The Talmud is a central text in Jewish tradition, comprising the Mishnah and Gemara, which together explore Jewish law, ethics, customs, and history in depth. It serves as a foundational guide for understanding religious principles and legal interpretations within Judaism. Dive into the rest of the article to discover how the Talmud shapes cultural and spiritual life.
Table of Comparison
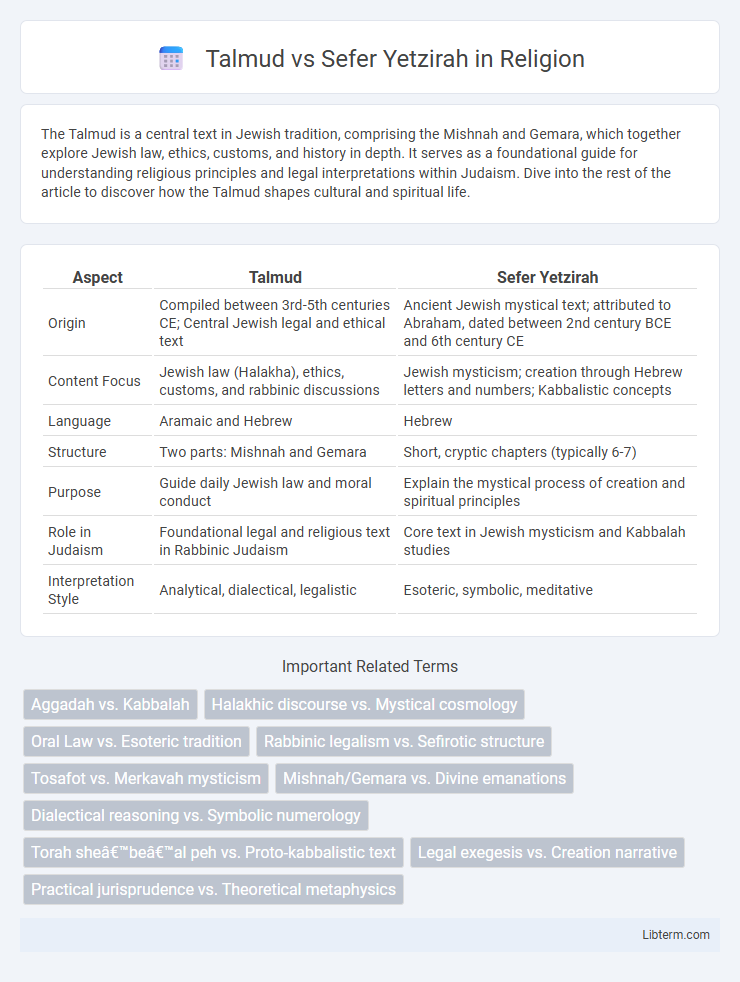
| Aspect | Talmud | Sefer Yetzirah |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Compiled between 3rd-5th centuries CE; Central Jewish legal and ethical text | Ancient Jewish mystical text; attributed to Abraham, dated between 2nd century BCE and 6th century CE |
| Content Focus | Jewish law (Halakha), ethics, customs, and rabbinic discussions | Jewish mysticism; creation through Hebrew letters and numbers; Kabbalistic concepts |
| Language | Aramaic and Hebrew | Hebrew |
| Structure | Two parts: Mishnah and Gemara | Short, cryptic chapters (typically 6-7) |
| Purpose | Guide daily Jewish law and moral conduct | Explain the mystical process of creation and spiritual principles |
| Role in Judaism | Foundational legal and religious text in Rabbinic Judaism | Core text in Jewish mysticism and Kabbalah studies |
| Interpretation Style | Analytical, dialectical, legalistic | Esoteric, symbolic, meditative |
Introduction: Understanding the Talmud and Sefer Yetzirah
The Talmud, comprising the Mishnah and Gemara, serves as a central text in Rabbinic Judaism, offering comprehensive legal discussions, interpretations, and ethical teachings. Sefer Yetzirah, an ancient kabbalistic work attributed to Rabbi Akiva, explores the mystical creation of the universe through the ten sefirot and twenty-two Hebrew letters. Understanding both texts unveils foundational dimensions of Jewish thought, blending legal tradition with esoteric cosmology.
Historical Origins and Authorship
The Talmud, compiled between the 3rd and 5th centuries CE, serves as a foundational text of Rabbinic Judaism, encompassing the Mishnah and Gemara with contributions from numerous rabbis over centuries. In contrast, the Sefer Yetzirah, traditionally attributed to the patriarch Abraham but likely composed between the 3rd and 6th centuries CE, represents one of the earliest mystical works in Jewish literature, emphasizing the creation of the universe through Hebrew letters and numbers. While the Talmud reflects legal and ethical discussions rooted in oral tradition, the Sefer Yetzirah offers a more esoteric and symbolic exploration of cosmology and divine emanation.
Core Themes and Philosophical Foundations
The Talmud centers on Jewish law, ethics, and oral traditions, emphasizing detailed legal analysis and moral guidance within rabbinic discourse. In contrast, Sefer Yetzirah explores cosmology and the mystical process of creation, highlighting the metaphysical significance of the Hebrew alphabet and the ten sefirot as foundational elements of existence. Together, these texts reflect divergent approaches to Jewish thought: the Talmud's legalistic framework and Sefer Yetzirah's esoteric and philosophical insights into the universe's spiritual structure.
Structure and Literary Style Comparison
The Talmud exhibits a complex, multi-layered structure combining Mishnah and Gemara with dialectical analysis, fostering expansive legal and ethical discussions. In contrast, Sefer Yetzirah features a concise, cryptic outline focusing on mystical concepts and the creative power of Hebrew letters, emphasizing symbolic brevity over analytic depth. While the Talmud's dynamic prose encourages interactive study through argumentation, Sefer Yetzirah's poetic and enigmatic style invites contemplative interpretation of metaphysical principles.
Central Teachings of the Talmud
The Talmud, central to Jewish law and ethics, extensively analyzes the Mishnah with detailed rabbinical discussions, emphasizing practical legal rulings and moral guidance. Unlike the mystical and cosmological focus of Sefer Yetzirah, which explores creation through the Hebrew alphabet and divine emanations, the Talmud prioritizes the application of Torah law in daily life. Its core teachings revolve around interpreting commandments, resolving legal disputes, and fostering community values through rigorous dialectical methods.
Mystical Concepts in the Sefer Yetzirah
The Sefer Yetzirah explores foundational mystical concepts through the configuration of the Hebrew alphabet and the ten sefirot as creative forces shaping the universe. Unlike the Talmud's legal and ethical discussions, the Sefer Yetzirah delves into metaphysical frameworks, emphasizing the process of divine emanation and the interplay between letters, numbers, and cosmic structures. Its esoteric teachings form the basis of Kabbalistic thought, contrasting the Talmud's rational jurisprudence with mystical symbolism.
Influence on Jewish Thought and Tradition
The Talmud profoundly shapes Jewish law, ethics, and customs through its extensive legal discussions and commentaries, serving as the cornerstone of Rabbinic Judaism. Sefer Yetzirah influences Jewish mysticism and Kabbalah by introducing early concepts of cosmology, the Hebrew alphabet, and the metaphysical structure of creation. Together, these texts underpin diverse aspects of Jewish intellectual, religious, and spiritual tradition, balancing legal rigor with mystical insight.
Interpretations by Jewish Scholars
Jewish scholars interpret the Talmud as a comprehensive legal and ethical compendium that explicates the Mishnah through rigorous debate and analysis, emphasizing its role in shaping Halakhic law. The Sefer Yetzirah, by contrast, is examined as a mystical text foundational to Kabbalistic thought, focusing on the creation of the universe through the ten sefirot and the twenty-two letters of the Hebrew alphabet. Interpretations highlight the Talmud's practical jurisprudential guidance versus the esoteric, symbolic dimensions of the Sefer Yetzirah's cosmology.
Modern Relevance and Applications
The Talmud offers extensive discussions on Jewish law, ethics, and customs that continue to influence contemporary religious practice and legal thought, serving as a foundational text for modern rabbinic interpretation. Sefer Yetzirah, one of the earliest mystical texts, informs contemporary Kabbalistic studies and inspires modern explorations in spirituality, linguistics, and cosmology. Both texts contribute distinctively to today's religious scholarship and spiritual philosophy, with the Talmud emphasizing legal discourse and Sefer Yetzirah focusing on mystical cosmology.
Conclusion: Contrasts and Complementarities
The Talmud and Sefer Yetzirah present distinct yet complementary facets of Jewish mystical thought, with the Talmud emphasizing legal discourse and rabbinical analysis, while Sefer Yetzirah focuses on cosmological creation and the metaphysical significance of Hebrew letters. Their contrasts lie in methodology and scope, as the Talmud adopts a dialectical approach to law and ethics, whereas Sefer Yetzirah explores esoteric concepts of divine emanation and the structure of the universe. Together, they enrich Jewish spirituality by providing both practical legal frameworks and profound mystical insights, highlighting the multifaceted nature of Judaic tradition.
Talmud Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com