Orphism is an influential abstract art movement emerging in the early 20th century, known for its vibrant colors and emphasis on pure abstraction inspired by Cubism and Fauvism. It focuses on creating a sense of rhythm and harmony through geometric forms and dynamic compositions that evoke musical qualities. Explore the article to uncover how Orphism continues to shape modern art and enhance your appreciation of visual creativity.
Table of Comparison
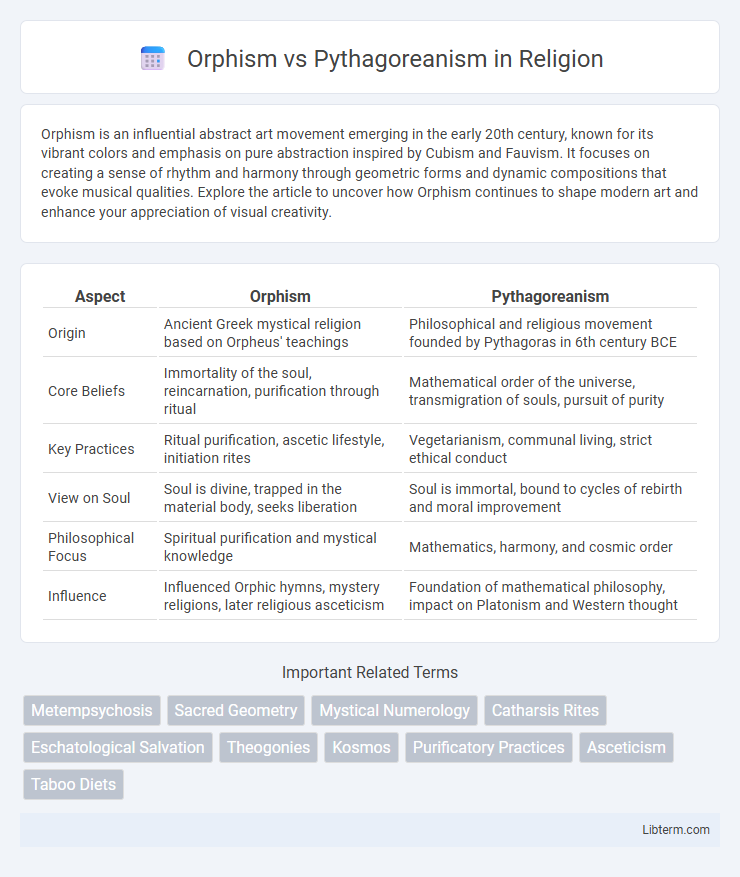
| Aspect | Orphism | Pythagoreanism |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Ancient Greek mystical religion based on Orpheus' teachings | Philosophical and religious movement founded by Pythagoras in 6th century BCE |
| Core Beliefs | Immortality of the soul, reincarnation, purification through ritual | Mathematical order of the universe, transmigration of souls, pursuit of purity |
| Key Practices | Ritual purification, ascetic lifestyle, initiation rites | Vegetarianism, communal living, strict ethical conduct |
| View on Soul | Soul is divine, trapped in the material body, seeks liberation | Soul is immortal, bound to cycles of rebirth and moral improvement |
| Philosophical Focus | Spiritual purification and mystical knowledge | Mathematics, harmony, and cosmic order |
| Influence | Influenced Orphic hymns, mystery religions, later religious asceticism | Foundation of mathematical philosophy, impact on Platonism and Western thought |
Introduction to Orphism and Pythagoreanism
Orphism and Pythagoreanism are ancient religious and philosophical movements centered on the soul's immortality and cosmic harmony. Orphism emphasizes purification rituals and mythological narratives linked to Orpheus, promoting spiritual transformation through divine music and mysticism. Pythagoreanism combines mathematics, metaphysics, and ethics, founded by Pythagoras, highlighting numerical relationships as the foundation of reality and advocating for a disciplined, harmonious life aligned with cosmic order.
Historical Origins and Development
Orphism emerged in ancient Greece around the 6th century BCE, characterized by mystical religious practices and beliefs attributed to the mythical poet Orpheus, emphasizing soul purification and the afterlife. Pythagoreanism, founded by Pythagoras in the 6th century BCE, combined mathematical philosophy with spiritual doctrines, stressing numerical relationships as the foundation of reality and the soul's transmigration. Both movements significantly influenced early Greek thought, with Orphism focusing on esoteric rites and Pythagoreanism on mathematical cosmology and ethical living.
Foundational Texts and Teachings
Orphism centers on the Theogonies and Orphic Hymns, emphasizing the soul's divine origin and reincarnation cycles tied to ritual purity and music. Pythagoreanism rests on the teachings of Pythagoras recorded in fragments and later Neopythagorean texts, promoting mathematics, harmony of the spheres, and the transmigration of souls as keys to spiritual and cosmic order. Both philosophies integrate metaphysical dualism and ethical asceticism but diverge in ritual emphasis and the role of numbers versus mythic cosmology.
Core Beliefs and Doctrines
Orphism centers on the soul's divine origin, emphasizing purification, reincarnation, and the escape from the physical body through ritual and ascetic practices, reflecting its belief in the soul's imprisonment within the material world. Pythagoreanism blends mathematics, mysticism, and ethics, focusing on numerical harmony as the foundation of reality, the transmigration of souls, and the pursuit of a virtuous life governed by rational principles and communal living. Both schools underscore the soul's immortality and purification but differ in their metaphysical frameworks: Orphism adopts a mythological and religious approach, while Pythagoreanism integrates mathematical order and philosophical discipline.
Views on the Soul and Afterlife
Orphism views the soul as divine and immortal, undergoing cycles of reincarnation until purification through ritual and ascetic practices. Pythagoreanism similarly believes in the transmigration of the soul, emphasizing mathematical harmony and ethical living as means to achieve spiritual liberation. Both philosophies stress the soul's journey beyond death, but Orphism focuses more on mystical rites while Pythagoreanism highlights intellectual discipline.
Rituals, Practices, and Initiation
Orphism and Pythagoreanism both emphasize esoteric rituals and initiation rites aimed at spiritual purification and cosmic harmony. Orphic practices center on rites of rebirth, dietary restrictions, and hymns invoking Orpheus for soul liberation from the cycle of reincarnation. Pythagorean rituals include communal living, strict ethical codes, mathematical meditation, and initiatory stages designed to align the soul with the cosmic order.
Ethical Codes and Lifestyle
Orphism emphasizes purification rituals, vegetarianism, and the soul's immortality, advocating for a life of spiritual cleansing and moral purity to achieve divine harmony. Pythagoreanism promotes a disciplined lifestyle based on mathematical harmony, ethical vegetarianism, and communal living, stressing self-control, justice, and the transmigration of the soul. Both philosophies intertwine ethics with metaphysical beliefs, prescribing temperance and respect for life to cultivate spiritual enlightenment.
Influence on Ancient Greek Philosophy
Orphism significantly influenced Ancient Greek philosophy by introducing concepts of the soul's immortality and reincarnation, themes later embraced by Pythagoreanism. Pythagoreanism expanded on Orphic mysticism through its emphasis on mathematical harmony and the belief in the soul's purification via numerical understanding. Both traditions shaped Platonic thought, particularly in metaphysics and ethics, by intertwining spiritual doctrines with rational inquiry.
Similarities and Differences
Orphism and Pythagoreanism both emphasize the immortality of the soul, reincarnation, and the pursuit of spiritual purification through ethical living and ritual practices. Orphism centers on mythological narratives and rituals derived from Orpheus's teachings, promoting music and mysticism, while Pythagoreanism integrates mathematical principles, harmony, and philosophy as pathways to understanding the cosmos and achieving spiritual enlightenment. Both traditions advocate asceticism, but Pythagoreanism uniquely combines religious beliefs with a systematic approach to science and mathematics.
Legacy and Modern Interpretations
Orphism influenced the development of mystical and esoteric traditions, emphasizing the soul's immortality and cycles of rebirth, which continue to inspire modern spiritual movements and philosophical studies. Pythagoreanism's legacy endures through its foundational contributions to mathematics, music theory, and cosmology, profoundly shaping scientific disciplines and Western philosophical thought. Contemporary interpretations often explore their shared focus on harmony and the metaphysical significance of numbers, bridging ancient wisdom with modern metaphysical and scientific inquiries.
Orphism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com