Sacred Tradition embodies the living transmission of the faith, handed down through generations by the apostles and preserved within the Church's teachings, liturgy, and practice. It serves as a foundation for interpreting Scripture and guiding moral and spiritual life, complementing the written Word and deepening Your understanding of Christian doctrine. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Sacred Tradition shapes faith and practice today.
Table of Comparison
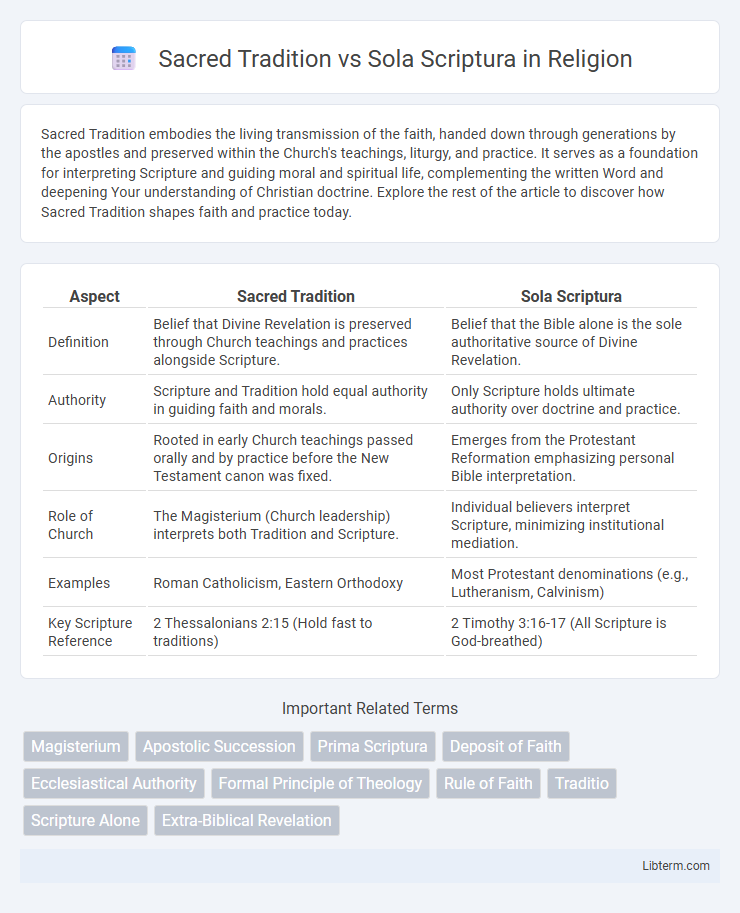
| Aspect | Sacred Tradition | Sola Scriptura |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief that Divine Revelation is preserved through Church teachings and practices alongside Scripture. | Belief that the Bible alone is the sole authoritative source of Divine Revelation. |
| Authority | Scripture and Tradition hold equal authority in guiding faith and morals. | Only Scripture holds ultimate authority over doctrine and practice. |
| Origins | Rooted in early Church teachings passed orally and by practice before the New Testament canon was fixed. | Emerges from the Protestant Reformation emphasizing personal Bible interpretation. |
| Role of Church | The Magisterium (Church leadership) interprets both Tradition and Scripture. | Individual believers interpret Scripture, minimizing institutional mediation. |
| Examples | Roman Catholicism, Eastern Orthodoxy | Most Protestant denominations (e.g., Lutheranism, Calvinism) |
| Key Scripture Reference | 2 Thessalonians 2:15 (Hold fast to traditions) | 2 Timothy 3:16-17 (All Scripture is God-breathed) |
Understanding Sacred Tradition: Definition and Origins
Sacred Tradition refers to the transmission of divine revelation through the teachings and practices handed down by the apostles, encompassing oral teachings, liturgy, and Church authority beyond the written Scriptures. It originates from the early Christian community, where apostolic witness and interpretation were preserved before the New Testament canon was formalized. Understanding Sacred Tradition is essential to grasp the Catholic and Orthodox view that Scripture and Tradition together form the deposit of faith.
What is Sola Scriptura? Key Principles Explained
Sola Scriptura is a Protestant doctrine asserting that the Bible alone is the supreme authority in all matters of faith and practice, rejecting traditions outside Scripture as binding. Key principles include the Bible's sufficiency, clarity, and exclusivity, meaning Scripture contains all knowledge necessary for salvation, is understandable by ordinary believers, and holds ultimate authority over church traditions. This principle contrasts with Sacred Tradition, which holds that alongside Scripture, apostolic teachings and church practices also carry authoritative weight.
Historical Development of Sacred Tradition and Sola Scriptura
Sacred Tradition emerged in early Christianity as the transmission of teachings, liturgical practices, and apostolic authority beyond the written texts, playing a crucial role in shaping Church doctrine. The principle of Sola Scriptura developed during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation, asserting the Bible alone as the ultimate authority in matters of faith and rejecting the equal weight of Tradition. Historical debates between these positions highlight the dynamic interplay between Scripture and Tradition in Christian theological development and ecclesiastical authority.
Scriptural Basis for Sacred Tradition
The scriptural basis for Sacred Tradition is rooted in passages such as 2 Thessalonians 2:15, where Paul instructs believers to hold fast to traditions taught either by word or letter, highlighting the authoritative role of unwritten teachings alongside Scripture. Jesus' commissioning of the apostles in Matthew 28:19-20 emphasizes the transmission of teachings through apostolic authority, underscoring the continuity of Tradition. Furthermore, 1 Corinthians 11:2 refers to traditions delivered by Paul, indicating that early Christian instruction included both written and oral components essential for preserving faith.
Scriptural Arguments for Sola Scriptura
Sola Scriptura asserts that the Bible alone is the ultimate authority for Christian faith and practice, citing 2 Timothy 3:16-17, which states all Scripture is God-breathed and sufficient for teaching, reproof, correction, and training in righteousness. Passages like Acts 17:11 praise the Bereans for examining Scriptures daily to verify teachings, emphasizing Scripture's self-authenticating authority. Furthermore, Jesus' statement in John 5:39 underscores that the Scriptures testify about Him, indicating Scripture's central role in revealing divine truth without requiring extra-biblical traditions.
Church Authority: Magisterium vs. Private Interpretation
Sacred Tradition upholds the Magisterium as the authoritative interpreter of Scripture, grounding Church teachings in apostolic succession and guided by the Holy Spirit. Sola Scriptura emphasizes Scripture alone as the ultimate authority, encouraging individual believers to interpret biblical texts without ecclesiastical mediation. This contrast shapes key theological debates about doctrinal development, the limits of private interpretation, and the role of Church authority in maintaining orthodoxy.
Early Christian Beliefs: Tradition or Scripture Alone?
Early Christian beliefs reveal a complex interplay between Sacred Tradition and Scripture, with the Church Fathers consistently emphasizing the authority of both oral teachings and written texts in preserving apostolic faith. Early councils and creeds, such as the Nicene Creed, were transmitted through tradition before being codified in Scripture, indicating that early Christians did not rely on Scripture alone (Sola Scriptura) but upheld Tradition as essential for interpreting and safeguarding doctrinal truths. Archaeological findings and patristic writings, including those of Ignatius of Antioch and Irenaeus, demonstrate that Sacred Tradition functioned as a living guide complementing the biblical canon during Christianity's formative centuries.
Impact on Christian Doctrine and Interpretation
Sacred Tradition serves as a foundational source alongside Scripture, preserving apostolic teachings that shape Christian doctrine and guide ecclesiastical interpretation. Sola Scriptura emphasizes Scripture alone as the ultimate authority, which leads to varied doctrinal interpretations and denominational diversity based solely on biblical texts. The tension between these approaches impacts theological consistency, with Sacred Tradition promoting continuity and Sola Scriptura encouraging individual engagement with biblical authority.
Key Theological Debates and Controversies
Sacred Tradition and Sola Scriptura remain central to theological debates, with Tradition emphasizing the Church's oral teachings alongside Scripture as authoritative sources for faith and practice, while Sola Scriptura asserts Scripture alone as the ultimate authority. Controversies arise over biblical interpretation authority, the role of Church Fathers, and the legitimacy of doctrines not explicitly found in Scripture, such as the veneration of saints and the Eucharist's nature. These debates impact ecclesiology, hermeneutics, and doctrinal development within Catholic, Orthodox, and Protestant traditions.
Sacred Tradition vs. Sola Scriptura: Modern Christian Perspectives
Modern Christian perspectives on Sacred Tradition vs. Sola Scriptura reveal a significant divide between denominations emphasizing the authority of Church teachings alongside Scripture and those advocating Scripture alone as the sole rule of faith. Catholic and Orthodox traditions uphold Sacred Tradition as a living transmission of apostolic teaching essential for interpreting and understanding the Bible, while many Protestant communities adhere strictly to Sola Scriptura, asserting that all necessary doctrine is contained within the canonical texts. This ongoing theological debate shapes contemporary Christian identity, worship, and doctrinal interpretation across diverse Christian contexts.
Sacred Tradition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com