Anagogical interpretation explores the deeper, spiritual meanings behind biblical texts, revealing insights about eternal truths and divine realities beyond the literal sense. This method encourages readers to connect scripture to their spiritual journey and ultimate destiny, enriching personal faith and understanding. Discover how this profound approach can transform your perspective by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
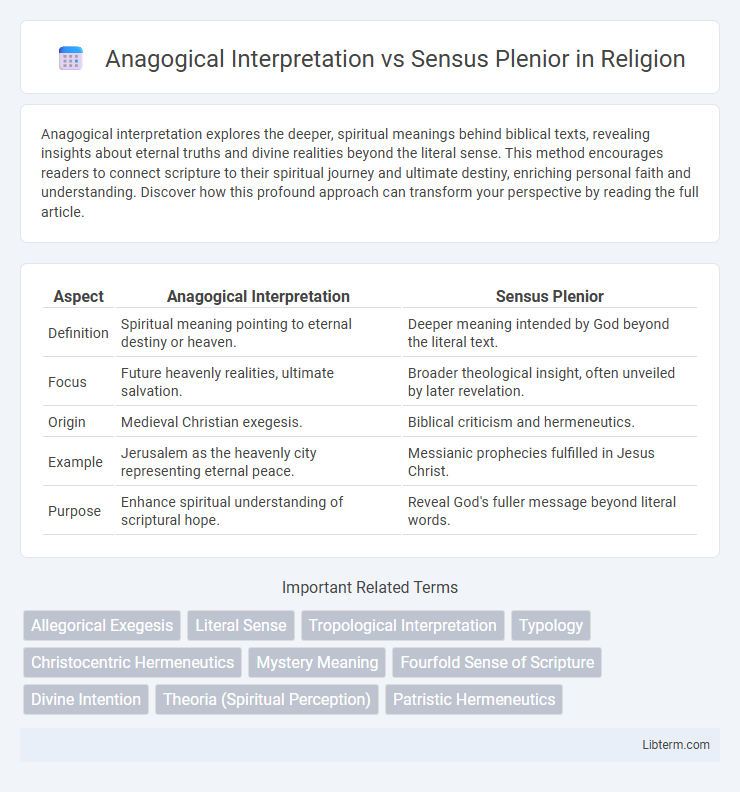
| Aspect | Anagogical Interpretation | Sensus Plenior |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Spiritual meaning pointing to eternal destiny or heaven. | Deeper meaning intended by God beyond the literal text. |
| Focus | Future heavenly realities, ultimate salvation. | Broader theological insight, often unveiled by later revelation. |
| Origin | Medieval Christian exegesis. | Biblical criticism and hermeneutics. |
| Example | Jerusalem as the heavenly city representing eternal peace. | Messianic prophecies fulfilled in Jesus Christ. |
| Purpose | Enhance spiritual understanding of scriptural hope. | Reveal God's fuller message beyond literal words. |
Introduction to Biblical Interpretation
Anagogical interpretation and sensus plenior represent distinct approaches within biblical hermeneutics, emphasizing different layers of meaning in Scripture. Anagogical interpretation reveals spiritual or eschatological significance, often relating to the afterlife or heavenly realities, while sensus plenior refers to the fuller meaning intended by God, encompassing deeper theological insights beyond the human author's understanding. Both methods enrich biblical interpretation by uncovering multidimensional truths that inform faith and doctrine in Christian theology.
Defining Anagogical Interpretation
Anagogical interpretation is a method of biblical exegesis that seeks to reveal the spiritual or mystical meaning underlying the literal text, emphasizing eternal truths and ultimate destiny, particularly concerning heaven and the afterlife. This approach contrasts with sensus plenior, which refers to the fuller meaning intended by God that may surpass the human author's original understanding, often uncovered through the entirety of Scripture and Christian Tradition. Anagogical interpretation specifically elevates the text beyond its immediate context to inspire hope and guide believers toward spiritual fulfillment.
Understanding Sensus Plenior
Sensus Plenior refers to the fuller or deeper meaning intended by God that surpasses the original human author's understanding in biblical texts. Unlike anagogical interpretation, which seeks spiritual or mystical significance often related to eschatology, sensus plenior emphasizes divine intent revealed through later scriptural fulfillment. This concept is fundamental for theological exegesis, highlighting how prophetic and typological passages acquire expanded meaning within the canonical context.
Historical Development of Both Approaches
The anagogical interpretation, rooted in medieval Christian exegesis, developed as one of the fourfold senses of Scripture, emphasizing spiritual and eschatological meanings beyond literal text. Sensus plenior emerged in 20th-century biblical scholarship, particularly through the work of scholars like Raymond E. Brown, highlighting a "fuller meaning" intended by God but not explicitly understood by the human author. Both approaches evolved to deepen theological insight, with anagogical interpretation reflecting early Church tradition and sensus plenior arising from modern hermeneutical frameworks.
Key Differences Between Anagogical and Sensus Plenior
Anagogical interpretation emphasizes spiritual or mystical meanings that guide believers toward ultimate realities such as heaven, contrasting with sensus plenior which reveals a fuller divine meaning intended by God beyond the human author's original intent. Anagogical meaning often complements literal and allegorical senses by focusing on transcendent fulfillment, while sensus plenior involves deeper layers of Scripture understood through divine inspiration and later revelation. The key difference lies in anagogical interpretation being a traditional fourfold exegesis method, whereas sensus plenior reflects a theological concept about progressive divine revelation in biblical texts.
Theological Implications of Each Method
Anagogical interpretation uncovers spiritual realities pointing to ultimate divine truths, often emphasizing eschatological hope and the soul's destiny, thereby enriching personal faith and liturgical meaning. Sensus plenior reveals a fuller divine intent within Scripture, understood through the Holy Spirit's guidance, enhancing doctrinal development and theological depth beyond the literal text. Theologically, anagogical reading nurtures mysticism and future-oriented salvation, while sensus plenior strengthens authoritative scriptural interpretation and continuity in divine revelation.
Prominent Scholars and Their Perspectives
Prominent scholars such as Origen emphasized the anagogical interpretation as a mystical reading that reveals the ultimate spiritual meaning beyond a biblical text's literal sense. Conversely, scholars like Gleason Archer championed sensus plenior as a divinely intended fuller sense of Scripture unveiled through Christ's revelation and apostolic insight. The distinction lies in anagogical interpretation's allegorical focus on heavenly realities, while sensus plenior pertains to God's deeper, often progressively disclosed truth within the canonical text.
Applications in Scriptural Analysis
Anagogical interpretation reveals spiritual mysteries by uncovering transcendent meanings in biblical texts, often applied to eschatological themes like heaven and divine fulfillment. Sensus plenior refers to the fuller sense intended by God but not understood by the human authors, broadening scriptural insights beyond the literal sense through divine inspiration. Both approaches enhance scriptural analysis by offering layered understandings that bridge historical context and divine revelation in theological studies.
Criticisms and Challenges
Anagogical interpretation often faces criticism for its subjective nature and lack of rigorous hermeneutical methodology, leading to varied and sometimes speculative conclusions. Sensus plenior, while offering a deeper theological insight beyond the literal text, encounters challenges related to the balance between authorial intent and divine revelation, raising debates among scholars about its legitimate application. Both approaches struggle with establishing clear criteria for validity, making them contentious in scholarly biblical exegesis and theological discourse.
Conclusion: Comparative Insights
Anagogical interpretation uncovers spiritual meanings pointing to ultimate divine realities, while sensus plenior reveals fuller, divinely intended meanings beyond the human author's understanding. Both approaches deepen biblical comprehension by transcending literal text, yet anagogical focuses on eschatological fulfillment, and sensus plenior emphasizes inspired layers of meaning within the canonical revelation. Together, they enrich theological study by integrating mystical and prophetic dimensions into scriptural exegesis.
Anagogical Interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com