Christian Mysticism explores the profound spiritual experiences and intimate union with God that transcend ordinary faith practices. Rooted in contemplative prayer and divine revelation, it seeks deeper understanding of the divine nature and the soul's journey toward God. Discover how this ancient tradition can transform Your spiritual path by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
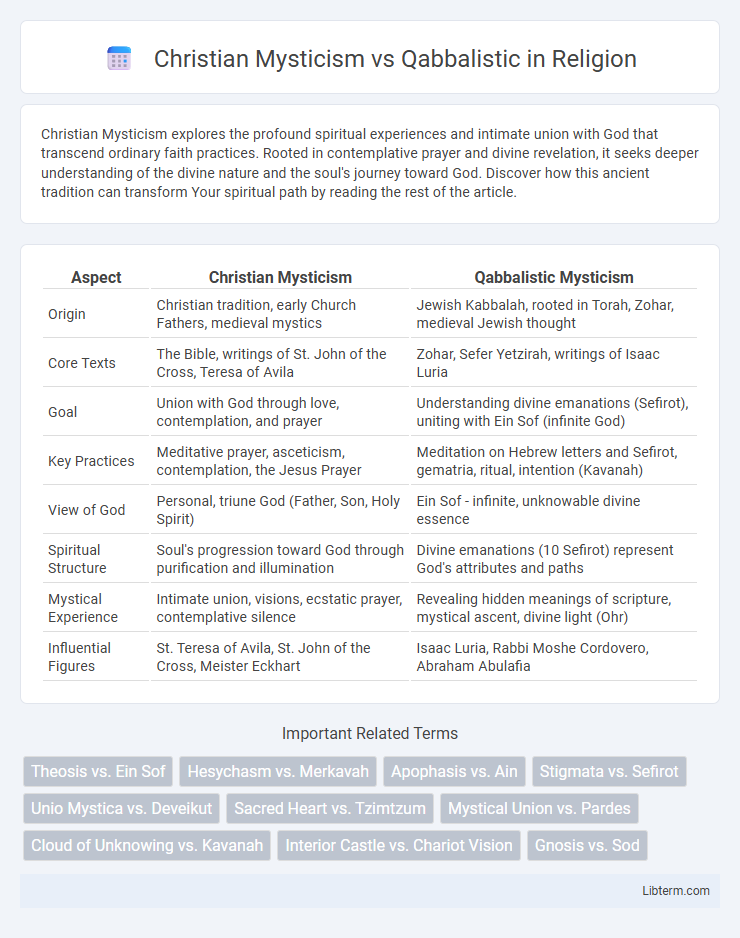
| Aspect | Christian Mysticism | Qabbalistic Mysticism |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Christian tradition, early Church Fathers, medieval mystics | Jewish Kabbalah, rooted in Torah, Zohar, medieval Jewish thought |
| Core Texts | The Bible, writings of St. John of the Cross, Teresa of Avila | Zohar, Sefer Yetzirah, writings of Isaac Luria |
| Goal | Union with God through love, contemplation, and prayer | Understanding divine emanations (Sefirot), uniting with Ein Sof (infinite God) |
| Key Practices | Meditative prayer, asceticism, contemplation, the Jesus Prayer | Meditation on Hebrew letters and Sefirot, gematria, ritual, intention (Kavanah) |
| View of God | Personal, triune God (Father, Son, Holy Spirit) | Ein Sof - infinite, unknowable divine essence |
| Spiritual Structure | Soul's progression toward God through purification and illumination | Divine emanations (10 Sefirot) represent God's attributes and paths |
| Mystical Experience | Intimate union, visions, ecstatic prayer, contemplative silence | Revealing hidden meanings of scripture, mystical ascent, divine light (Ohr) |
| Influential Figures | St. Teresa of Avila, St. John of the Cross, Meister Eckhart | Isaac Luria, Rabbi Moshe Cordovero, Abraham Abulafia |
Introduction to Christian Mysticism and Qabbalistic
Christian mysticism centers on direct, personal experience of God through contemplation, prayer, and the transformative union with the Divine, emphasizing themes like theosis and spiritual ascent. Qabbalistic tradition, rooted in Jewish mysticism, explores the nature of God through symbolic interpretation of the Torah and the Tree of Life, focusing on divine emanations (Sefirot) and the metaphysical structure of the universe. Both systems seek deeper spiritual knowledge, yet Christian mysticism often prioritizes experiential union with Christ, while Qabbalah emphasizes mystical knowledge and cosmic harmony.
Historical Origins and Development
Christian Mysticism traces its historical origins to early Christian contemplative practices, heavily influenced by Jewish mysticism and Hellenistic philosophy, evolving through figures like Pseudo-Dionysius and Meister Eckhart. Qabbalistic tradition originated in 12th-13th century Spain and Southern France, rooted in ancient Jewish esoteric lore, particularly the Sefer Yetzirah and Zohar texts, developing a complex system of divine emanations (Sefirot). Both traditions emphasize experiential knowledge of the divine but diverge in theological frameworks, with Christian Mysticism centered on a Trinitarian God and Qabbalah focusing on the interplay of the Ein Sof (Infinite) and the Sefirot.
Core Beliefs and Worldviews
Christian Mysticism centers on a personal union with God through prayer, contemplation, and the experience of divine love, emphasizing inner transformation and the indwelling of the Holy Spirit. Qabbalistic teachings explore the structure of the divine realm through the Sephirot, offering a metaphysical map of creation and the soul's ascent to divine knowledge, highlighting the interplay between emanation and the infinite Ein Sof. Both systems pursue spiritual enlightenment but diverge in theology, with Christian Mysticism rooted in Christ's incarnation and redemption, while Qabbalah focuses on esoteric wisdom within a Jewish mystical framework.
Sacred Texts and Influential Figures
Christian Mysticism centers on sacred texts such as the Bible, particularly the writings of the New Testament and works by mystics like St. John of the Cross and Teresa of Avila, emphasizing direct experiential knowledge of God. Qabbalistic tradition relies on the Zohar and the Sefer Yetzirah, with key figures including Isaac Luria and Moses de Leon, focusing on mystical interpretations of the Hebrew Scriptures and the Tree of Life. Both traditions explore the divine through symbolic language and esoteric teachings but diverge in their theological frameworks and scriptural sources.
Spiritual Practices and Rituals
Christian mysticism emphasizes contemplative prayer, meditation on scripture, and the pursuit of union with God through practices like the Jesus Prayer and silent worship. Qabbalistic traditions center on complex rituals involving Hebrew letters, gematria, and the Tree of Life meditation to access divine knowledge and spiritual ascent. Both systems employ symbolic rituals and spiritual disciplines, but Christian mysticism prioritizes inner divine union while Qabbalah focuses on esoteric knowledge and cosmic harmony.
Paths to Divine Union: Methods and Experiences
Christian mysticism emphasizes contemplative prayer, the via negativa, and sacramental participation as primary methods to achieve union with God, often described as the mystical marriage or theosis. Qabbalistic mysticism employs the sefirot on the Tree of Life as a symbolic framework, utilizing meditation, visualization, and the study of Hebrew letters and divine names to ascend through spiritual worlds toward divine unity. Both traditions value transformative experiences of divine presence but differ in symbolic language and ritual practices guiding the seeker on their path to spiritual union.
Symbolism and Esoteric Language
Christian mysticism employs rich symbolism rooted in Biblical narratives and sacramental themes, emphasizing union with the Divine through metaphorical language such as light, fire, and the cross. Qabbalistic tradition centers on the Tree of Life, Sephirot, and Hebrew letters as symbolic vessels encoding esoteric knowledge and cosmic processes, utilizing gematria and intricate allegories. Both systems use esoteric language to transcend ordinary understanding, but Christian mysticism often focuses on experiential union and grace, whereas Qabbalah deciphers hidden divine structures and mystical cosmology.
Transformation and Inner Alchemy
Christian Mysticism emphasizes transformation through union with the Divine, focusing on the purification of the soul and contemplation of God's presence, leading to spiritual rebirth. Qabbalistic teachings center on inner alchemy by decoding the Tree of Life's sefirot, guiding practitioners in harmonizing divine energies within to achieve personal and cosmic transformation. Both traditions cultivate profound inner change, using symbolism and meditative practices to transcend the ego and access higher states of consciousness.
Comparative Themes and Key Differences
Christian Mysticism centers on direct union with God through prayer, contemplation, and the experience of divine love, emphasizing the transformative journey of the soul toward holiness and salvation. Qabbalistic traditions explore the mystical dimensions of the Hebrew Scriptures using symbolic interpretations of the sefirot and the Tree of Life, focusing on the structure of the divine and cosmology. Key differences include Christian Mysticism's focus on Christ as the incarnate God and personal salvation, whereas Qabbalah often highlights a broader metaphysical system involving emanations and secret knowledge within Judaic theology.
Contemporary Relevance and Influence
Christian mysticism continues to shape modern spiritual practices through its emphasis on personal union with the Divine, influencing contemplative prayer and meditation across various Christian denominations. Qabbalistic teachings have experienced renewed interest in contemporary esoteric and psychological circles, offering symbolic frameworks for understanding the cosmos and inner transformation. Both traditions contribute to today's interfaith dialogues and holistic approaches to spirituality, highlighting timeless quests for divine knowledge and transcendence.
Christian Mysticism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com