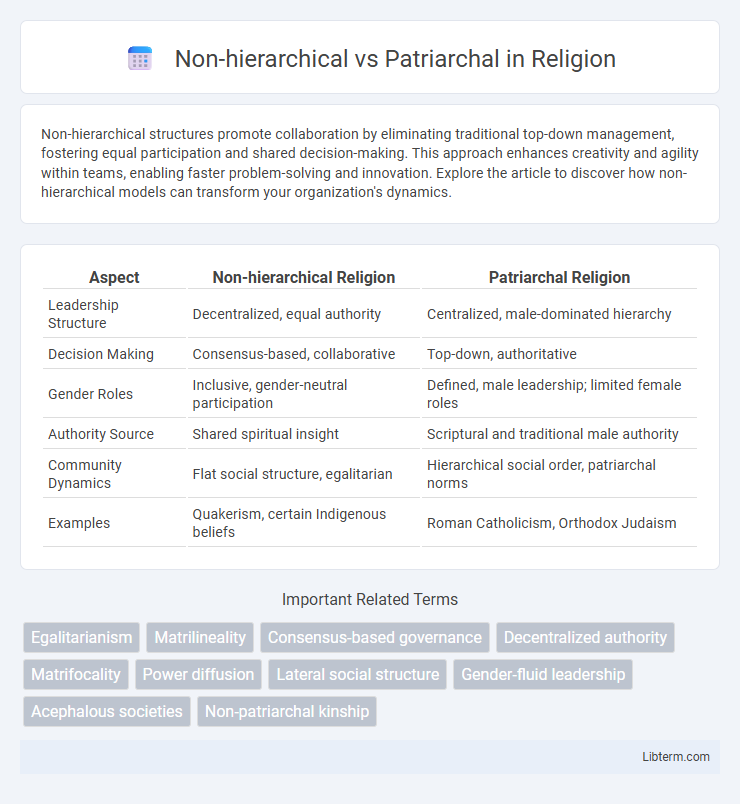
| Aspect | Non-hierarchical Religion | Patriarchal Religion |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership Structure | Decentralized, equal authority | Centralized, male-dominated hierarchy |
| Decision Making | Consensus-based, collaborative | Top-down, authoritative |
| Gender Roles | Inclusive, gender-neutral participation | Defined, male leadership; limited female roles |
| Authority Source | Shared spiritual insight | Scriptural and traditional male authority |
| Community Dynamics | Flat social structure, egalitarian | Hierarchical social order, patriarchal norms |
| Examples | Quakerism, certain Indigenous beliefs | Roman Catholicism, Orthodox Judaism |
Understanding Non-hierarchical and Patriarchal Structures
Non-hierarchical structures emphasize egalitarian decision-making where power and authority are distributed equally among members, fostering collaboration and shared responsibility. Patriarchal structures concentrate authority primarily in male figures, often reinforcing gender-based power imbalances within social, familial, or organizational contexts. Understanding these frameworks involves analyzing how authority, gender roles, and decision-making processes shape group dynamics and societal organization.
Historical Roots of Patriarchal Systems
Patriarchal systems have deep historical roots tracing back to ancient agricultural societies where male dominance was linked to land ownership and physical strength essential for survival. These systems institutionalized male authority in family, legal, and political domains, contrasting with non-hierarchical societies that emphasize egalitarian relationships without rigid authority structures. The entrenched patriarchal norms shaped social institutions, religious doctrines, and cultural practices, reinforcing male dominance across generations.
Key Principles of Non-hierarchical Models
Non-hierarchical models prioritize decentralization, encouraging equal participation and collaborative decision-making among all members, contrasting with patriarchal systems that centralize authority in a singular male figure or group. These models emphasize autonomy, mutual respect, and shared responsibility to foster inclusive environments free from rigid power structures. Key principles include horizontal communication lines, collective leadership, and the dismantling of traditional authority gradients to promote equity and innovation.
Power Dynamics: Centralization vs Decentralization
Non-hierarchical structures emphasize decentralized power dynamics, enabling equal participation and shared decision-making across all members. Patriarchal systems centralize authority, typically consolidating power within a dominant male figure or group, reinforcing top-down control and limiting diverse input. This contrast highlights how power distribution shapes organizational governance and social interactions.
Gender Roles in Patriarchal Societies
Patriarchal societies establish gender roles where men hold primary power in leadership, moral authority, and control over property, while women are often relegated to domestic and caregiving duties. Non-hierarchical systems promote gender equality by minimizing rigid, predefined roles and encouraging shared responsibilities. The reinforcement of traditional masculinity and femininity in patriarchal contexts shapes social expectations and limits opportunities for women's participation in public and economic spheres.
Decision-Making Processes: Consensus vs Authority
Non-hierarchical decision-making processes emphasize consensus, encouraging equal participation and collaborative problem-solving to reach collective agreement. Patriarchal systems rely on authority, where decisions are made by a dominant figure or a select group, often limiting input from others. Consensus fosters inclusivity and shared responsibility, while authoritative decisions can streamline actions but may suppress diverse perspectives.
Impact on Social and Organizational Equality
Non-hierarchical structures promote social and organizational equality by distributing power evenly among members, fostering collaboration and inclusivity. Patriarchal systems often concentrate authority in the hands of a few, typically reinforcing gender and social inequalities. The shift towards non-hierarchical models enhances diverse participation and mitigates entrenched disparities in decision-making processes.
Challenges of Implementing Non-hierarchical Systems
Non-hierarchical systems face challenges such as decision-making inefficiencies, role ambiguity, and resistance from employees accustomed to patriarchal structures. Maintaining accountability and coordination becomes complex without clear authority lines, often leading to conflicts and slowed project progress. Organizations adopting non-hierarchical models must invest in cultural change and communication frameworks to address these operational difficulties effectively.
Case Studies: Examples from Communities and Workplaces
Non-hierarchical communities such as worker cooperatives demonstrate increased collaboration and shared decision-making, as observed in the Mondragon Corporation, where democratic practices empower all members equally. In contrast, patriarchal workplaces like traditional family-owned businesses often exhibit centralized authority and gendered power dynamics, limiting diverse participation and reinforcing male dominance. Case studies reveal that non-hierarchical models foster inclusivity and innovation, while patriarchal systems frequently perpetuate inequality and restrict upward mobility for women and marginalized groups.
Future Trends: Moving Beyond Patriarchy
Future trends indicate a significant shift from patriarchal structures toward non-hierarchical models that emphasize equality and shared leadership. Organizations and societies are increasingly adopting inclusive decision-making processes that dismantle traditional power imbalances rooted in patriarchy. Emerging frameworks prioritize collaboration, diversity, and equity to foster sustainable social and economic development beyond patriarchal constraints.
Non-hierarchical Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com